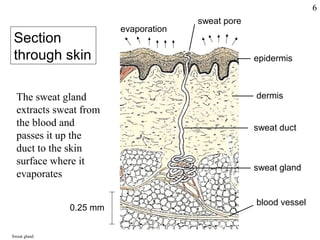
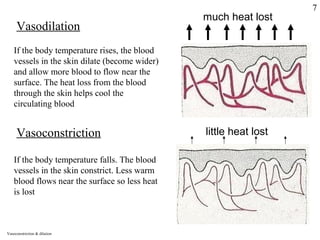
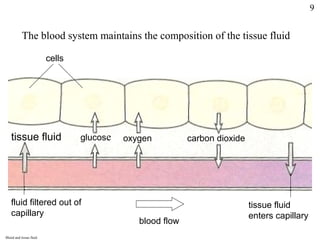
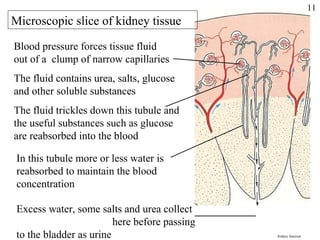
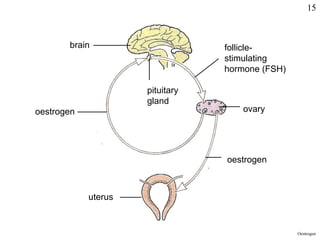
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of stable internal conditions in the body despite changes in the external environment. It allows cells to function properly through regulatory processes like negative feedback. The skin, kidneys, liver, endocrine and nervous systems all work to keep conditions like temperature, pH, water concentration, and glucose levels within narrow limits. When deviations occur, feedback mechanisms activate processes like sweating or vasoconstriction to return the internal environment to its optimal range for cellular activity.