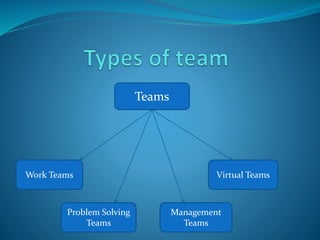
A team is a small group of people with complementary skills who are committed to a common goal and approach. An effective team has interaction and influence between members to function well. Team members need technical, problem-solving, decision-making, and interpersonal skills. There are different types of teams including work teams focused on using resources, problem-solving teams to address specific issues, management teams of managers from different areas, and virtual teams that may never meet in person.