The document discusses data modeling and database characteristics, data centers, and data modeling. It provides information on:
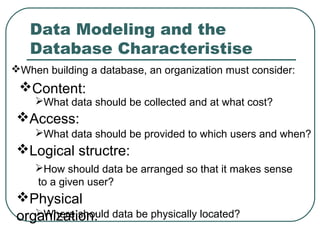
1) Factors to consider when building a database including data content and cost, user access and data structure, and physical data organization and location.
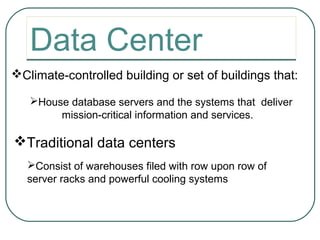
2) What a data center is and its purpose of housing mission-critical database servers and systems in a climate-controlled building.
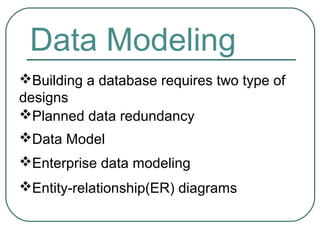
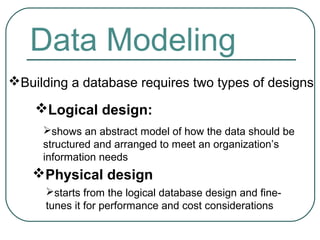
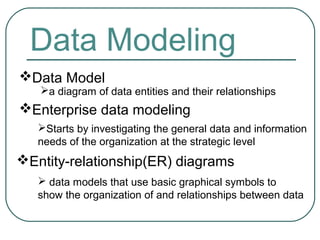
3) The two types of designs needed for building a database - logical design showing an abstract data structure and physical design optimizing performance and costs. It also discusses data models, enterprise data modeling using ER diagrams, and their purposes.