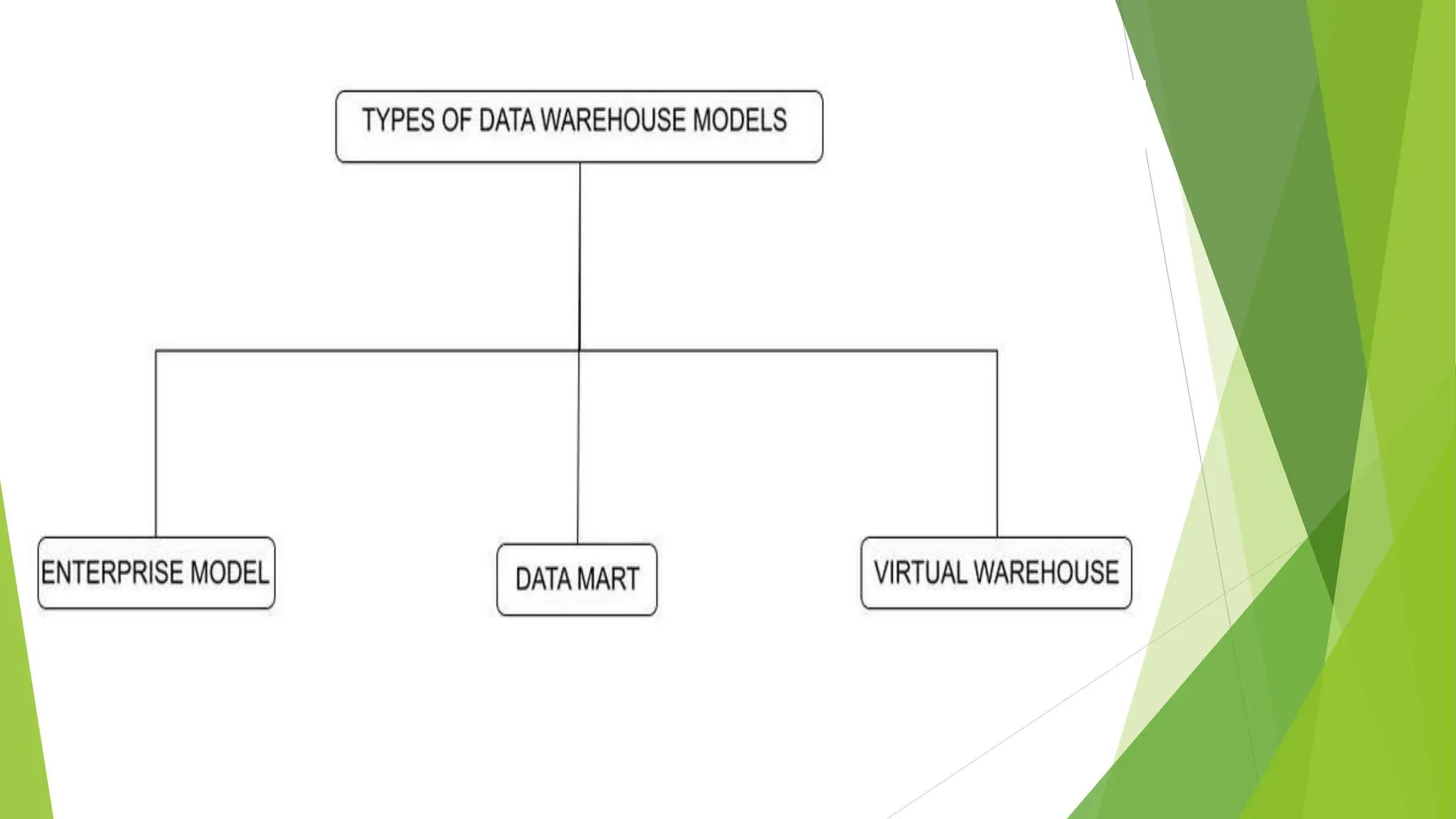
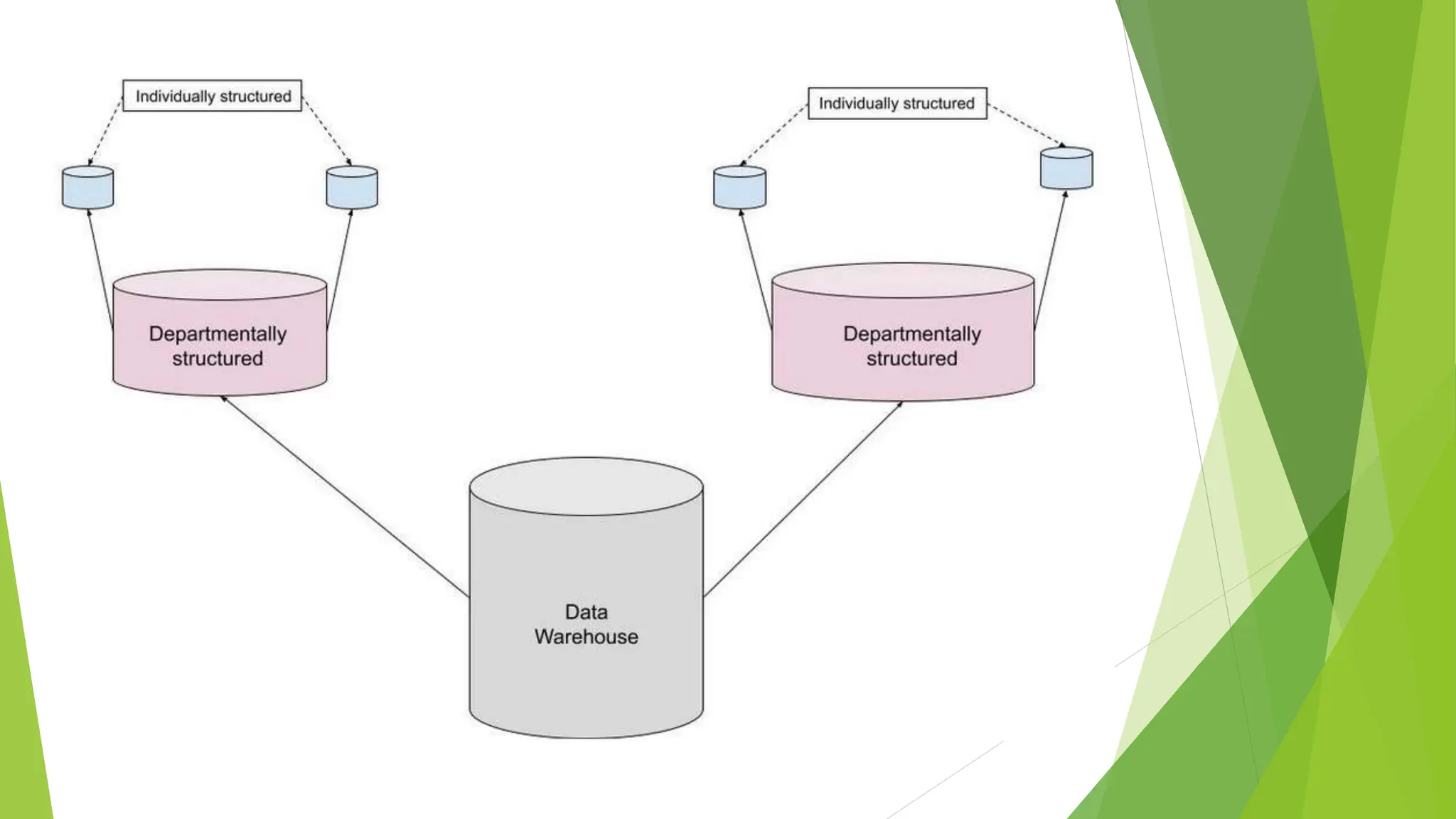
The document discusses data warehousing and multidimensional modeling in the context of computer science, emphasizing the importance of data warehouse modeling for visualizing relationships and optimizing structure. It describes the life cycle and types of data models—conceptual, logical, and physical—and outlines three types of data warehouse models: enterprise warehouses, data marts, and virtual warehouses. Each model serves different purposes, from comprehensive data storage for organizational analysis to specific task-oriented data access for departments.

![Introduction to Data Warehouse
Modelling
The process of developing the schemas for the data warehouse's detailed and
summarized information is known as data warehouse modeling [a schema
refers to the organization or structure of data within the data warehouse].
The purpose of data warehouse modeling is to create a schema that describes
the reality, or at least a portion of the reality, that the data warehouse must
support.
Data warehouse modeling is essential in building a data warehouse for two
essential reasons.
The first reason is to visualize the relationships among the warehouse data, and
the second reason is to optimize the schema to make a well-structured data
warehouse.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datawarehousesession2-240523054516-4dcfbfb4/75/Introduction-to-Data-Warehouse-Modelling-2-2048.jpg)