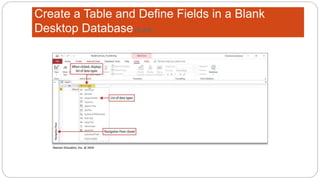
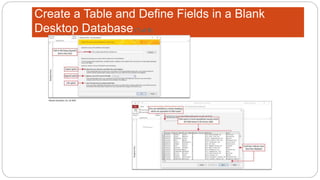
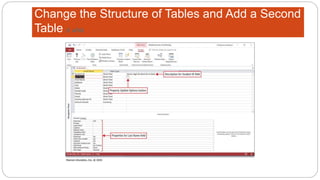
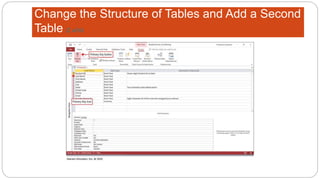
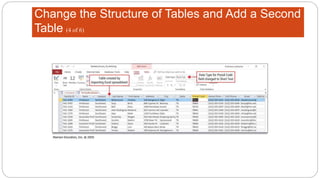
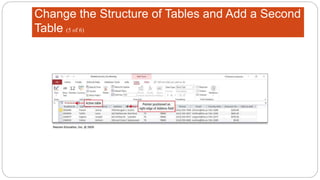
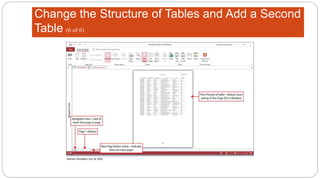
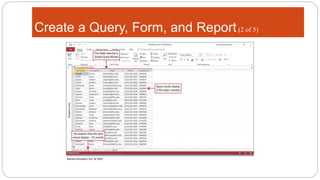
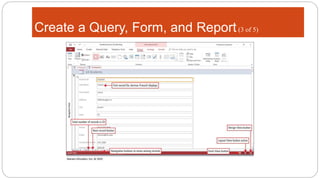
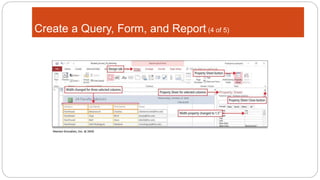
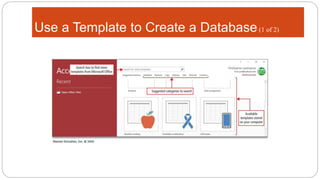
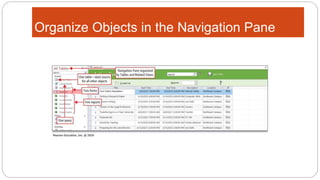
This document provides an overview of MS Access and database design. It discusses key concepts like relational databases, tables, records, and fields. It also outlines the steps to create tables and define fields, add additional tables, create queries, forms and reports, and use templates to design a database in MS Access. The goal is to organize data without duplication and ensure consistency through techniques like normalization.