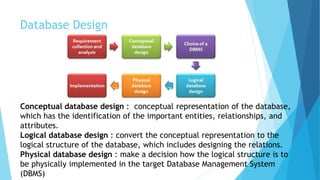
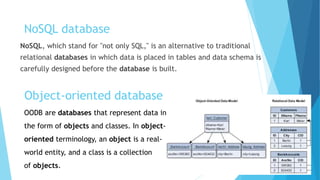
The document defines key database concepts such as data, information, databases, data modeling, and database management systems (DBMS). It describes what a database is, the basic database structure, and the process of data modeling. It also discusses different types of DBMS software, database designs, and types of databases including relational, distributed, cloud, NoSQL, object-oriented, and graph databases. Additionally, it covers data manipulation using SQL and database advantages like redundancy control and disadvantages like costs.


















![DML- Data Manipulation Language
Sub language of SQL which enables users to access and
manipulate data such as selection, insertion, deletion or
modification.
Keywords
SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3,...columnN)] VALUES
(value1, value2, value3,...valueN)
SELECT * FROM table_name;
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
WHERE condition;
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-190916164128/85/Database-System-21-320.jpg)


