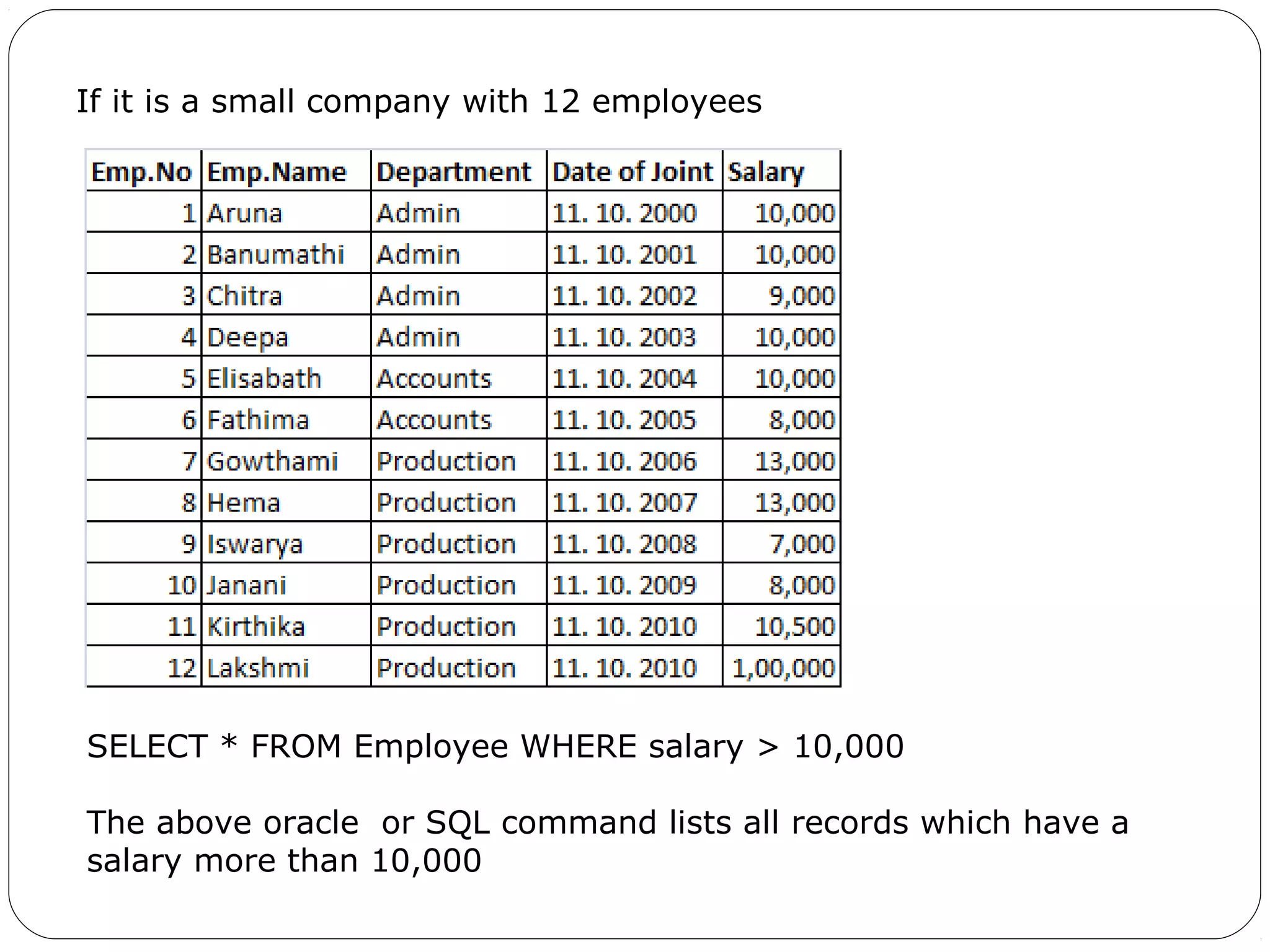
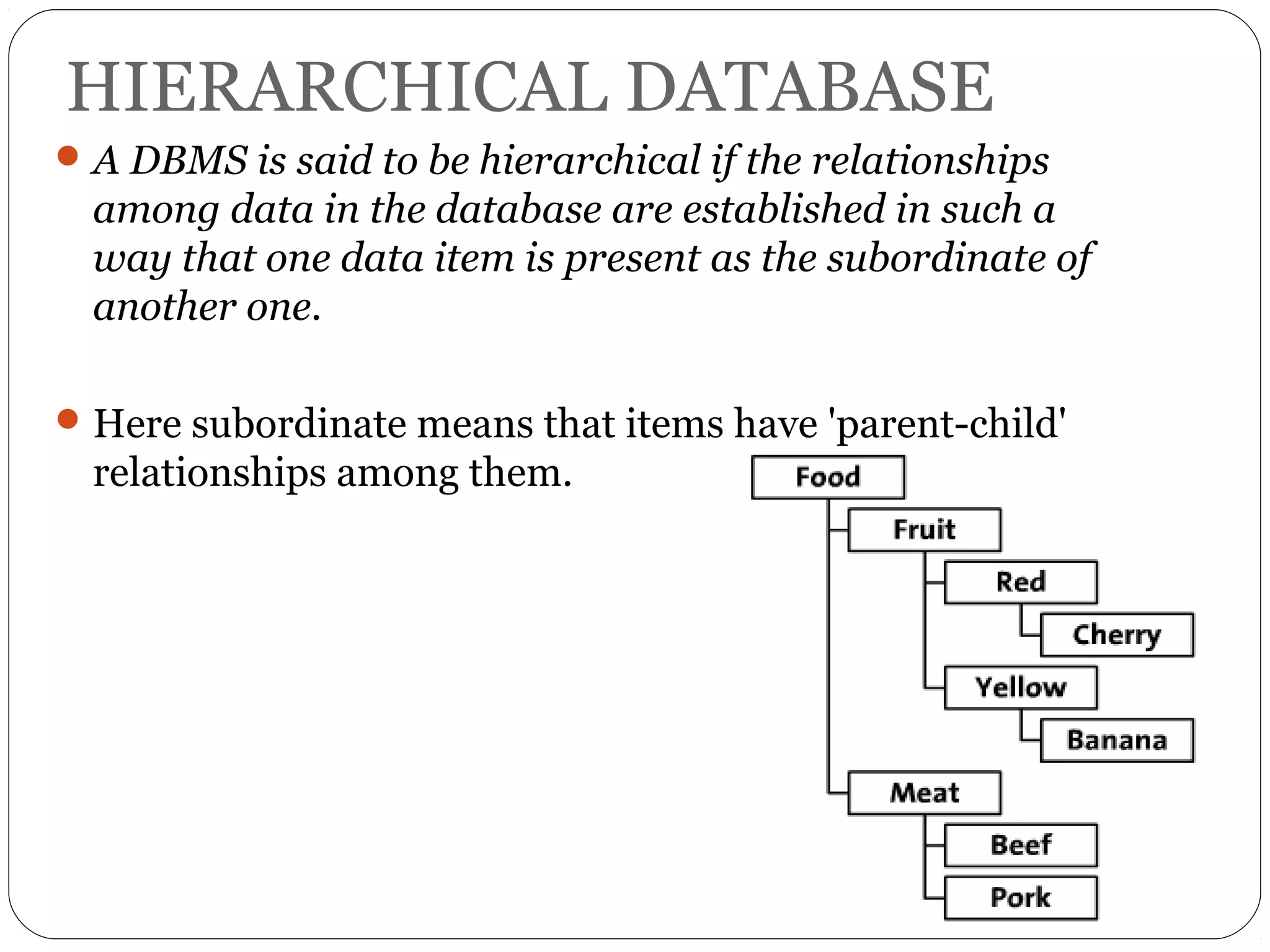
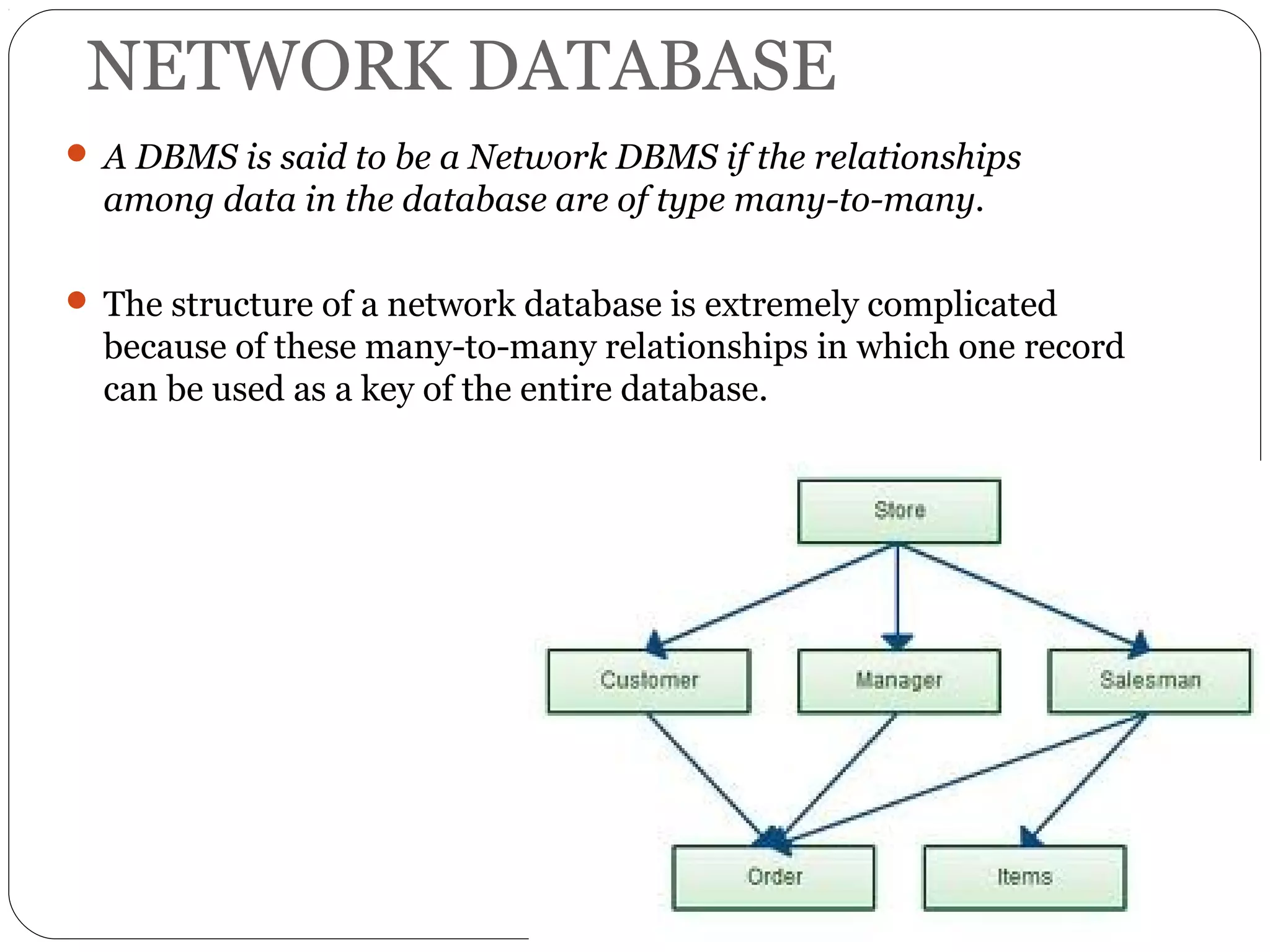
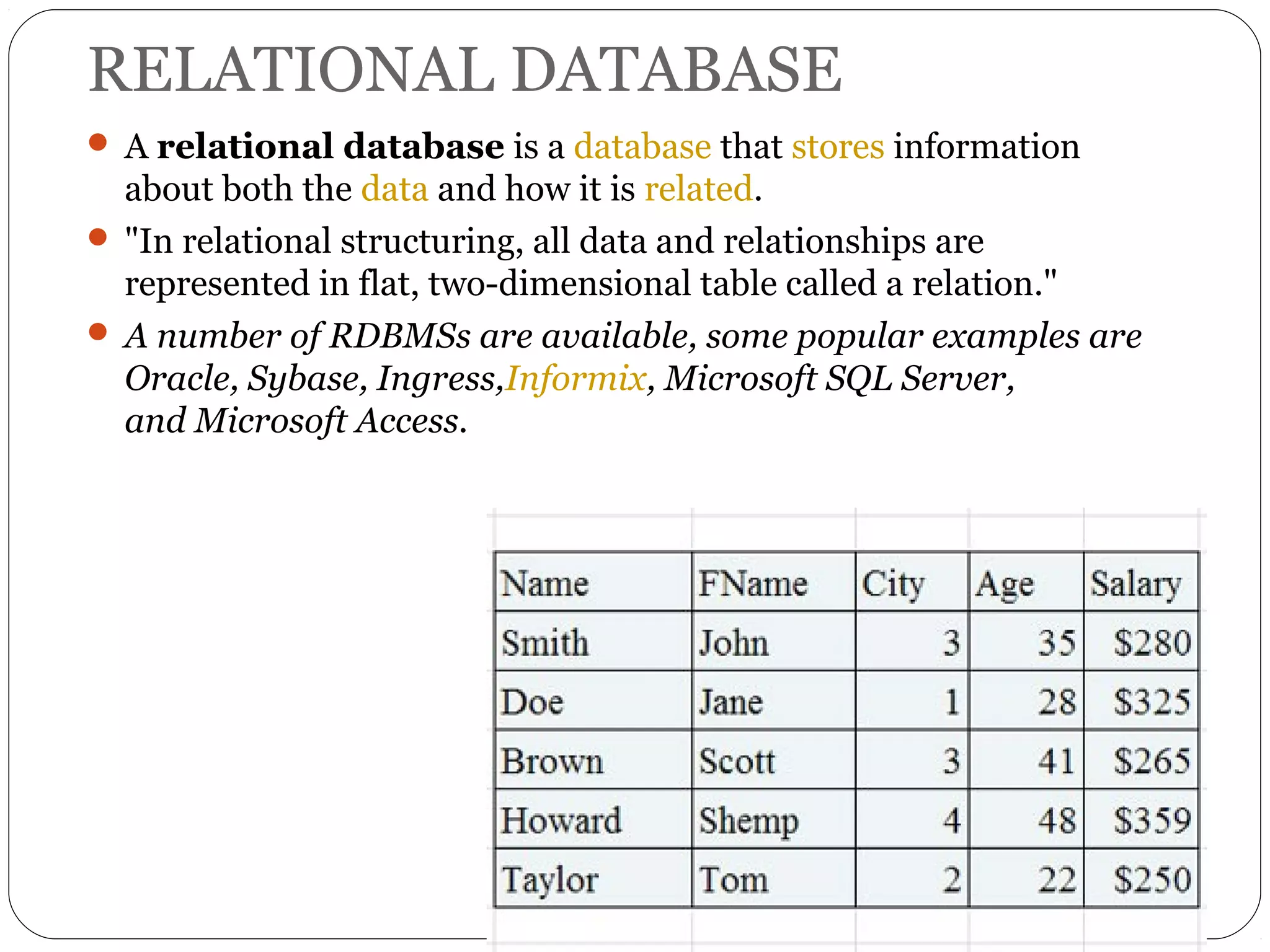
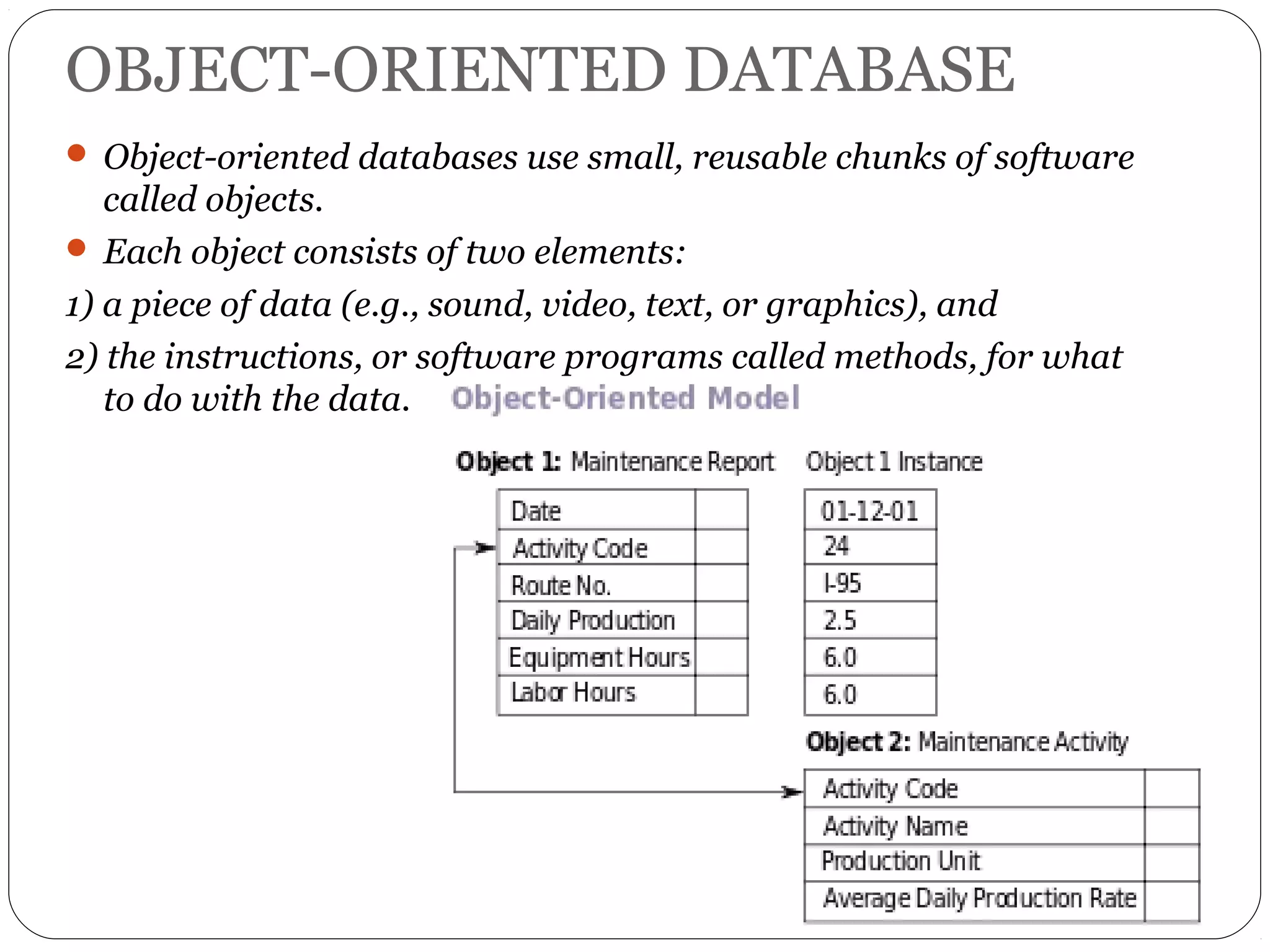
A database is a set of related data. A database management system (DBMS) allows users to access and perform operations on data in a database. Some key benefits of a DBMS include easy data use, centralized data control, and data security. Traditional file systems have disadvantages like data redundancy, inconsistency, and lack of integrity and security. There are different types of database models including hierarchical, network, relational, and object-oriented.