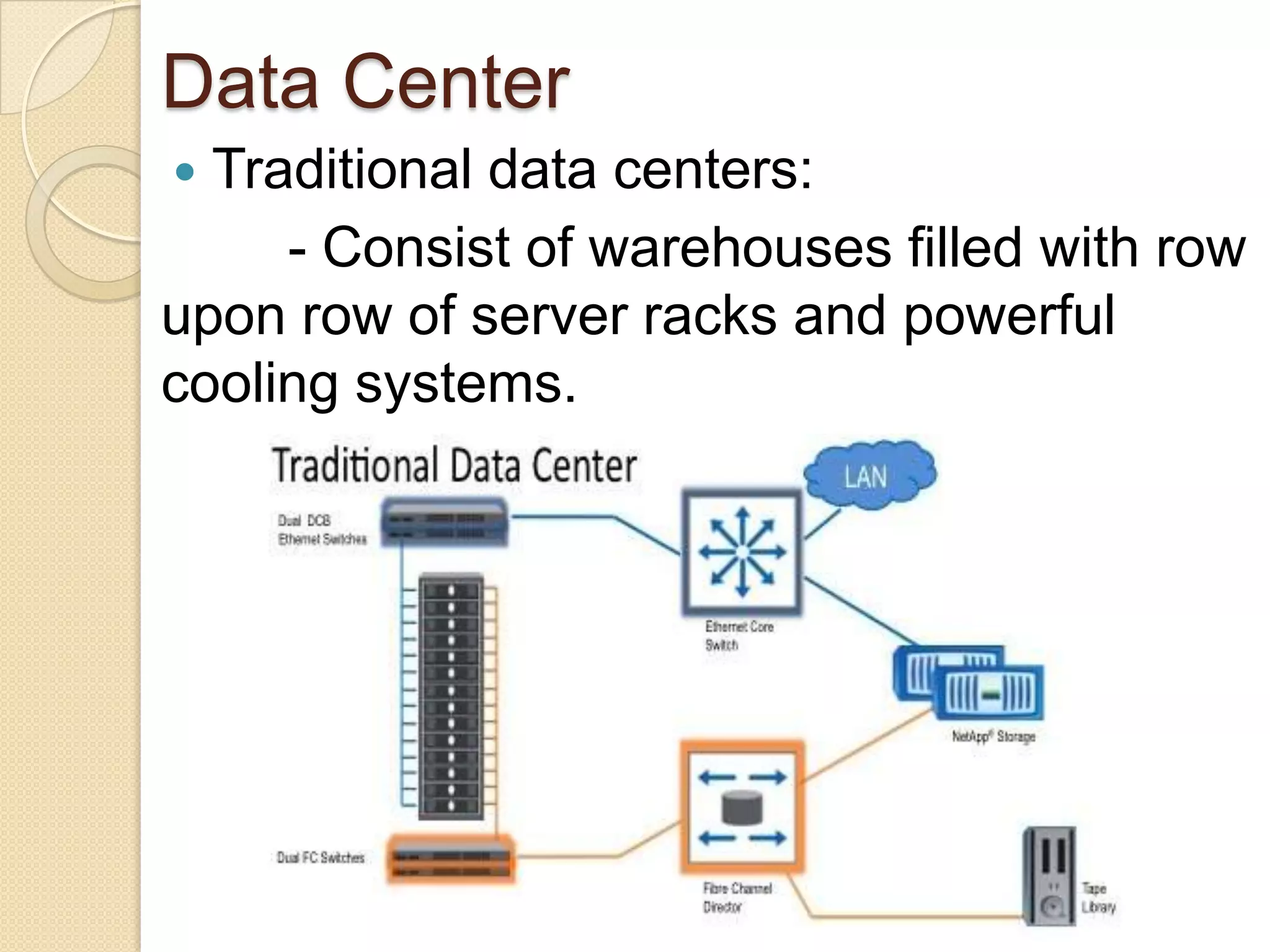
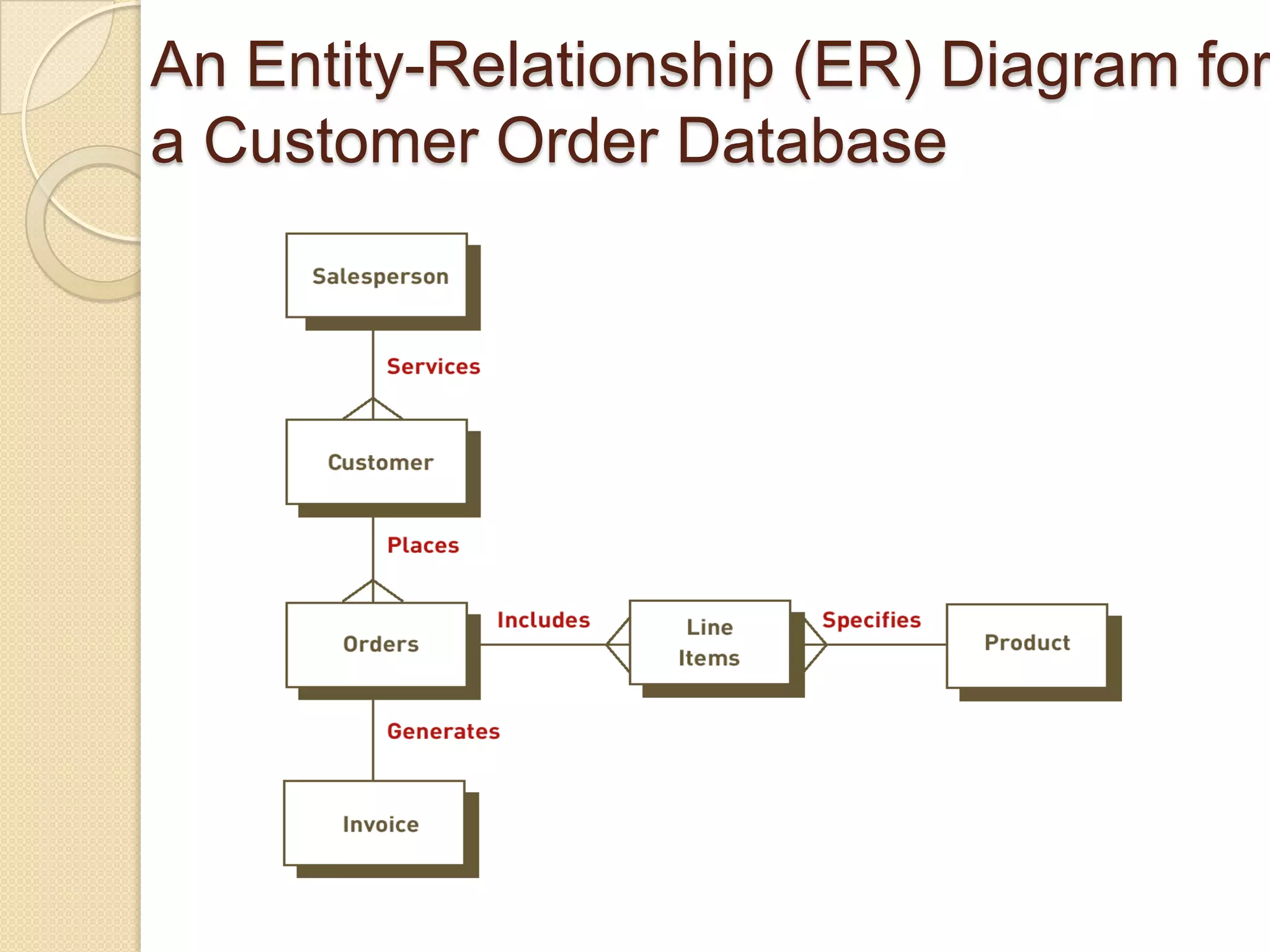
When building a database, an organization must consider the content, access, logical structure, and physical organization of the data. This includes determining what data to collect, who can access what data and when, how the data should be logically arranged, and the physical location and infrastructure to store the data. Building an effective database requires both a logical design that models how the data should be structured, as well as a physical design that optimizes performance and costs based on the logical design.