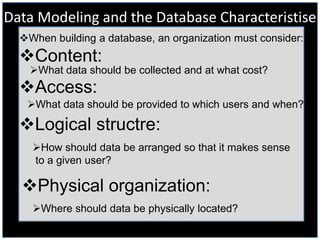
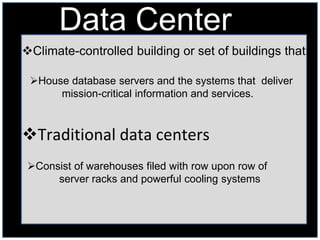
The document discusses data modeling and database characteristics. It describes how organizations must consider content, access, logical structure, and physical organization when building a database. It also discusses data centers, explaining they are climate-controlled buildings that house database servers and systems to deliver critical information. Finally, it outlines the two types of designs needed for data modeling: logical design showing an abstract model of how data is structured, and physical design which fine-tunes the logical design for performance.