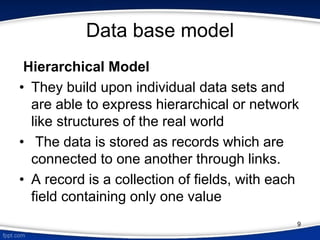
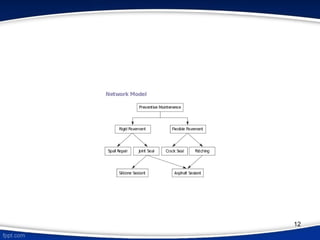
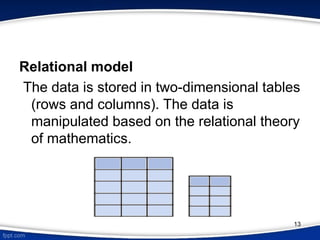
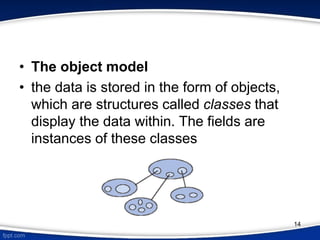
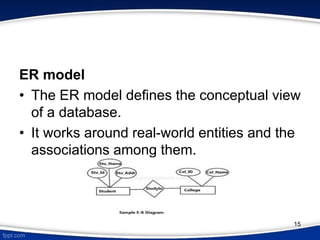
This document provides an introduction to database management systems (DBMS). It discusses that a DBMS is a collection of data and software programs used to store and retrieve large amounts of data. The key purposes of a DBMS are to organize data, store and transform data into information to support decision making. It also describes three levels of data abstraction (physical, logical, and view levels) and several common database models, including hierarchical, network, relational, object, and entity-relationship models.