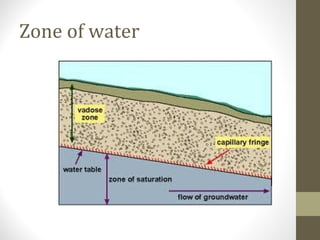
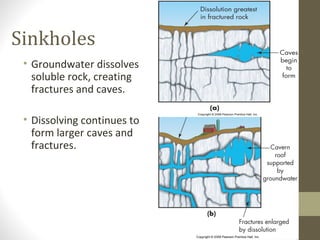
Karst topography forms in areas with soluble rock like limestone and dolomite. Groundwater dissolves the rock through chemical processes, forming distinctive landforms. Key features include sinkholes, caves, underground streams, and karst plains. Karst regions exist worldwide, including parts of Europe, Asia, and North America, requiring soluble bedrock and adequate rainfall for dissolution to occur.