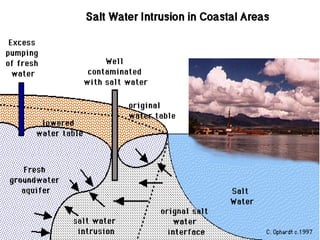
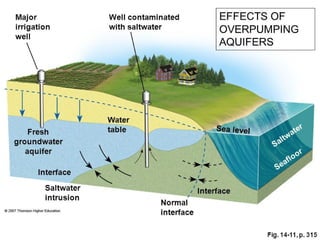
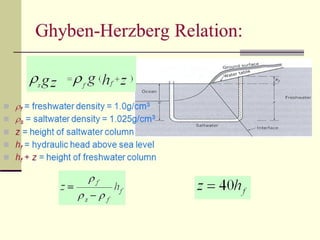
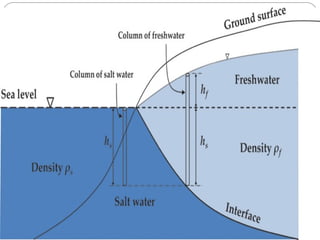
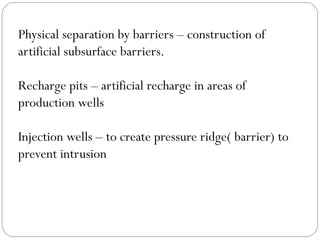
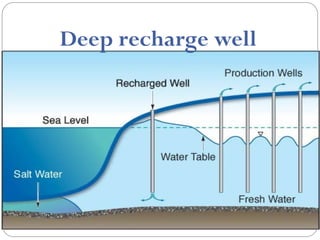
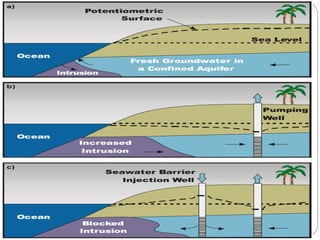
Saltwater intrusion occurs when saline water from the ocean moves into freshwater aquifers located near the coast. It is often caused by groundwater pumping or construction activities that provide pathways for saltwater. Saltwater intrusion impacts freshwater resources and can lead to the loss of vegetation. The Ghyben-Herzberg relation describes the interaction between fresh and saltwater, and estimates that for every foot of freshwater above sea level, there will be 40 feet below. Management strategies aim to maintain groundwater levels and include conservation, alternative water sources, recharge, and monitoring wells.