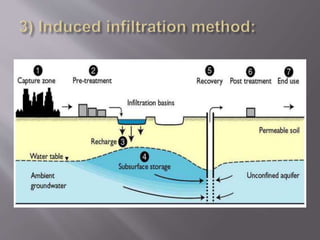
This document discusses various methods of artificially recharging groundwater. It describes techniques such as spreading water over permeable land or pits for it to infiltrate shallow aquifers. Other methods discussed are storing water in shallow ditches or low earth dykes, injecting water into boreholes, and using wells near riverbanks with radial collectors to increase the water table gradient. The key benefits of artificial groundwater recharge are augmenting the groundwater reservoir beyond natural replenishment rates and improving groundwater levels, yields, and quality.