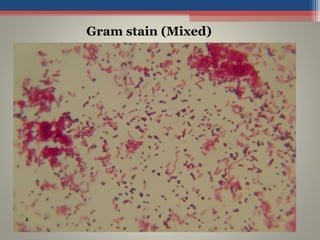
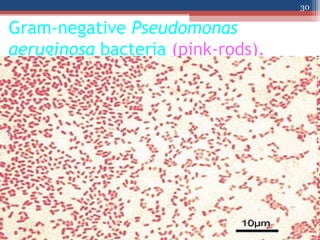
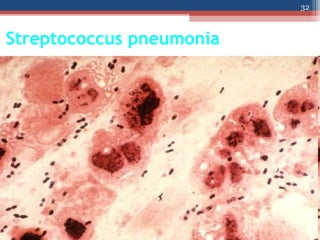
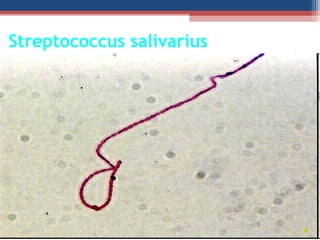
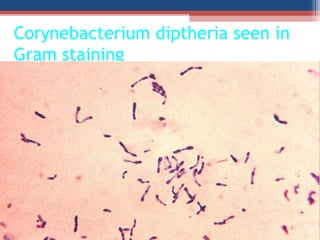
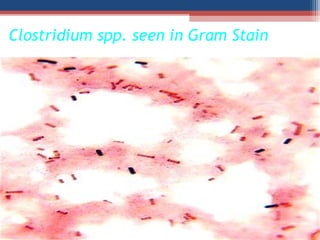
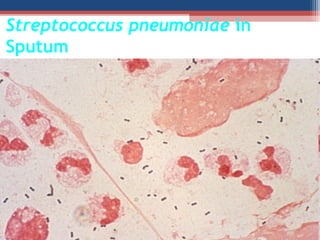
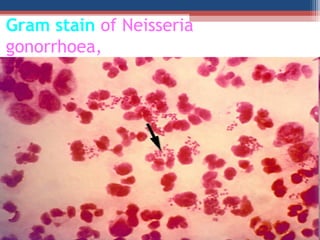
- The Gram staining technique was developed in 1884 by Hans Christian Gram as a way to classify bacteria.
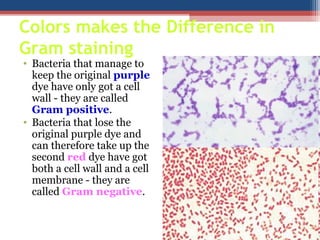
- Gram staining involves staining a bacterial smear with crystal violet dye followed by iodine to form a crystal violet-iodine complex. Bacteria are then decolorized with alcohol or acetone and counterstained with safranin.
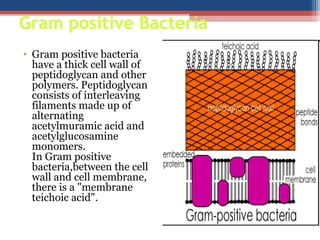
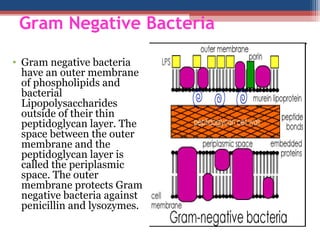
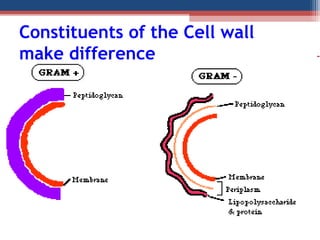
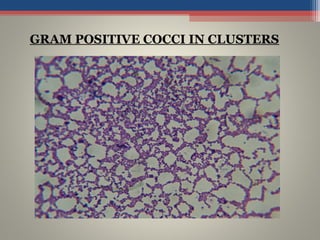
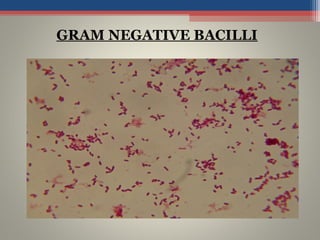
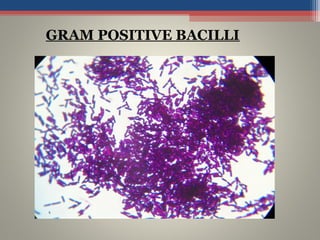
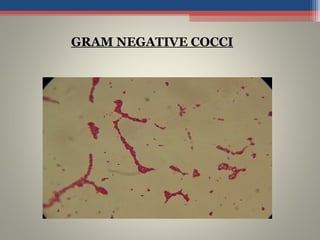
- Based on whether they retain the crystal violet dye after decolorization, bacteria are classified as either Gram-positive or Gram-negative. Gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet due to their thick peptidoglycan cell wall, appearing purple under the microscope, while Gram-negative bacteria do not retain the dye due to their thinner cell wall