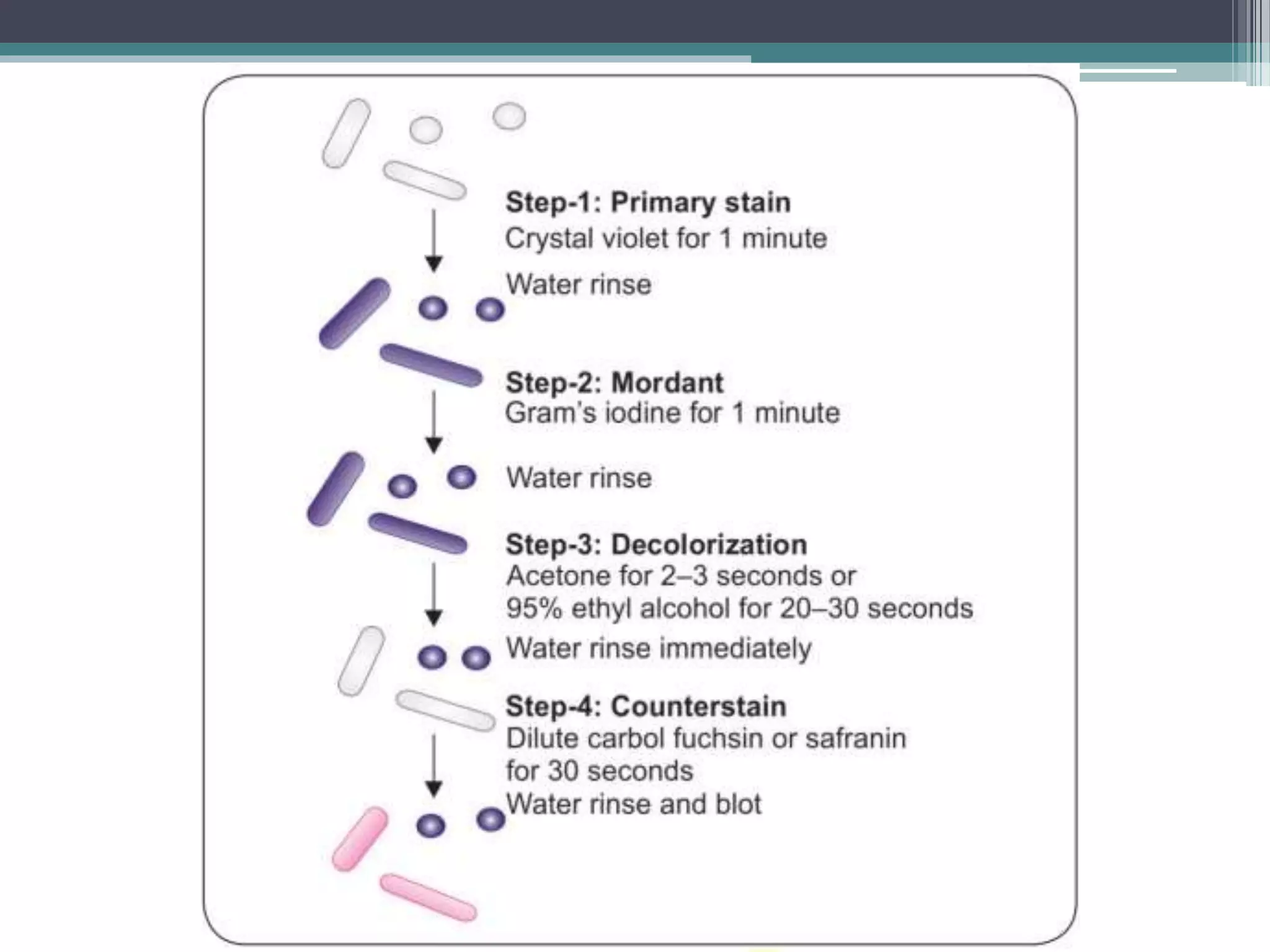
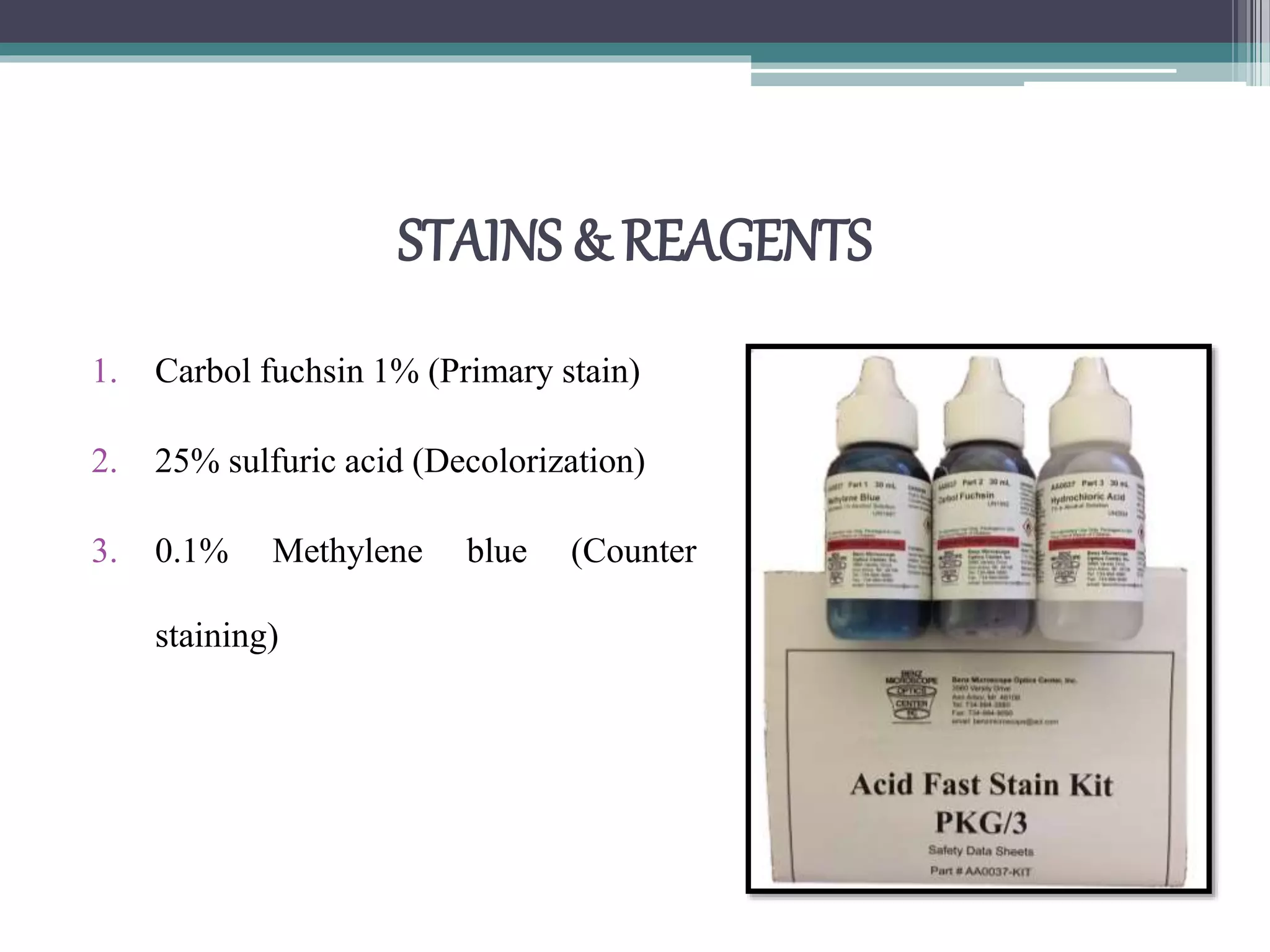
Staining techniques are used in microbiology to increase the visibility and contrast of bacterial structures under a light microscope. There are several types of staining including simple stains that color all bacteria the same hue, differential stains that color different types of bacteria differently, and special stains like acid-fast stains. Gram staining is a common differential technique that divides bacteria into Gram-positive or Gram-negative based on differences in cell wall structure. Acid-fast staining identifies bacteria with high mycolic acid in their cell walls like Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proper fixation of smears is also important to preserve cell structure before staining.