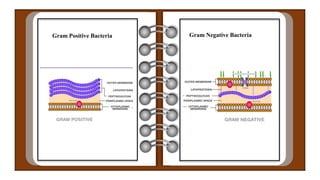
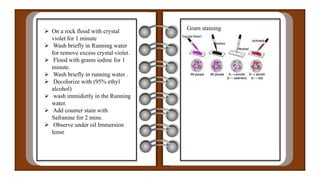
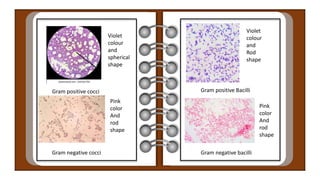
Hans Christian Gram developed the Gram staining technique in 1884 to classify bacteria. Gram staining involves staining bacteria with crystal violet dye, treating it with iodine to form a complex with the dye, decolorizing with alcohol, and counterstaining with safranin. Bacteria that retain the crystal violet dye after decolorization appear violet and are Gram-positive, while those that lose the dye and appear pink are Gram-negative. The Gram staining characteristics help differentiate between bacteria with thick peptidoglycan cell walls that are Gram-positive from those with thin cell walls and an outer membrane that are Gram-negative.