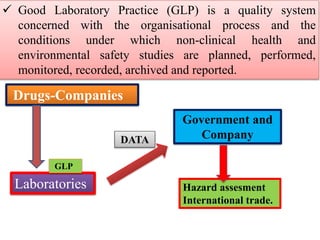
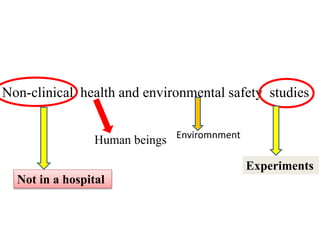
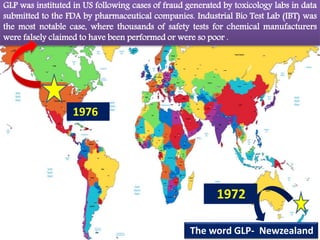
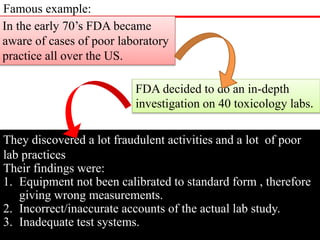
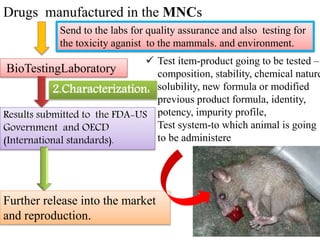
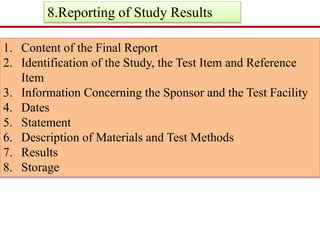
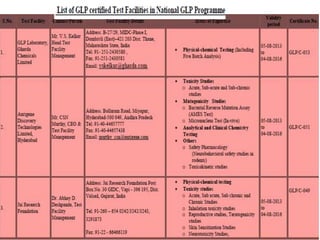
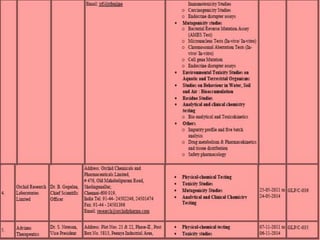
GLP (Good Laboratory Practice) is a quality system for non-clinical health and environmental safety studies. It was instituted in the US after fraudulent data was submitted by toxicology labs. GLP aims to ensure studies are properly planned, monitored, and reported, and that data accurately reflects results. It promotes international acceptance of safety tests. The OECD principles provide an international standard for GLP, covering topics like facility organization, test system and item characterization, and record keeping. India has established a National GLP Compliance Monitoring Authority to oversee GLP standards.