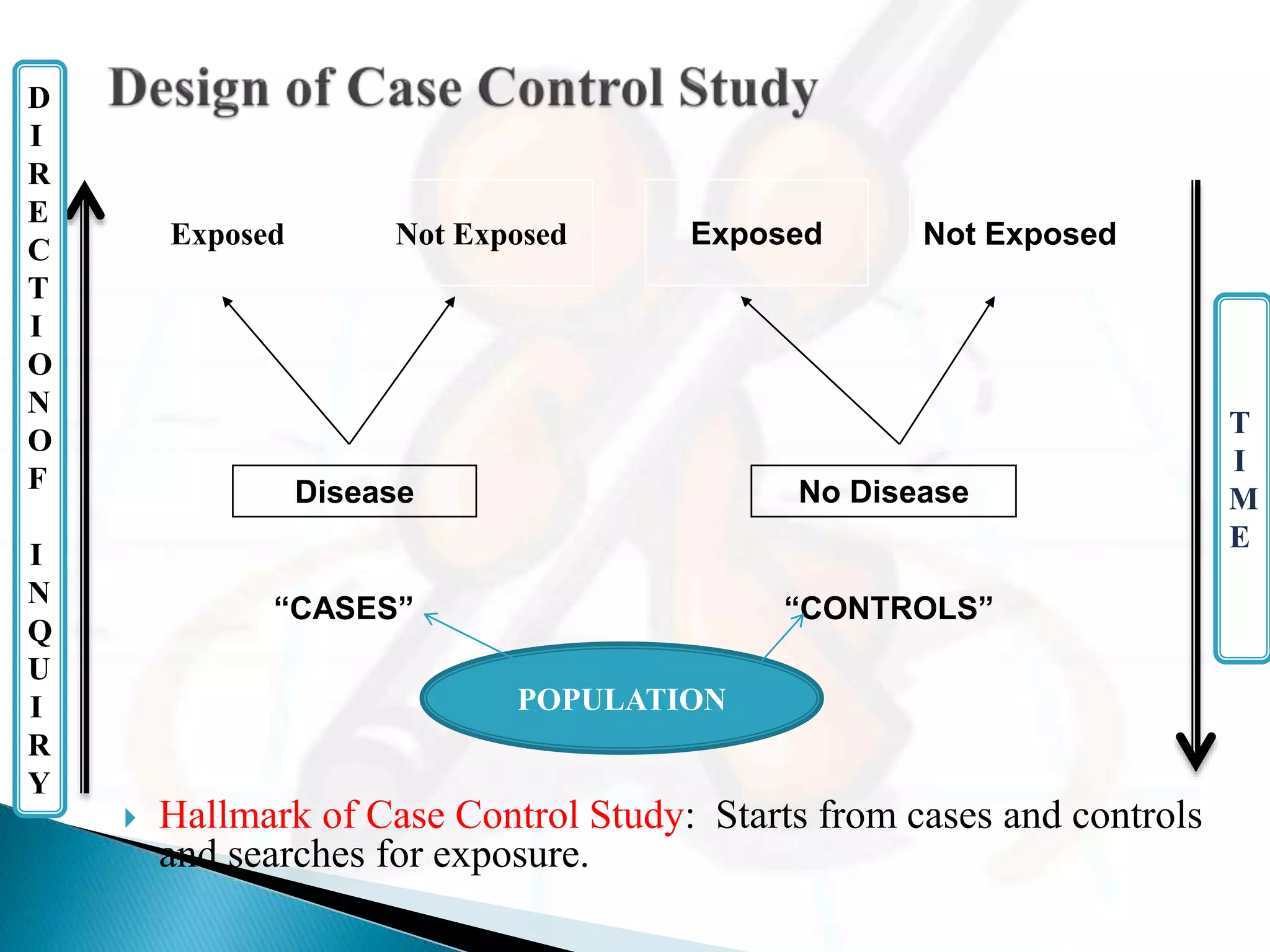
This document summarizes a presentation on case-control studies. It defines epidemiology and different types of studies. It then discusses the key aspects of case-control studies including:
- They proceed backwards from the effect (disease) to the potential cause (exposure).
- Cases and controls are selected and their exposure status is determined. Exposure rates, relative risk, and odds ratios can then be estimated.
- Important steps include properly defining cases and controls, selecting controls, matching, measuring exposure, and analyzing for bias. Case-control studies are useful for investigating rare diseases and establishing causal relationships.