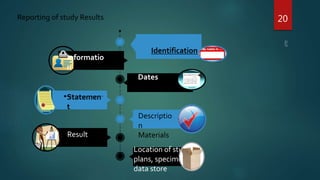
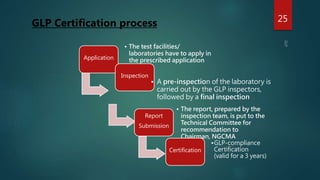
Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) regulations were created by the FDA in the 1970s after discovering fraudulent activities and poor lab practices that undermined the quality and integrity of data submitted to the FDA. GLP aims to ensure that studies are conducted properly according to standardized operating procedures and that accurate records are kept. This allows data from non-clinical studies to be reliably submitted to regulatory authorities. Key aspects of GLP include requirements for facilities, test systems, operating procedures, personnel qualifications, quality assurance programs, and record keeping. Following GLP helps assure reproducibility and quality of results.