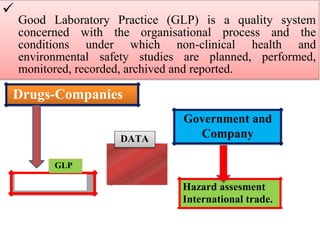
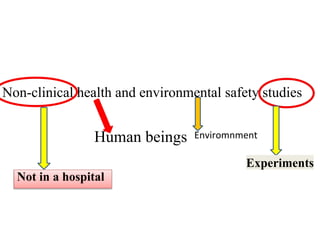
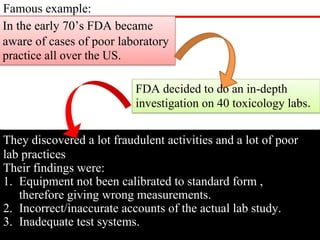
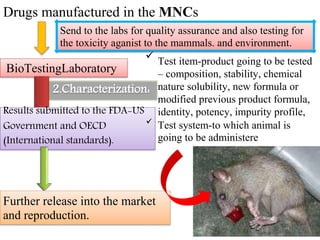
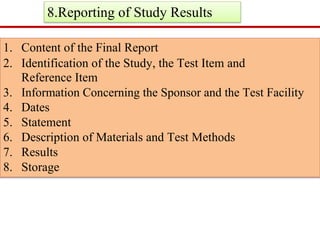
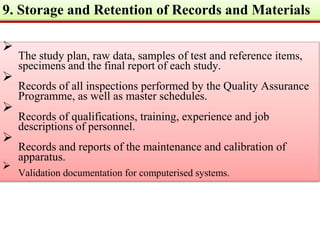
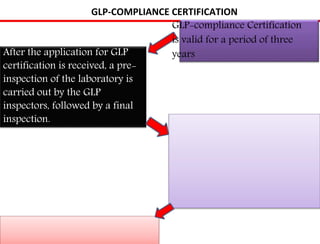
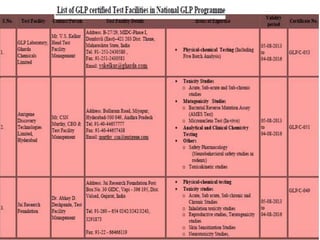
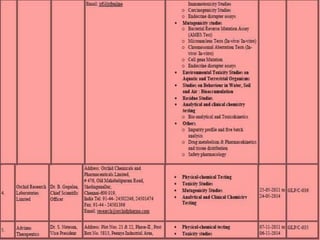
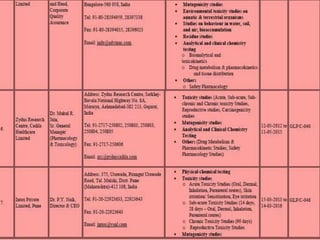
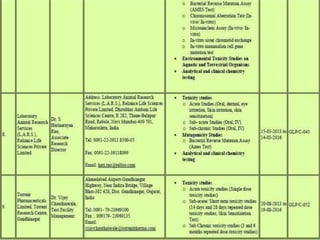
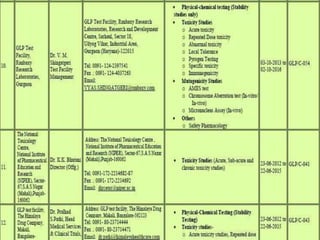
GLP (Good Laboratory Practice) is a quality system concerned with the organization and conditions under which non-clinical health and environmental safety studies are conducted. It was instituted in the US after fraudulent data was submitted by toxicology labs to the FDA. The OECD then established principles of GLP to harmonize standards internationally. The key principles cover organization and personnel, quality assurance, facilities, equipment, test systems, study conduct, reporting and record keeping. Compliance ensures the validity and integrity of study data submitted to regulatory authorities like the FDA. India has a National GLP Compliance Monitoring Authority that inspects and certifies laboratories according to OECD GLP principles.