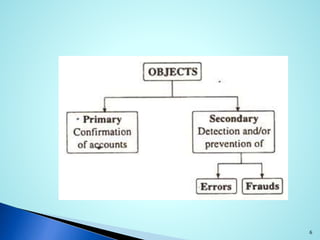
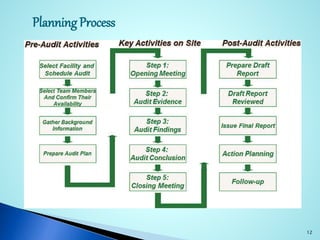
This document provides an introduction to auditing and the audit process. It defines an audit as the on-site verification of a process or quality system to ensure compliance. Audits can be conducted internally or externally according to ICH guidelines. The objectives of an audit are to determine conformity or nonconformity with quality systems and to improve quality. Pharmaceutical manufacturers use GMP audits to verify manufacturing controls and permit timely problem correction. Management audits comprehensively examine an organization. Audits can be first, second, or third party. An auditor's responsibilities include providing audit reports and identifying issues. The planning process for an audit involves announcing a schedule, conducting meetings, performing the audit, and providing follow-up.