Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COUNTER
•
9 likes•8,064 views
Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows It is not in range of human senses or un-aided detection for measurement.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Electron spin resonance(ESR) spectroscopy

ESR spectroscopy: introduction,principle, phenomenon of ESR, hyperfine splitting, instrumentation, schematic diagram,instruments used in ESR spectroscopy, application, analytical application, biological application.
Recommended
Electron spin resonance(ESR) spectroscopy

ESR spectroscopy: introduction,principle, phenomenon of ESR, hyperfine splitting, instrumentation, schematic diagram,instruments used in ESR spectroscopy, application, analytical application, biological application.
Radioisotope technique and methods

An isotope is one of two or more atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Unstable isotopes are called Radioisotopes.
uses of radioisotopes are many which are discussed in this slide.
transmission Electron Microscopy (Tem)

Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)- by sivasangari Shanmugam. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a technique used to observe the features of very small specimens.
Radioisotopes in biological system

I want to share my work with others.
"A man without EDUCATION is like a building without Foundation"
so keep sharing
Spectroscopy techniques, it's principle, types and applications 

Spectroscopy and it's applications as well as it's types like Infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet spectroscopy and principle of spectroscopy why we use spectroscopy.
Ultracentrifugation

It is an important tool in biochemical research. Which through rapid spinning imposes high centrifugal forces on suspended particles, or even molecules in solution, and causes separations of such matter on the basis of differences in weight.
Detection and Applications of Radioactivity in Clinical Chemistry

Basic aspects of Radioactivity for MD and MSc Biochemistry students. Includes description of RIA and RAST.
Prepared on Jan 2015
Phase contrast microscope

Phase contrast microscope, Types of phase contrast, Parts of Phase contrast microscope, Application of Phase contrast microscope
Radio immunoassay (RIA)

introduction to Immunoassay, Definition of immunoassay, Principle and Theory, Methods in RIA, Other immunoassays, Applications.
Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-detection & measurement of radioactivity

Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-detection & measurement of radioactivityDepartment of Biochemistry, Veer Bahadur Singh Purvanchal Univarsity, Jaunpur
Prabhakar Singh- II_SEM-Paper V_DETECTION & MEASUREMENT OF RADIOACTIVITYAutoradiography

Autoradigraphy, In vivo autoradiography, In vitro autoradiography, SPECT, radiolabelled p32 and C14,
Uv visible spectrophotometer

Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometry is a technique used to measure light absorbance across the ultraviolet and visible ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. When incident light strikes matter it can either be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted. The absorbance of radiation in the UV-Vis range causes atomic excitation, which refers to the transition of molecules from a low-energy ground state to an excited state.
ELECTRON SPIN RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY

Describes about the principle,application and instrumentation of electron spin resonance spectroscopy
Radiopharmaceuticals

Radiopharmaceutical is topic of subject Pharmaceutical inorganic Chemistry for B. Pharmacy First year students. This slide is presented with an aim to enable the students to easily understand and grasp unfamiliar concept of this topic
More Related Content
What's hot
Radioisotope technique and methods

An isotope is one of two or more atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Unstable isotopes are called Radioisotopes.
uses of radioisotopes are many which are discussed in this slide.
transmission Electron Microscopy (Tem)

Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)- by sivasangari Shanmugam. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a technique used to observe the features of very small specimens.
Radioisotopes in biological system

I want to share my work with others.
"A man without EDUCATION is like a building without Foundation"
so keep sharing
Spectroscopy techniques, it's principle, types and applications 

Spectroscopy and it's applications as well as it's types like Infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet spectroscopy and principle of spectroscopy why we use spectroscopy.
Ultracentrifugation

It is an important tool in biochemical research. Which through rapid spinning imposes high centrifugal forces on suspended particles, or even molecules in solution, and causes separations of such matter on the basis of differences in weight.
Detection and Applications of Radioactivity in Clinical Chemistry

Basic aspects of Radioactivity for MD and MSc Biochemistry students. Includes description of RIA and RAST.
Prepared on Jan 2015
Phase contrast microscope

Phase contrast microscope, Types of phase contrast, Parts of Phase contrast microscope, Application of Phase contrast microscope
Radio immunoassay (RIA)

introduction to Immunoassay, Definition of immunoassay, Principle and Theory, Methods in RIA, Other immunoassays, Applications.
Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-detection & measurement of radioactivity

Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-detection & measurement of radioactivityDepartment of Biochemistry, Veer Bahadur Singh Purvanchal Univarsity, Jaunpur
Prabhakar Singh- II_SEM-Paper V_DETECTION & MEASUREMENT OF RADIOACTIVITYAutoradiography

Autoradigraphy, In vivo autoradiography, In vitro autoradiography, SPECT, radiolabelled p32 and C14,
Uv visible spectrophotometer

Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometry is a technique used to measure light absorbance across the ultraviolet and visible ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. When incident light strikes matter it can either be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted. The absorbance of radiation in the UV-Vis range causes atomic excitation, which refers to the transition of molecules from a low-energy ground state to an excited state.
ELECTRON SPIN RESONANCE SPECTROSCOPY

Describes about the principle,application and instrumentation of electron spin resonance spectroscopy
What's hot (20)
Spectroscopy techniques, it's principle, types and applications 

Spectroscopy techniques, it's principle, types and applications
Detection and Applications of Radioactivity in Clinical Chemistry

Detection and Applications of Radioactivity in Clinical Chemistry
Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-detection & measurement of radioactivity

Prabhakar singh ii sem-paper v-detection & measurement of radioactivity
Similar to Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COUNTER
Radiopharmaceuticals

Radiopharmaceutical is topic of subject Pharmaceutical inorganic Chemistry for B. Pharmacy First year students. This slide is presented with an aim to enable the students to easily understand and grasp unfamiliar concept of this topic
Introduction to radioactivity

general introduction of radioactivity, it include discovery of radioactivity, types of radiation, isotopes and radioactive isotopes difference, half life, prevention and precaution from radiation. detecting devices used in laboreatory for radiation spillage and protection.
Detection of Radioactive Contamination 

An overview about contamination occuring throgh radionuclides.
SOLID SCINTILLATION WRITE UP.docx

A scintillation counter is an instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation by using the excitation effect of incident radiation on a scintillating material, and detecting the resultant light pulses or it can be defined as it is used to detect gamma rays and the presence of a particle. It can also measure the radiation in the scintillating medium, the energy loss, or the energy gain. The medium can be solid and liquid.
The phenomenon in which the nucleus of the atom of an element undergoes spontaneous and uncontrollable disintegration or decay and emit alpha, beta, or gamma rays
It is the property of some unstable atoms to spontaneously emit nuclear radiation to gain stability.
The heavy elements are called radioactive elements and rays emitted these elements are called radioactive rays.
The phenomenon of radioactivity is discovered by HENRI BACQUEREL IN 1896.
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay (α-decay), beta decay (β-decay), and gamma decay (γ-decay), all of which involve emitting one or more particles.
Radiopharmaceuticals

radiopharmaceuticals introduction isotopes types of radioisotopes measurement of radioactivity handling and storage of radioactive material applications
UNIT 5.pptx

Radio activity
Measurement of radioactivity
Properties of α, β, γ radiations
Half life, radio isotopes
Study of radio isotopes - Sodium iodide I131,
Storage conditions, precautions & pharmaceutical application of radioactive substances
Photometry and spectrophotometry 

in this we can learn what is Photometry?, what is spectrophotometry ? and application of spectrophotometry?, uses of photometry? etc..
Similar to Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COUNTER (20)
More from Nethravathi Siri
Human genetics and holistic health

This presentation was live on July 8th 2020, here is the link for YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2DvAot_L2QU
LIVE AND LET IVE
QUANTITATIVE INHERITANCE - KERNEL COLOR IN WHEAT

Nilsson-Ehle (1909) and East (1910, 1916) documented first significant evidence of
quantitative inheritance by their individual works in wheat.
Their analysis started from one-locus control which continued to two locus control
and concluded at three-locus control.
Evolutionary genetics - Theories, 

Overview
In simpler terms, Evolutionary Genetics is the study to understand how genetic
variation leads to evolutionary change.
Evolutionary Genetics attempts to account for evolution in terms of changes in gene
and genotype frequencies within populations and the processes that convert the
variation with populations into more or less permanent variation between species.
The central challenge of Evolutionary Genetics is to describe how the evolutionary
forces shape the patterns of biodiversity.
Evolutionary Genetics majorly deals with;
a. Evolution of genome structure
b. The genetic basis of speciation and adaptation
c. Genetic change in response to selection within populations
Upstream processing 

Overview
Industrial fermentations comprise both upstream (USP) and downstream processing
(DSP) stages. USP involves all factors and processes leading to and including the
fermentation. It consists of three main areas: the producer organism, the medium
and the fermentation process.
Retro copia transposons

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
RNA TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTS (COPIA) IN Drosophila
within host genomes.
As TEs comprise more than 40% of the human genome and are linked to
numerous diseases, understanding their mechanisms of mobilization and
regulation is important.
Drosophila melanogaster is an ideal model organism for the study of eukaryotic
TEs as its genome contains a diverse array of active TEs.
Also referred to as “jumping genes,” TEs move, or transpose, to different locations
throughout the genomes in which they reside.
Eukaryotic transcription 

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Transcription is more complicated in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes because
eukaryotes possess three different classes of RNA polymerases and because of the
way in which transcripts are processed to their functional forms.
More proteins and transcription factors are involved in eukaryotic transcription.
Holliday model of crossing over

One of the first plausible models to account for the preceding observations was
formulated by Robin Holliday.
The key features of the Holliday model are the formation of heteroduplex DNA; the
creation of a cross bridge; its migration along the two heteroduplex strands,
termed branch migration; the occurrence of mismatch repair; and the
subsequent resolution, or splicing, of the intermediate structure to yield different
typesof recombinant molecules.
Vitamins - Basics

A Vitamin is an organic compound by an organism as a vital nutrient in limited
amounts.
• We need vitamins in our diet, because our bodies can’t synthesize them quickly
enough to meet our daily needs.
• The term vitamin was derived from ‘vitamine’ meaning vital and amine.
• It was coined by K FUNK (1912).
3. Special chromosome - B chromosome 

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Supernumerary chromosomes are the additional or extra chromosomal set present in a
cell, which are dissimilar to normal A-Chromosomal set in the species.
They are also called as Accessory Chromosomes and lack homologous chromosome part.
In wild populations, around 100 animal species, 600 plant species especially fungi
contain supernumerary / B-chromosomes
3. Special chromosomes - Lampbrush chromosomes 

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Paired chromosome in meiosis in immature amphibian eggs, in which the chromatin
forms large stiff loops extending out from the linear axis of the chromosome
The lampbrush chromosomes derive their name from the lateral loops that extrude from
the chromomeres at certain point.
They are very transcriptionally active DNA, where loops of DNA emerging from an
apparently continuous chromosomal axis are coated with RNA polymerase.
2. Special chromosomes - Polytene chromosomes

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Since, these chromosomes were discovered in the salivary gland cells, they are called
as "Salivary Gland Chromosomes".
The present name polytene chromosome was suggested by kollar due to the
occurrence of many chromonemata (DNA) in them.
Bridges (~1936) 1st constructed a salivary chromosome map of D melanogaster and
found 5000 special bands in polytene chromosomes.
1. Special chromosomes - Introduction

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
In some organisms, there are special tissues in which chromosomes undergo structural
specializations.
Such specialized chromosomes are generally termed as SPECIAL TYPES OF
CHROMOSOMES
Crossing over basics

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Crossing over is exchange of strictly homologous segments of a genome between their
respective non-sister chromatids during cell division, which results in chromosomal
recombinations of linked genes in daughter cells.
NUCLEOSOME MODEL OF CHROMOSOME

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Nucleosome model of chromosome is proposed by ROGER KORNBERG (son of Arthur
Kornberg) in 1974.
It was confirmed and crystalised by P. Oudet et al., (1975).
Nucleosome is the lowest level of Chromosome organization in eukaryotic cells.
Nucleosome model is a scientific model which explains the organization of DNA and
associated proteins in the chromosomes.
Nucleosome model also explains the exact mechanism of the folding of DNA in
thenucleus.
It is the most accepted model of chromatin organization.
4. Gene interaction - Epistasis - Dominant & Recessive, Non-epistatsis

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Epistasis is a Greek word that means standing over.
BATESON used term epistasis to describe the masking effect in 1909
The term epistasis describes a certain relationship between genes, where an allele of
one gene hides or masks the visible output or phenotype of another gene.
When two different genes which are not alleles, both affect the same character in such
a way that the expression of one masks (inhibits or suppresses) the expression of the
other gene, the phenomenon is said to be epistasis.
The gene that suppresses other gene expression is known as Epistatic gene.
The gene that is suppressed or remain obscure is called Hypostatic gene
The classical phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 F2 ratio becomes modified by epistasis.
3. Gene interaction - supplementary

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
In supplementary gene action, the dominant allele of one gene is essential for the
development of the concerned phenotype, while the other gene modifies the expression of the first gene.
2. Gene interaction - complementary

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Complementation between two non-allelic genes (C and P) are essential for production
of a particular or special phenotype i.e., complementary factor.
Two genes involved in a specific pathway and their functional products are required
for gene expression, then one recessive allelic pair at either allelic pair would result in
the mutant phenotype.
When Dominant alleles are present together, they complement each other to yield
complementary factor resulting in a special phenotype.
They are called complementary genes.
When either of gene loci have homozygous recessive alleles (i.e., genotypes of ccPP,
ccPp, CCpp, Ccpp and ccpp), they produce identical phenotypes and change F2 ratio
to 9:7.
1. Gene interaction - Introduction

Basics for undergraduate/university students
The phenomenon of two or more genes affecting the expression of each other in various
ways in the development of a single character of an organism is known as GENE
INTERACTION.
Comparative account on different types of microscopes

Basics
SIMPLE
MICROSCOPE
BRIGHTFIELD
MICROSCOPE
DARK-FIELD
MICROSCOPE
STEREO
ZOOM
MICROSCOPE
PHASE
CONTRAST
MICROSCOPE
FLUORESCENT
MICROSCOPE
TRANSMISSION
ELECTRON
MICROSCOPE
SCANNING
ELECTRON
MICROSCOPE
SOURCE OF ILLUMINATION
SAMPLEVISUALIZATION
CONDENSER
ADDITIONAL SUPPORT SYSTEM
SPECIMEN STAINING
MAGNIFICATION POWER
RESOLUTION
APPLICATION
5. Microsocope ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM & SEM ) - Basics

Basics only
Electron beam is the source of illumination.
Image is produced by magnetic field.
Contrasting features between light microscope and electron microscope are
construction, working principle, specimen preparation, cost-expenses and designed
room (vacuum chamber).
More from Nethravathi Siri (20)
4. Gene interaction - Epistasis - Dominant & Recessive, Non-epistatsis

4. Gene interaction - Epistasis - Dominant & Recessive, Non-epistatsis
Comparative account on different types of microscopes

Comparative account on different types of microscopes
5. Microsocope ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM & SEM ) - Basics

5. Microsocope ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM & SEM ) - Basics
Recently uploaded
Observation of Io’s Resurfacing via Plume Deposition Using Ground-based Adapt...

Since volcanic activity was first discovered on Io from Voyager images in 1979, changes
on Io’s surface have been monitored from both spacecraft and ground-based telescopes.
Here, we present the highest spatial resolution images of Io ever obtained from a groundbased telescope. These images, acquired by the SHARK-VIS instrument on the Large
Binocular Telescope, show evidence of a major resurfacing event on Io’s trailing hemisphere. When compared to the most recent spacecraft images, the SHARK-VIS images
show that a plume deposit from a powerful eruption at Pillan Patera has covered part
of the long-lived Pele plume deposit. Although this type of resurfacing event may be common on Io, few have been detected due to the rarity of spacecraft visits and the previously low spatial resolution available from Earth-based telescopes. The SHARK-VIS instrument ushers in a new era of high resolution imaging of Io’s surface using adaptive
optics at visible wavelengths.
FAIR & AI Ready KGs for Explainable Predictions

The increased availability of biomedical data, particularly in the public domain, offers the opportunity to better understand human health and to develop effective therapeutics for a wide range of unmet medical needs. However, data scientists remain stymied by the fact that data remain hard to find and to productively reuse because data and their metadata i) are wholly inaccessible, ii) are in non-standard or incompatible representations, iii) do not conform to community standards, and iv) have unclear or highly restricted terms and conditions that preclude legitimate reuse. These limitations require a rethink on data can be made machine and AI-ready - the key motivation behind the FAIR Guiding Principles. Concurrently, while recent efforts have explored the use of deep learning to fuse disparate data into predictive models for a wide range of biomedical applications, these models often fail even when the correct answer is already known, and fail to explain individual predictions in terms that data scientists can appreciate. These limitations suggest that new methods to produce practical artificial intelligence are still needed.
In this talk, I will discuss our work in (1) building an integrative knowledge infrastructure to prepare FAIR and "AI-ready" data and services along with (2) neurosymbolic AI methods to improve the quality of predictions and to generate plausible explanations. Attention is given to standards, platforms, and methods to wrangle knowledge into simple, but effective semantic and latent representations, and to make these available into standards-compliant and discoverable interfaces that can be used in model building, validation, and explanation. Our work, and those of others in the field, creates a baseline for building trustworthy and easy to deploy AI models in biomedicine.
Bio
Dr. Michel Dumontier is the Distinguished Professor of Data Science at Maastricht University, founder and executive director of the Institute of Data Science, and co-founder of the FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable) data principles. His research explores socio-technological approaches for responsible discovery science, which includes collaborative multi-modal knowledge graphs, privacy-preserving distributed data mining, and AI methods for drug discovery and personalized medicine. His work is supported through the Dutch National Research Agenda, the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research, Horizon Europe, the European Open Science Cloud, the US National Institutes of Health, and a Marie-Curie Innovative Training Network. He is the editor-in-chief for the journal Data Science and is internationally recognized for his contributions in bioinformatics, biomedical informatics, and semantic technologies including ontologies and linked data.
Richard's aventures in two entangled wonderlands

Since the loophole-free Bell experiments of 2020 and the Nobel prizes in physics of 2022, critics of Bell's work have retreated to the fortress of super-determinism. Now, super-determinism is a derogatory word - it just means "determinism". Palmer, Hance and Hossenfelder argue that quantum mechanics and determinism are not incompatible, using a sophisticated mathematical construction based on a subtle thinning of allowed states and measurements in quantum mechanics, such that what is left appears to make Bell's argument fail, without altering the empirical predictions of quantum mechanics. I think however that it is a smoke screen, and the slogan "lost in math" comes to my mind. I will discuss some other recent disproofs of Bell's theorem using the language of causality based on causal graphs. Causal thinking is also central to law and justice. I will mention surprising connections to my work on serial killer nurse cases, in particular the Dutch case of Lucia de Berk and the current UK case of Lucy Letby.
Citrus Greening Disease and its Management

Citrus Greening was one of the major causes of decline in the citrus production. So, effective management cultural practices should be incorporated
SCHIZOPHRENIA Disorder/ Brain Disorder.pdf

This pdf is about the Schizophrenia.
For more details visit on YouTube; @SELF-EXPLANATORY;
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCAiarMZDNhe1A3Rnpr_WkzA/videos
Thanks...!
Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology

As consumer awareness of health and wellness rises, the nutraceutical market—which includes goods like functional meals, drinks, and dietary supplements that provide health advantages beyond basic nutrition—is growing significantly. As healthcare expenses rise, the population ages, and people want natural and preventative health solutions more and more, this industry is increasing quickly. Further driving market expansion are product formulation innovations and the use of cutting-edge technology for customized nutrition. With its worldwide reach, the nutraceutical industry is expected to keep growing and provide significant chances for research and investment in a number of categories, including vitamins, minerals, probiotics, and herbal supplements.
Structures and textures of metamorphic rocks

It is useful for the Under Graduating students for easy understanding and it's useful for the exam preparations.
Cancer cell metabolism: special Reference to Lactate Pathway

Normal Cell Metabolism:
Cellular respiration describes the series of steps that cells use to break down sugar and other chemicals to get the energy we need to function.
Energy is stored in the bonds of glucose and when glucose is broken down, much of that energy is released.
Cell utilize energy in the form of ATP.
The first step of respiration is called glycolysis. In a series of steps, glycolysis breaks glucose into two smaller molecules - a chemical called pyruvate. A small amount of ATP is formed during this process.
Most healthy cells continue the breakdown in a second process, called the Kreb's cycle. The Kreb's cycle allows cells to “burn” the pyruvates made in glycolysis to get more ATP.
The last step in the breakdown of glucose is called oxidative phosphorylation (Ox-Phos).
It takes place in specialized cell structures called mitochondria. This process produces a large amount of ATP. Importantly, cells need oxygen to complete oxidative phosphorylation.
If a cell completes only glycolysis, only 2 molecules of ATP are made per glucose. However, if the cell completes the entire respiration process (glycolysis - Kreb's - oxidative phosphorylation), about 36 molecules of ATP are created, giving it much more energy to use.
IN CANCER CELL:
Unlike healthy cells that "burn" the entire molecule of sugar to capture a large amount of energy as ATP, cancer cells are wasteful.
Cancer cells only partially break down sugar molecules. They overuse the first step of respiration, glycolysis. They frequently do not complete the second step, oxidative phosphorylation.
This results in only 2 molecules of ATP per each glucose molecule instead of the 36 or so ATPs healthy cells gain. As a result, cancer cells need to use a lot more sugar molecules to get enough energy to survive.
Unlike healthy cells that "burn" the entire molecule of sugar to capture a large amount of energy as ATP, cancer cells are wasteful.
Cancer cells only partially break down sugar molecules. They overuse the first step of respiration, glycolysis. They frequently do not complete the second step, oxidative phosphorylation.
This results in only 2 molecules of ATP per each glucose molecule instead of the 36 or so ATPs healthy cells gain. As a result, cancer cells need to use a lot more sugar molecules to get enough energy to survive.
introduction to WARBERG PHENOMENA:
WARBURG EFFECT Usually, cancer cells are highly glycolytic (glucose addiction) and take up more glucose than do normal cells from outside.
Otto Heinrich Warburg (; 8 October 1883 – 1 August 1970) In 1931 was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology for his "discovery of the nature and mode of action of the respiratory enzyme.
WARNBURG EFFECT : cancer cells under aerobic (well-oxygenated) conditions to metabolize glucose to lactate (aerobic glycolysis) is known as the Warburg effect. Warburg made the observation that tumor slices consume glucose and secrete lactate at a higher rate than normal tissues.
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Article written for leader telegram
Seminar of U.V. Spectroscopy by SAMIR PANDA

Spectroscopy is a branch of science dealing the study of interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter.
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflect spectroscopy in the UV-VIS spectral region.
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the amount of light received by the analyte.
The ASGCT Annual Meeting was packed with exciting progress in the field advan...

The ASGCT Annual Meeting was packed with exciting progress in the field advancing efforts to deliver highly promising therapies to more patients.
Recently uploaded (20)
Mammalian Pineal Body Structure and Also Functions

Mammalian Pineal Body Structure and Also Functions
Observation of Io’s Resurfacing via Plume Deposition Using Ground-based Adapt...

Observation of Io’s Resurfacing via Plume Deposition Using Ground-based Adapt...
Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology

Nutraceutical market, scope and growth: Herbal drug technology
erythropoiesis-I_mechanism& clinical significance.pptx

erythropoiesis-I_mechanism& clinical significance.pptx
Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx

Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx
Cancer cell metabolism: special Reference to Lactate Pathway

Cancer cell metabolism: special Reference to Lactate Pathway
Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...

Astronomy Update- Curiosity’s exploration of Mars _ Local Briefs _ leadertele...
The ASGCT Annual Meeting was packed with exciting progress in the field advan...

The ASGCT Annual Meeting was packed with exciting progress in the field advan...
Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COUNTER
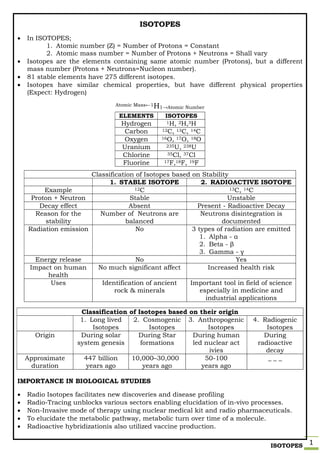
- 1. ISOTOPES 1 ISOTOPES In ISOTOPES; 1. Atomic number (Z) = Number of Protons = Constant 2. Atomic mass number = Number of Protons + Neutrons = Shall vary Isotopes are the elements containing same atomic number (Protons), but a different mass number (Protons + Neutrons=Nucleon number). 81 stable elements have 275 different isotopes. Isotopes have similar chemical properties, but have different physical properties (Expect: Hydrogen) Atomic Mass←1H1→Atomic Number IMPORTANCE IN BIOLOGICAL STUDIES Radio Isotopes facilitates new discoveries and disease profiling Radio-Tracing unblocks various sectors enabling elucidation of in-vivo processes. Non-Invasive mode of therapy using nuclear medical kit and radio pharmaceuticals. To elucidate the metabolic pathway, metabolic turn over time of a molecule. Radioactive hybridizationis also utilized vaccine production. ELEMENTS ISOTOPES Hydrogen 1H, 2H,3H Carbon 12C, 13C, 14C Oxygen 16O, 17O, 18O Uranium 235U, 238U Chlorine 35Cl, 37Cl Fluorine 17F,18F, 19F Classification of Isotopes based on Stability 1. STABLE ISOTOPE 2. RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPE Example 12C 13C, 14C Proton + Neutron Stable Unstable Decay effect Absent Present - Radioactive Decay Reason for the stability Number of Neutrons are balanced Neutrons disintegration is documented Radiation emission No 3 types of radiation are emitted 1. Alpha - α 2. Beta - β 3. Gamma - γ Energy release No Yes Impact on human health No much significant affect Increased health risk Uses Identification of ancient rock & minerals Important tool in field of science especially in medicine and industrial applications Classification of Isotopes based on their origin 1. Long lived Isotopes 2. Cosmogenic Isotopes 3. Anthropogenic Isotopes 4. Radiogenic Isotopes Origin During solar system genesis During Star formations During human led nuclear act ivies During radioactive decay Approximate duration 447 billion years ago 10,000–30,000 years ago 50-100 years ago _ _ _
- 2. ISOTOPES 2 In clinicaldiagnosis to detect tumor, blood clots, infection. Neuro imaging, pharmacological studies, non-invasive therapies for hyper-thyrodism and cancer (Radio-immunotherapy). Based on the radioactivity of the elements in the nature, evolutionarist speculate the phyllogenetic tree. Radiation is used as a mutagen to produce mutants for scientific studies. OTHER USES Sterilization and food irradiation in Industries. Geochemists use radio isotopes to analyze the composition of geological materials. MEASURE OF RADIOACTIVITY It is not in range of human senses or un-aided detection for measurement. Unit for measurement of Radioactivity For Chemicals For Human For Risk Assessment S.I unit Becquerel (Bq) Gray (Gy) Sievert (Sv) Conventional unit Curie (Ci) Radiation absorbed dose (rad) Roentgen equivalent man (rem) Comparison Amount of Rain fall Amount of rain drops on any object Amount of rain drop precipitating on object Basic general principle for measurement of Radioactivity Measurement of Radioactivity 1. Gas-filled Counters (example: Geiger Muller [GM] Counter) 2. Scintillation Counter 3. Semi-Conductor Detectors 1. Geiger Muller [GM] Counter Nuclear physicist Hans Geigeris the co-inventor of Geiger-Muller counter (GM tube), a device used for the detection and measurement of all types of radiation: alpha, beta and gamma radiation. GM tube is a gas filled device used to detect ionising radiation, monitor and counted by electric circuit. Output is reported as counts per second or Rontgens per hour. WORKING PRINCIPLE GM tube filled with inert gas (Helium, Neon & Argon) at low pressure connected to High voltage source conducts electrical charge on particles or photons, ionising the gas conductives followed by amplification and according to discharge effect electrical charge released are counted as pulse, displayed as digital output in the meanwhile generates audio beeps in the speaker confirming the presence of radiation.
- 3. ISOTOPES 3 APPLICATIONS 1. To detect alpha, beta and gamma radiation from given sample. 2. To check for environmental levels of radioactivity. 3. In risk assessment in various working places. 4. To identify radioactivity in rocks and minerals. ADVANTAGES 1. Relatively less expensive 2. Durable 3. Easily portable 4. Detect all types of ionising radiation DISADVANTAGES 1. Fails to differentiate between or β or γ radiation. 2. Cant estimate exact energy level. 3. Very low efficiency. SCINTILLATION COUNTER It is one among the oldest and commoniest methods of particle detection. In 1945, photomultiplier tubes were invented to detect slightiest light particles. Scintillation counter is an instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation by using the excitation effect of incident radiation on a scintillator material, and detecting the resultant light pulses. It consists of a scintillator which generates photons in response to incident radiation. a sensitive photomultiplier tube (PMT) which converts the light to an electrical signal and electronics to process this signal.
- 4. ISOTOPES 4 WORKING PRINCIPLE When radiation is passed on fluroscent material (example: Zinc sulfide, thallium-activated sodium iodide), Scintillations (flashes of light) are produced and are converted into electric pulses by Photoelectric alloy (either of cesium and antimony), amplified about million times by photomultiplier tube and counted in the counter. Applications of Scintillation Counter 1. Scintillation Counters are widely used in radioactive contamination, radiation survey meters, radiometric assay, nuclear plant safety and medical imaging, that are used to measure radiation. 2. There are several counters of mounted on helicopters and some pickup trucks for rapid response in case of a security situation due to radioactive waste or dirty bombs. 3. Scintillation counters designed for weighbridge applications, freight terminals, scrap metal yards, border security, contamination monitoring of nuclear waste and ports. 4. It is widely used in Screening technologies, In vivo and ELISA alternative technologies, cancer research, epigenetics and Cellular research. 5. It also has its applications in Protein interaction and detection, academic research and Pharmaceutical. 6. Liquid Scintillation Counter is a type of scintillation counter that is used for measuring the beta emission from the nuclides.
