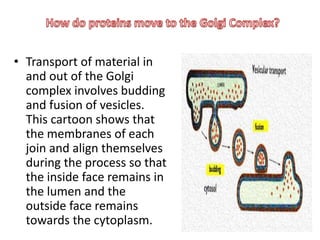
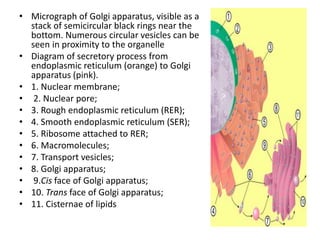
The Golgi apparatus, discovered by Camillo Golgi in 1897, is a crucial organelle in eukaryotic cells that processes and packages macromolecules like proteins and lipids. It consists of stacked membrane-bound structures called cisternae, performing vital functions such as protein sorting for secretion and modifications like phosphorylation and sulfation. Overall, the Golgi complex is essential for directing carbohydrates and proteins to their correct destinations within the cell.





![• Found in both plant and animal cells
• The Golgi is composed of stacks of membrane-
bound structures known
as cisternae (singular: cisterna).
• An individual stack is sometimes called a
dictyosome (from Greek dictyon: net + soma:
body),[4] especially in plant cell
• A mammalian cell typically contains 40 to 100
stacks.
• Between four and eight cisternae are usually
present in a stack; however, in some protists as
many as sixty have been observed
• Each cisterna comprises a flat, membrane
enclosed disc that includes special Golgi enzymes.
• The cisternae stack has four functional regions:
the cis- Golgi network, medial-Golgi, endo -Golgi,
and trans-Golgi network. Each region contains
different enzymes .
This electron micrograph illustrates
a Golgi Complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200502174956/85/Function-of-golgi-complex-By-KK-Sahu-Sir-6-320.jpg)
![• This includes the production of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), long unbranched polysaccharides .
• Enzymes in the Golgi polymerize several of these GAGs via a xylose link onto the core protein
• Another task of the Golgi involves the sulfation of certain molecules passing through its lumen via
sulphotranferases that gain their sulphur molecule from a donor called PAPs.
• This process occurs on the GAGs of proteoglycans as well as on the core protein.
• The level of sulfation is very important to the proteoglycans' signalling abilities as well as giving the
proteoglycan its overall negative charge.[13]
• The phosphorylation of molecules requires that ATP is imported into the lumen of the Golgi[15] and
then utilised
• by resident kinases such as casein kinase 1 and casein kinase 2
• One molecule that is phosphorylated in the Golgi is Apolipoprotein, which forms a molecule known
as VLDL that is a constituent of blood serum. It is thought that the phosphorylation of these
molecules is important to help aid in their sorting for secretion into the blood serum.
• A newly characterized protein, GAAP (Golgi anti-apoptotic protein), almost exclusively resides in the
Golgi and protects cells from apoptosis
• The bcl2 genes present in the Golgi are used for this purpose.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-200502174956/85/Function-of-golgi-complex-By-KK-Sahu-Sir-8-320.jpg)