Embed presentation
Downloaded 73 times
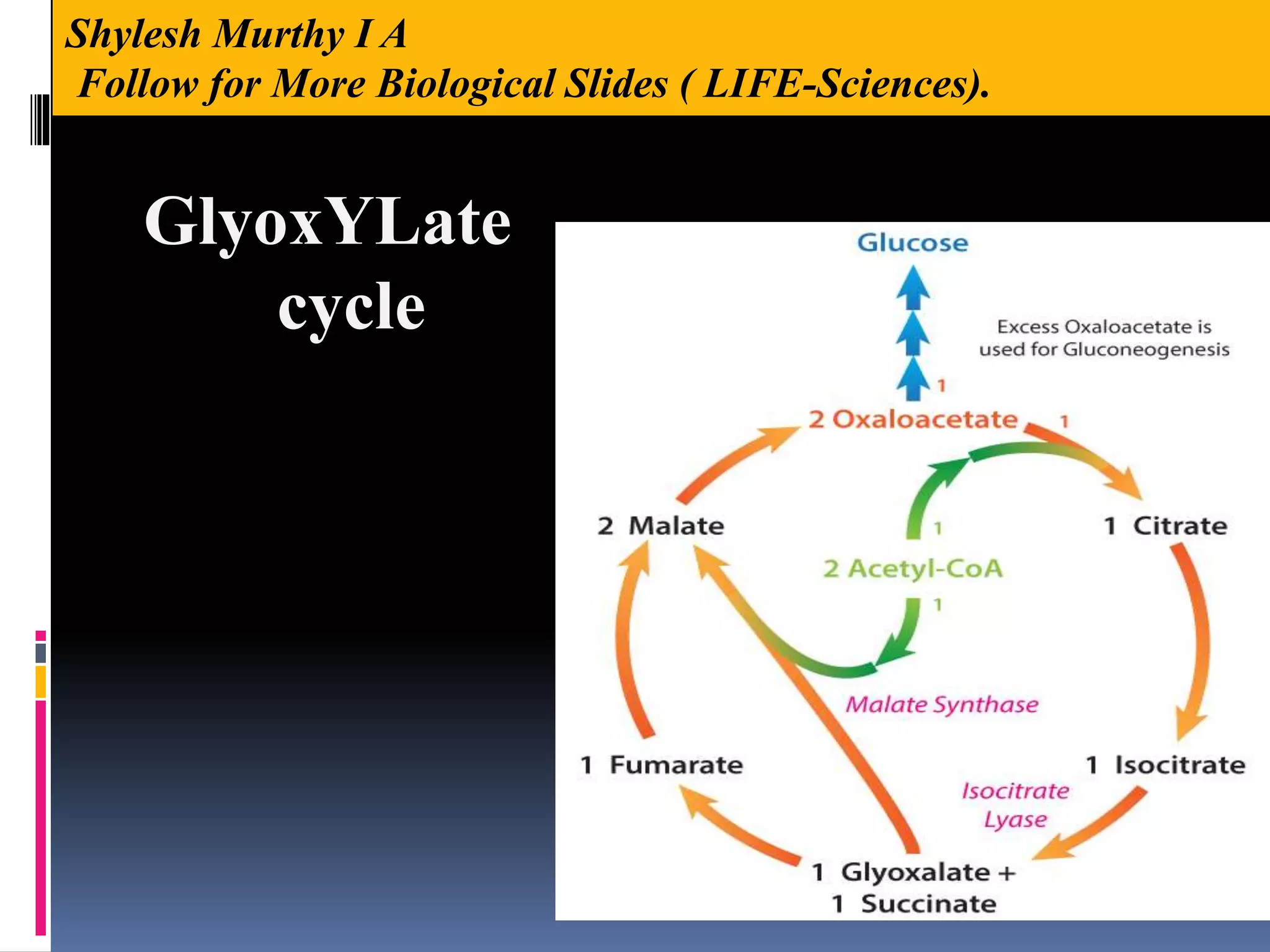



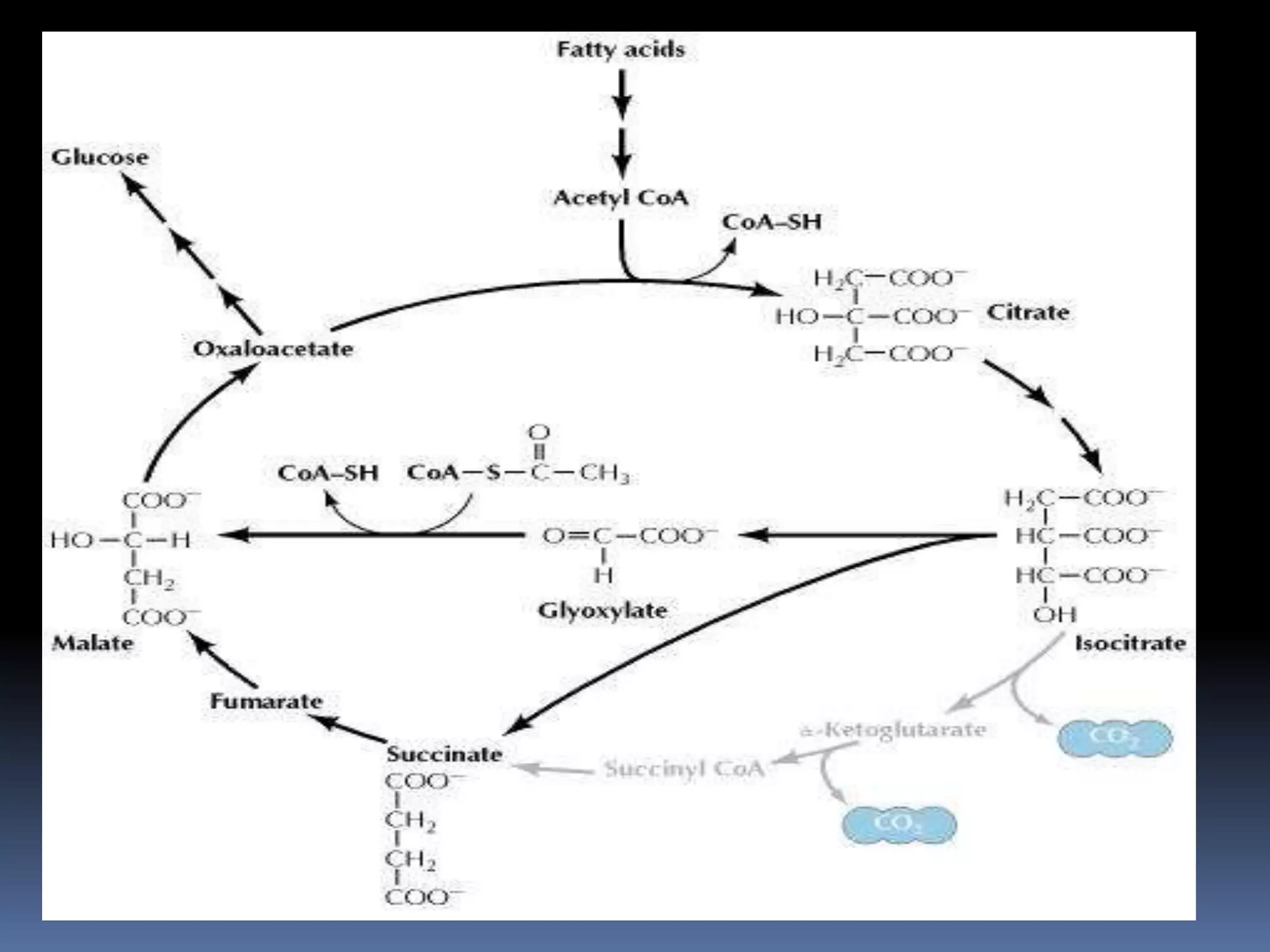
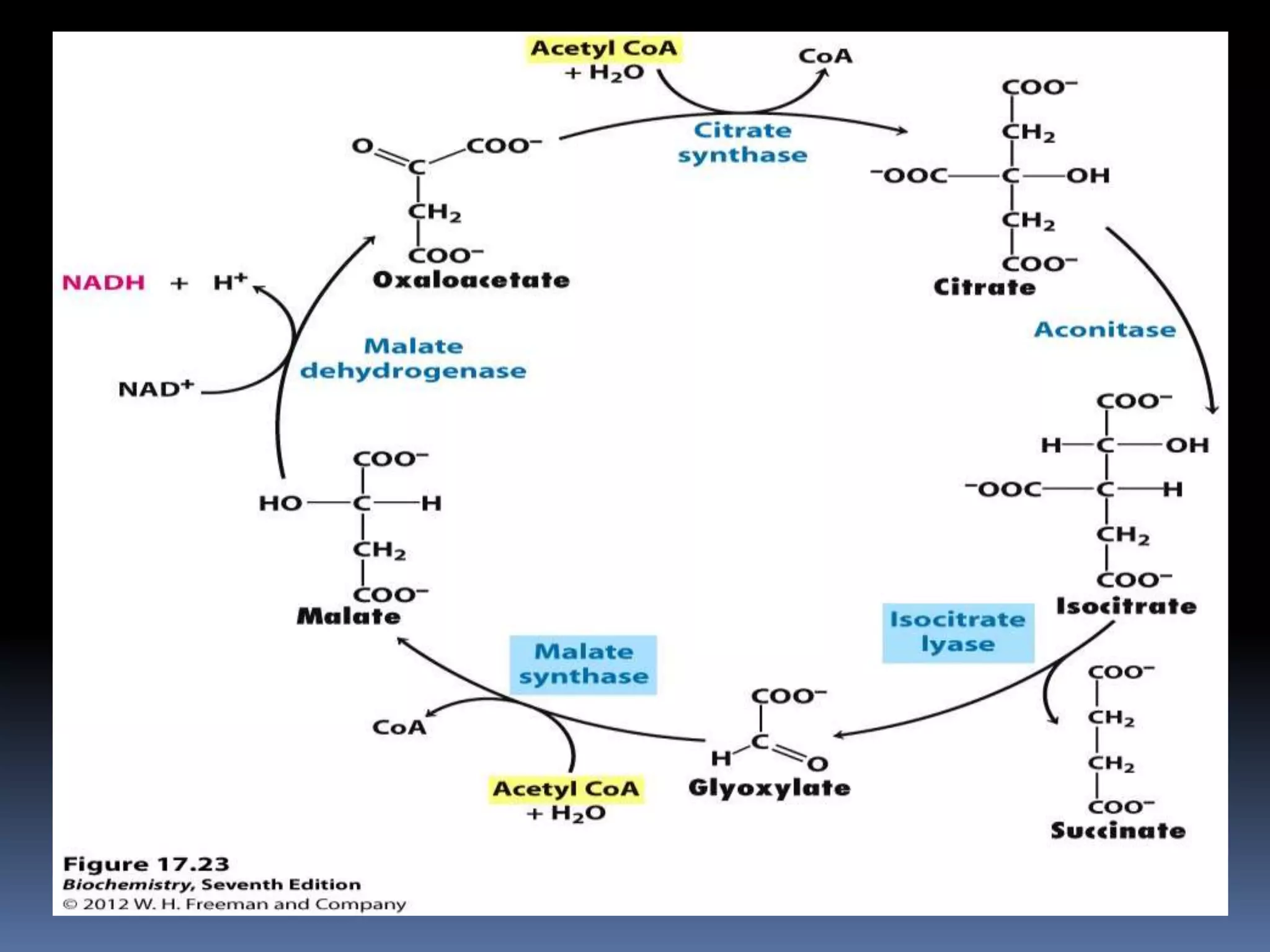




The glyoxylate cycle is an anabolic metabolic pathway that allows certain organisms, such as plants and fungi, to convert fats into carbohydrates by utilizing acetyl-CoA derived from the β-oxidation of fatty acids. This cycle occurs in glyoxysomes and involves enzymes that are isoenzymes of the TCA cycle, facilitating the production of succinate and ultimately glucose. It is regarded as a variant of the citric acid cycle, crucial for carbon assimilation and energy storage in these organisms.









