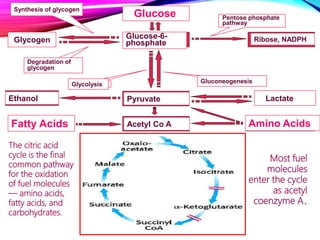
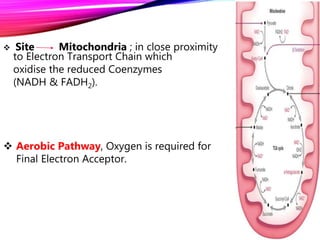
The document provides an overview of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle. It discusses the 8 steps of the cycle, from the entry of acetyl-CoA to the regeneration of oxaloacetate. Key enzymes involved in each step are described, as well as cofactors and regulation of the cycle. The TCA cycle serves as the final common pathway for the complete oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to produce ATP, NADH, and FADH2.