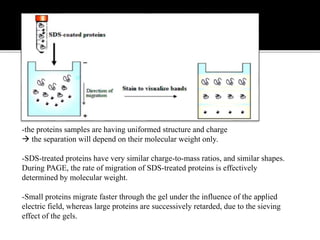
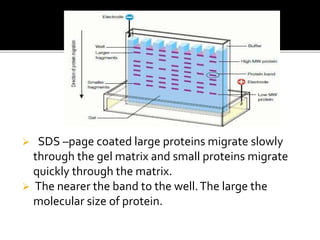
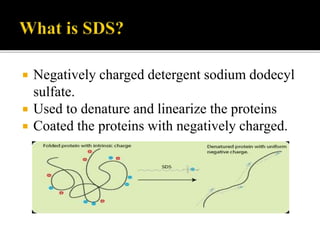
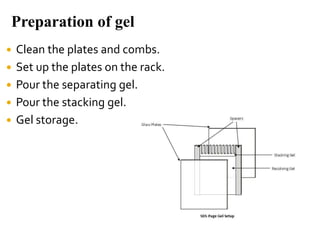
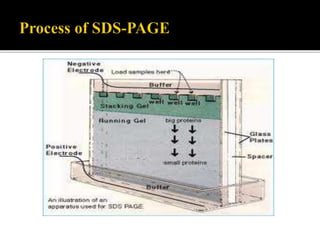
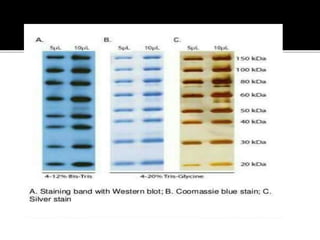
SDS-PAGE is a widely used electrophoresis technique to separate and identify proteins and nucleic acids based on their molecular weight. It employs sodium dodecyl sulfate to denature proteins, allowing for their separation in a gel under an electric field, where smaller proteins migrate faster than larger ones. The method can quantify proteins, determine molecular weight, and assess sample purity using various staining techniques.