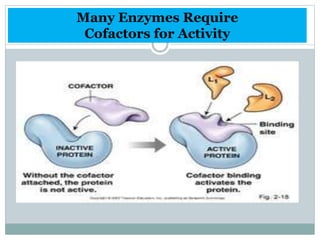
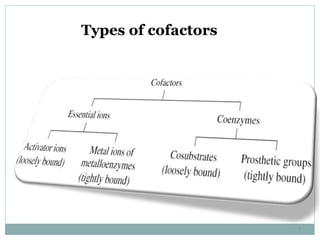
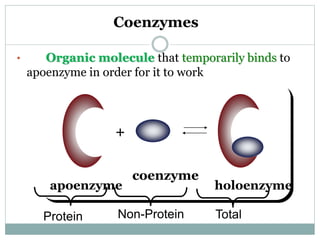
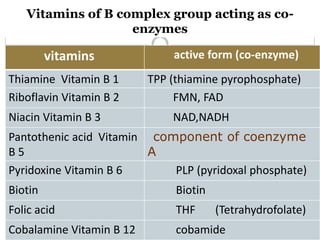
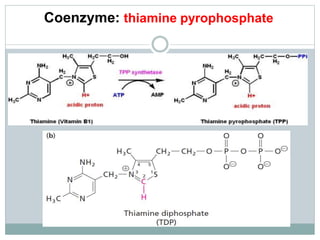
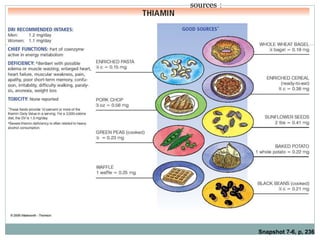
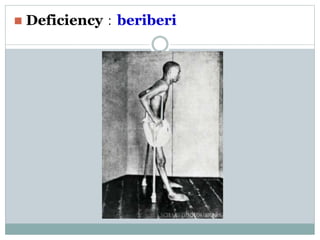
This document summarizes information about vitamin B1 (thiamine) and its active coenzyme form, thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP). It discusses the history of thiamine discovery and its chemical structure. Thiamine is converted to TPP in the liver and intestinal mucosa by the enzyme thiamine pyrophosphokinase using ATP. TPP acts as a coenzyme, transferring aldehyde groups in metabolic reactions. Sources of thiamine are mentioned and a deficiency can cause beriberi. Functions include roles in growth, nervous system maintenance, and metabolism.