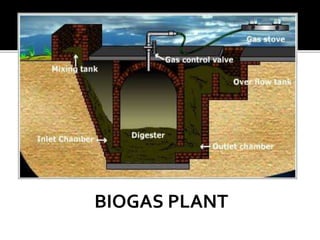
The document discusses solid waste, its sources, management, and biogas production, highlighting various types of solid waste and their characteristics. It explains the anaerobic digestion process used to produce biogas, primarily from agricultural waste like cow dung, and outlines the uses of biogas as a fuel. Additionally, it covers sugar industry by-products like molasses and bagasse, emphasizing their value in producing various chemicals and as biofuels.