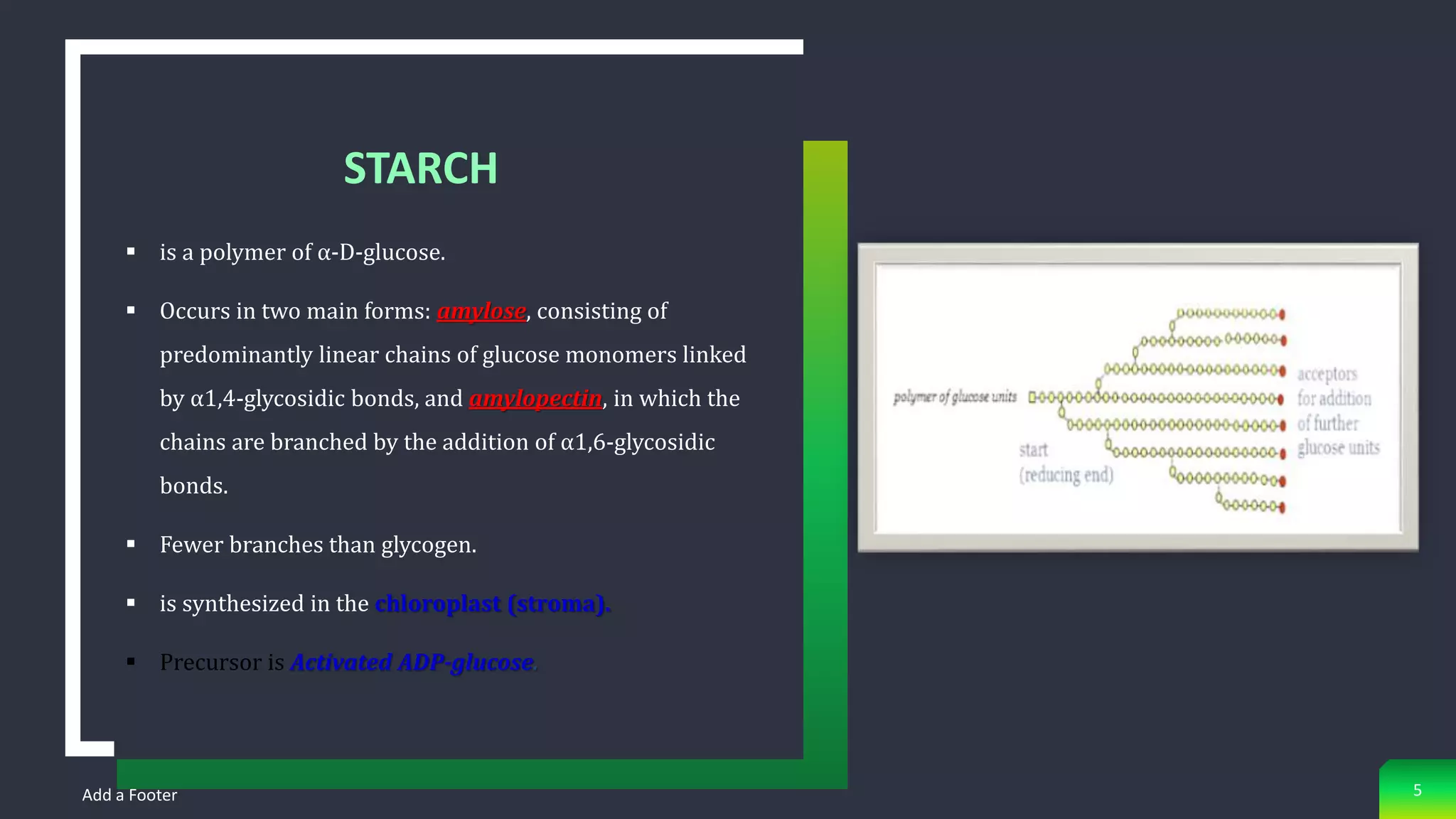
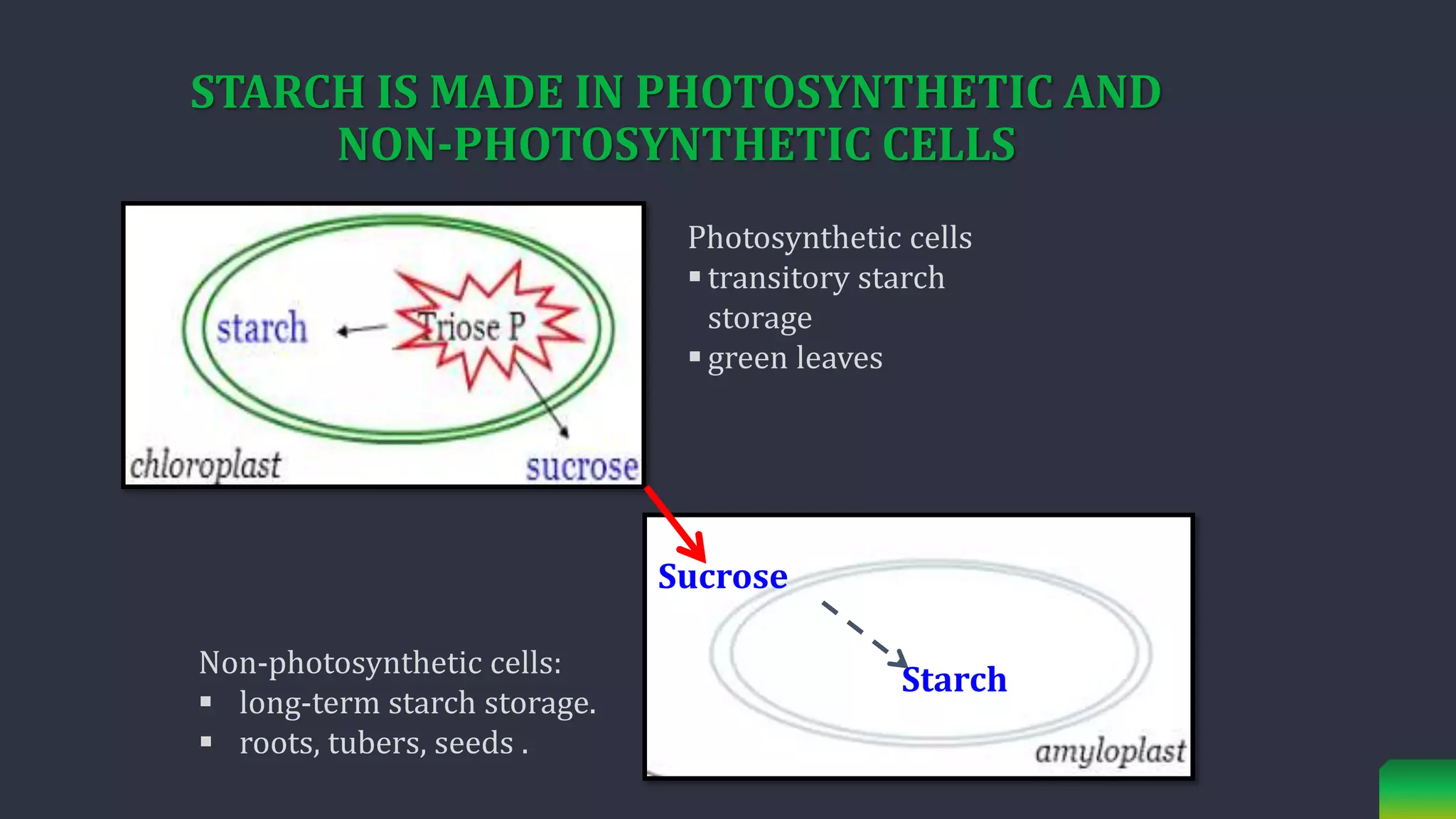
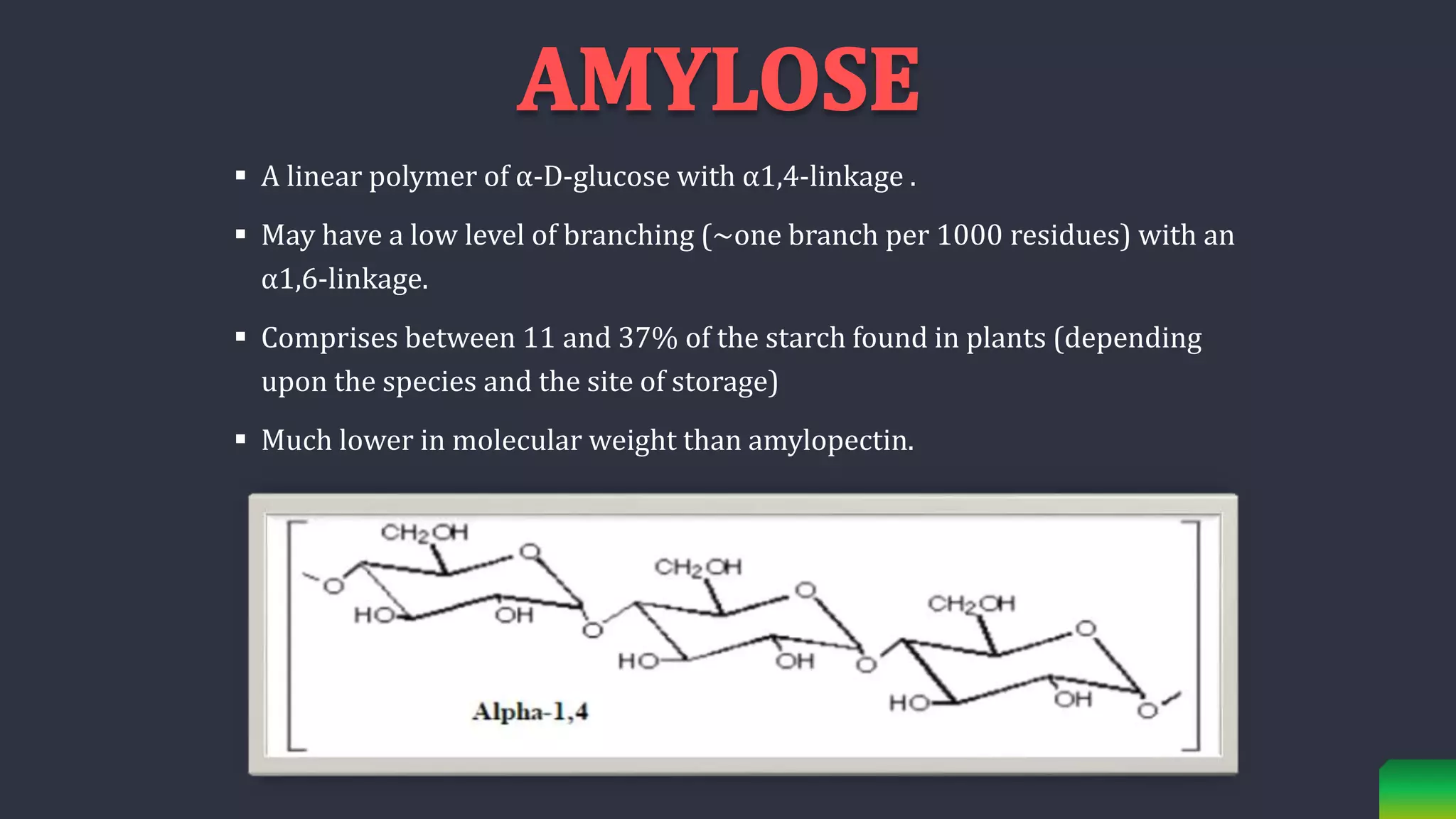
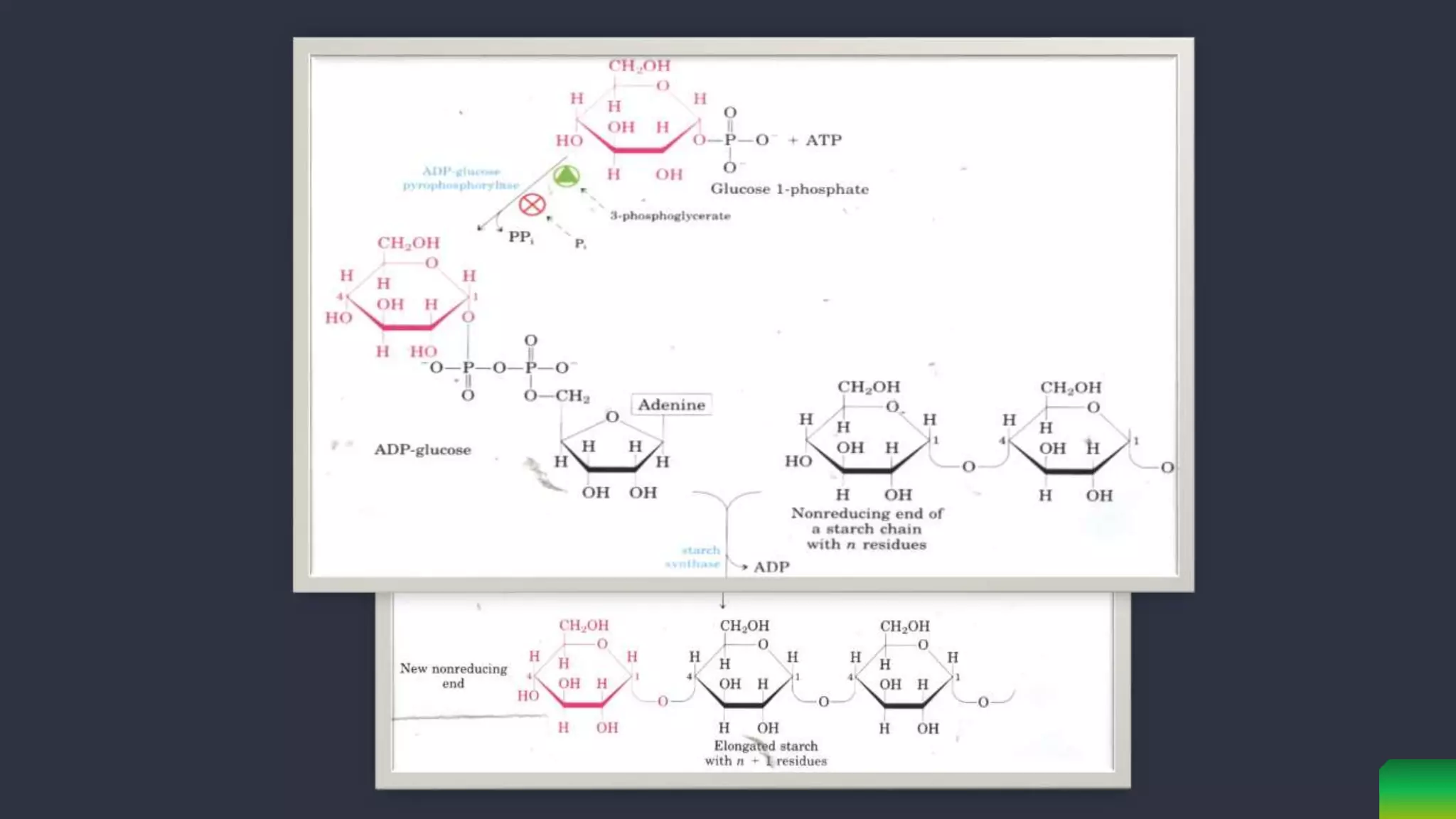
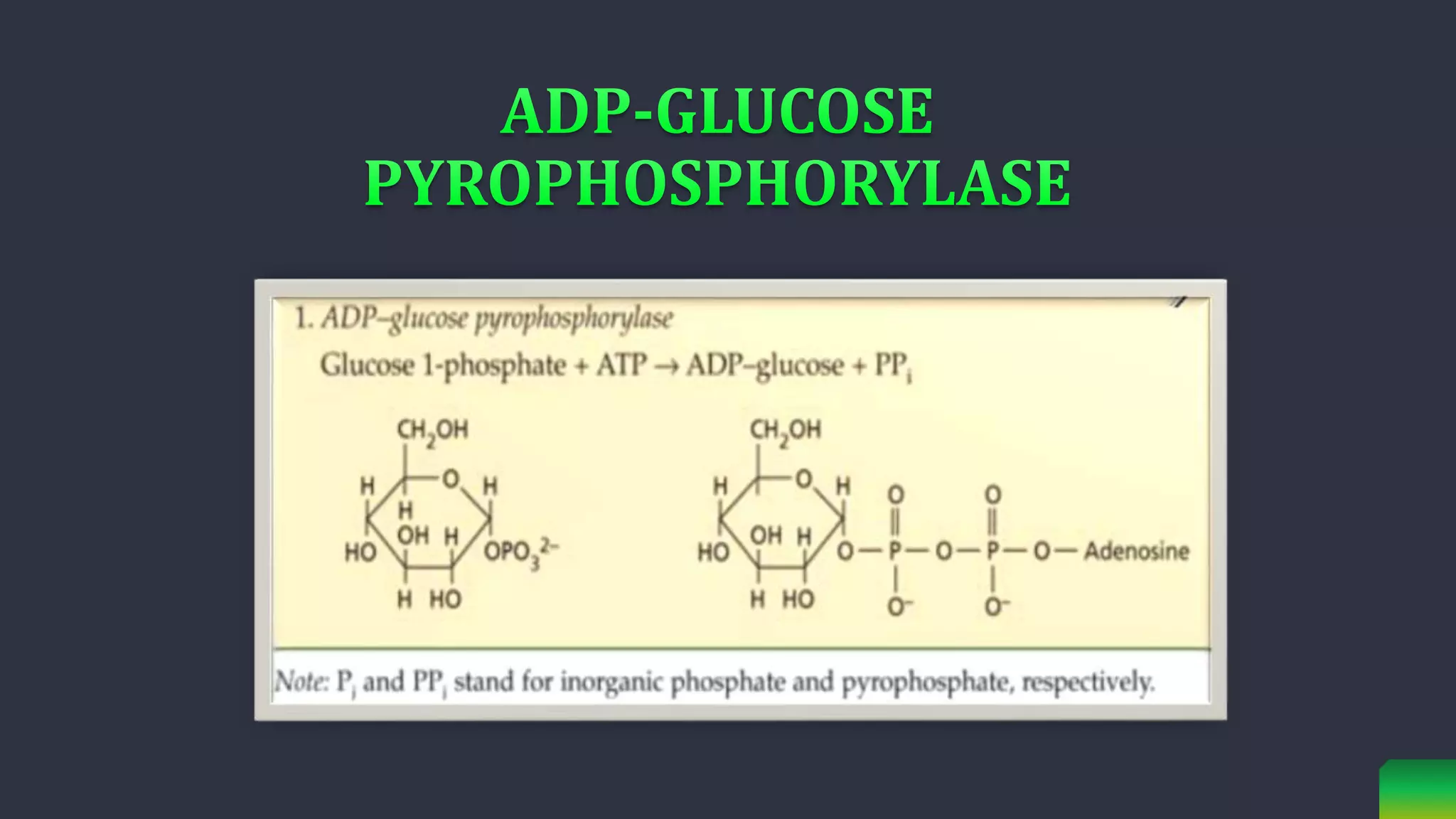
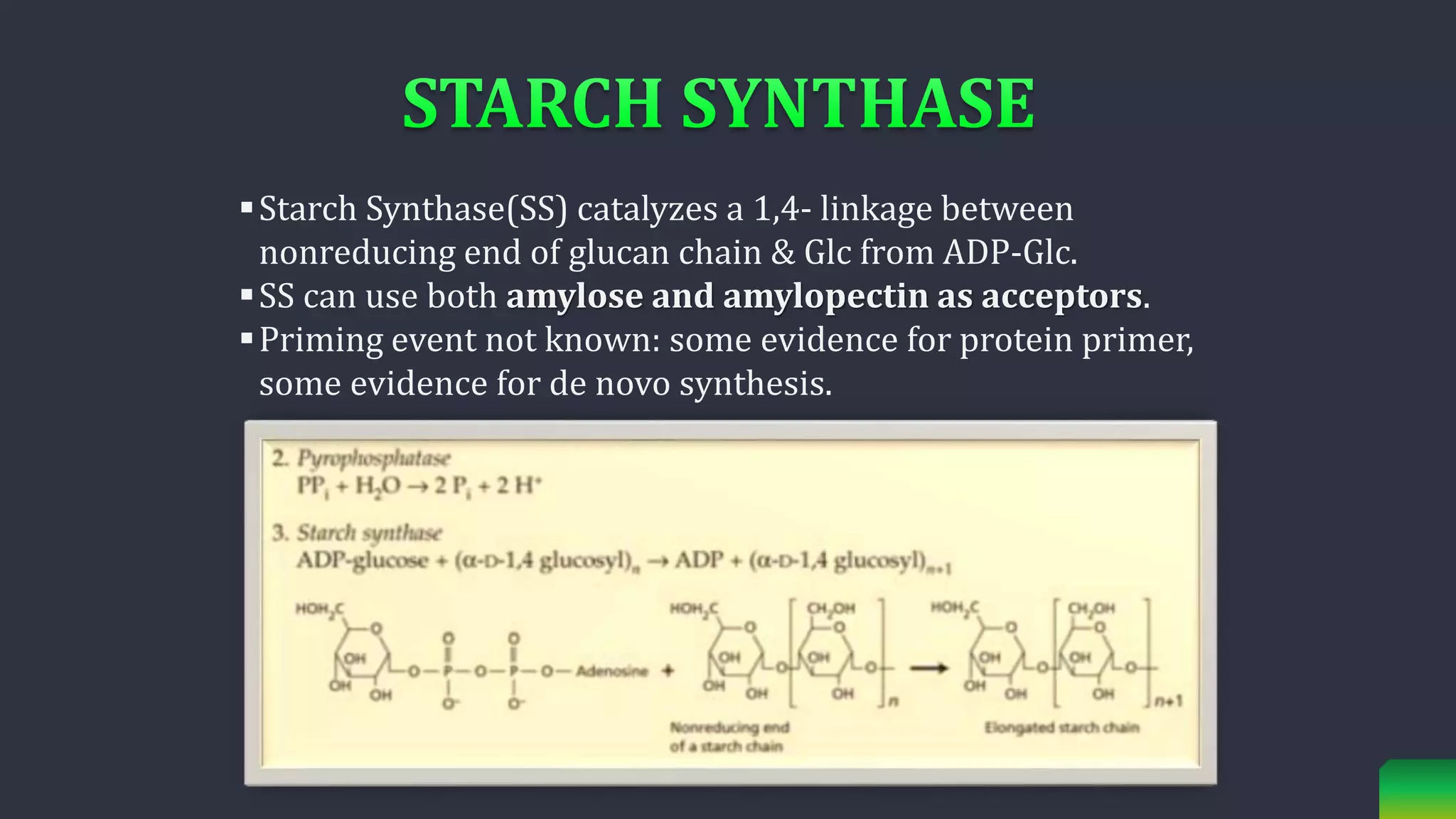
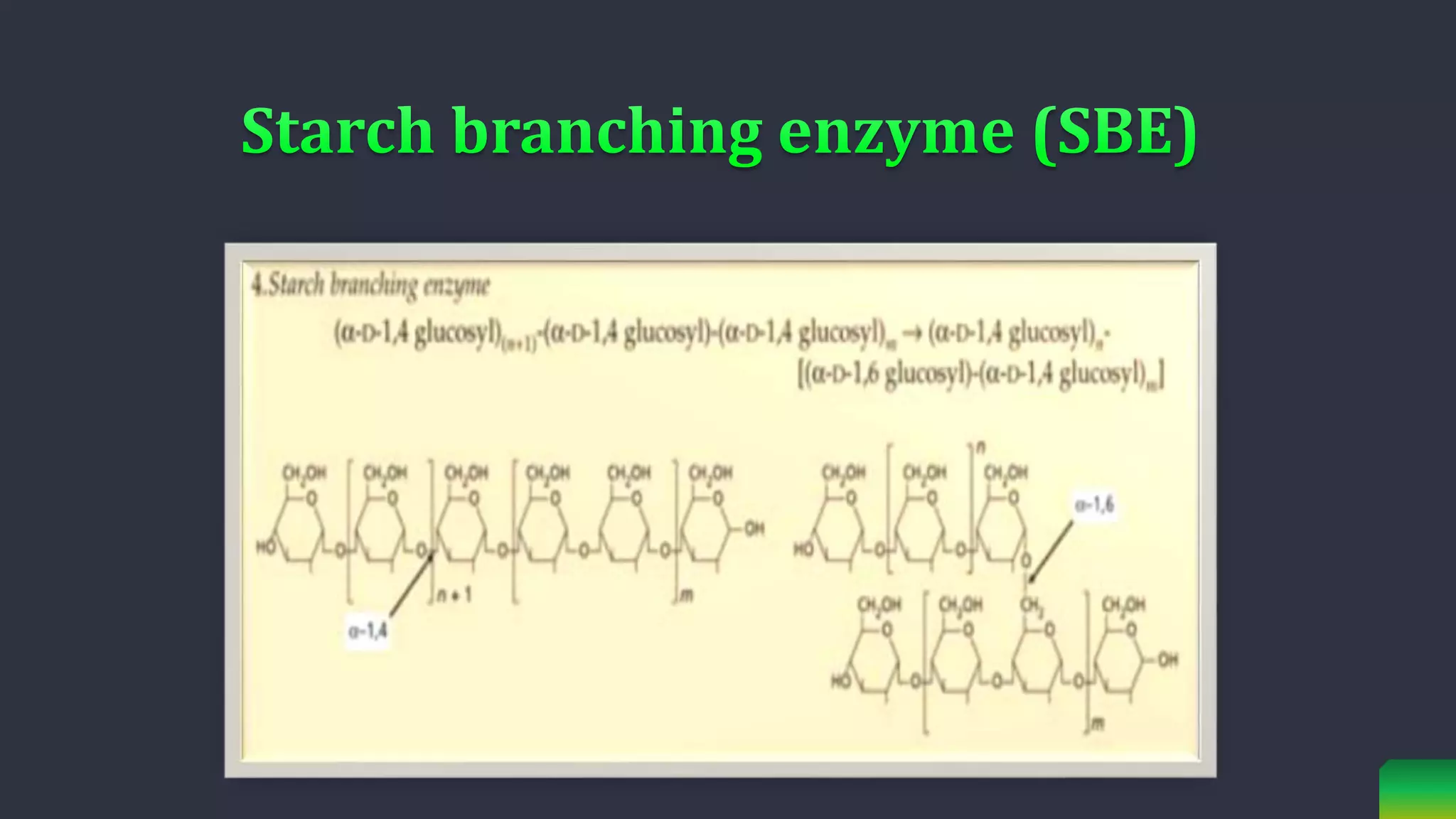
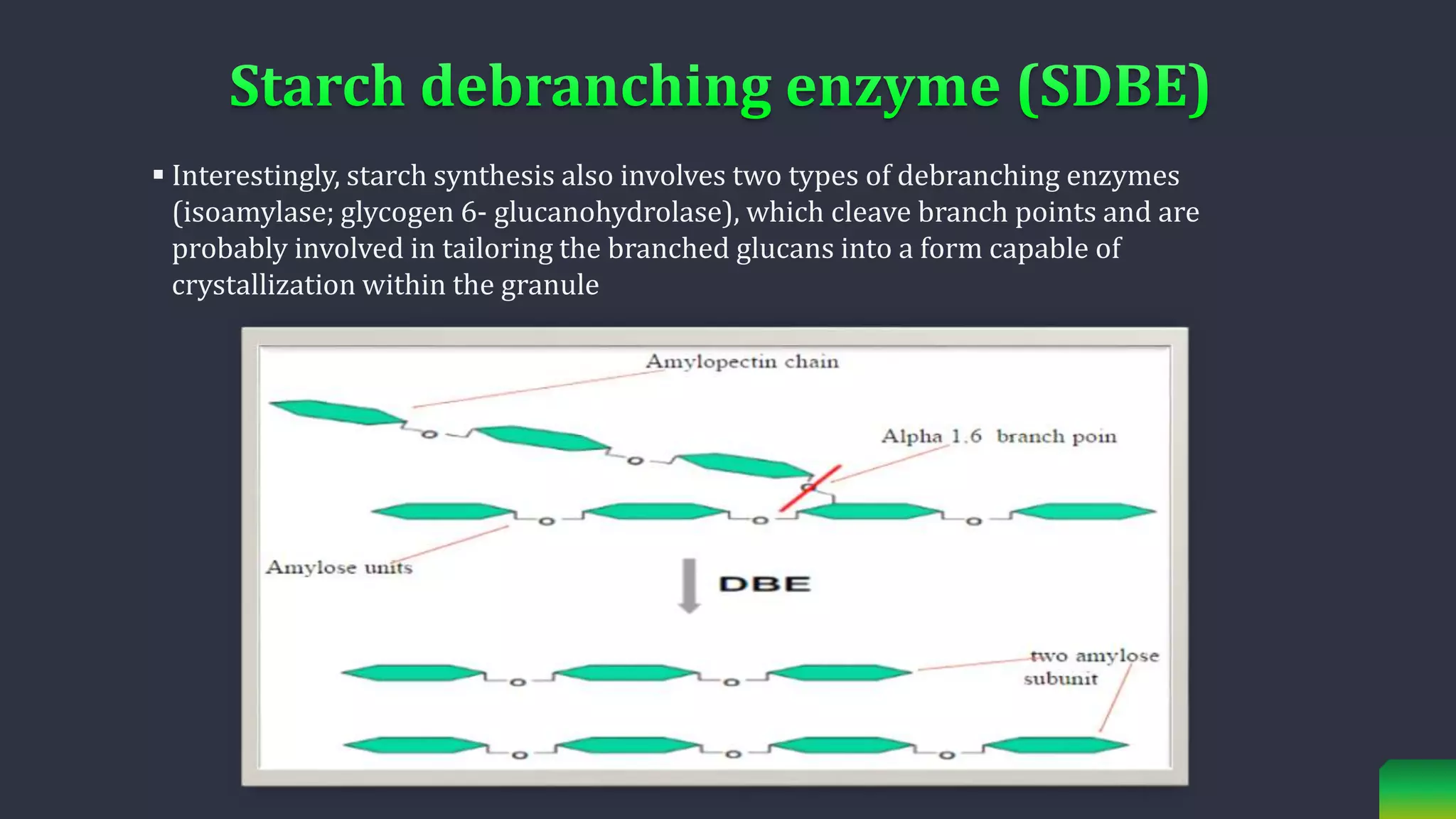
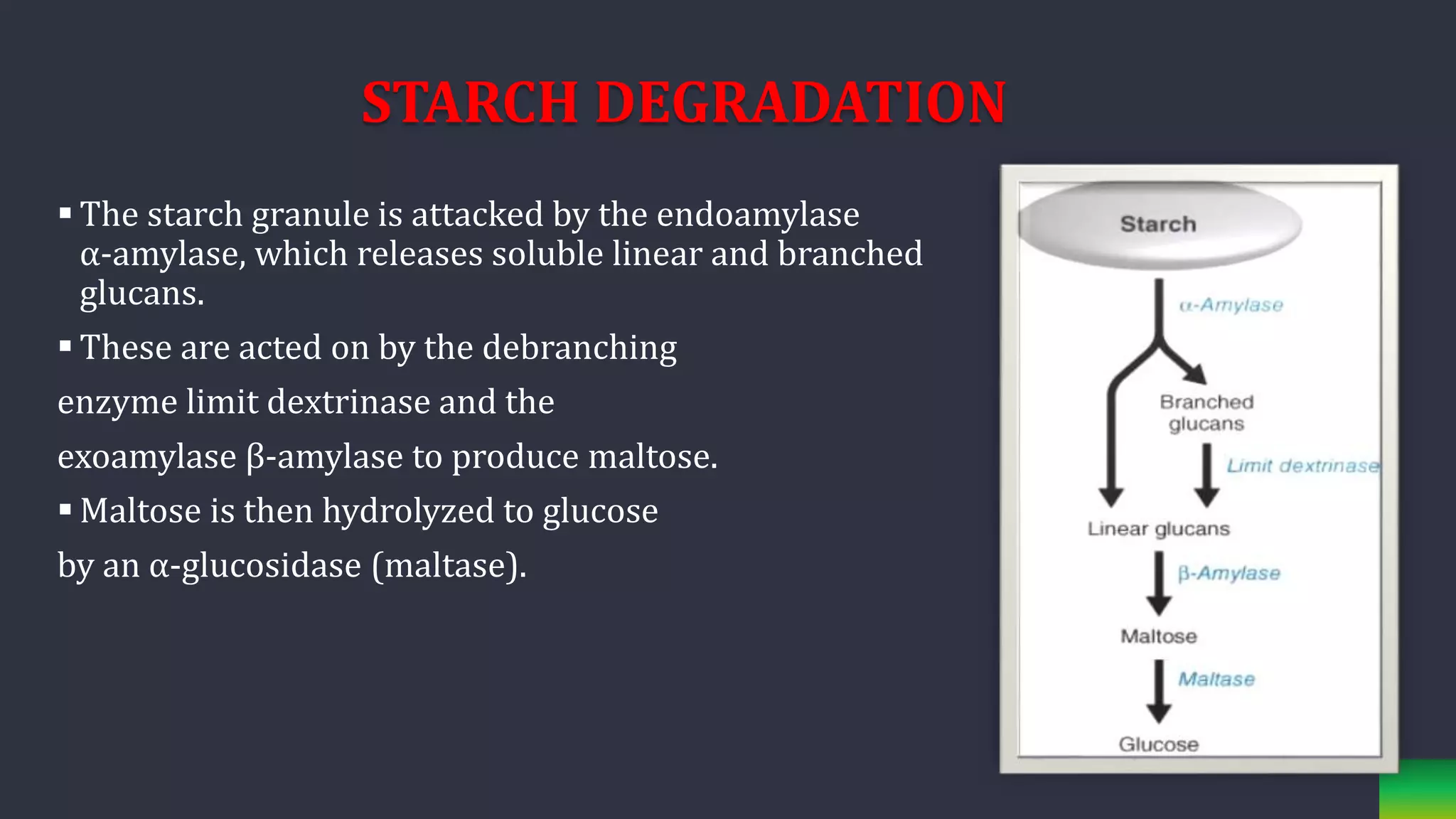
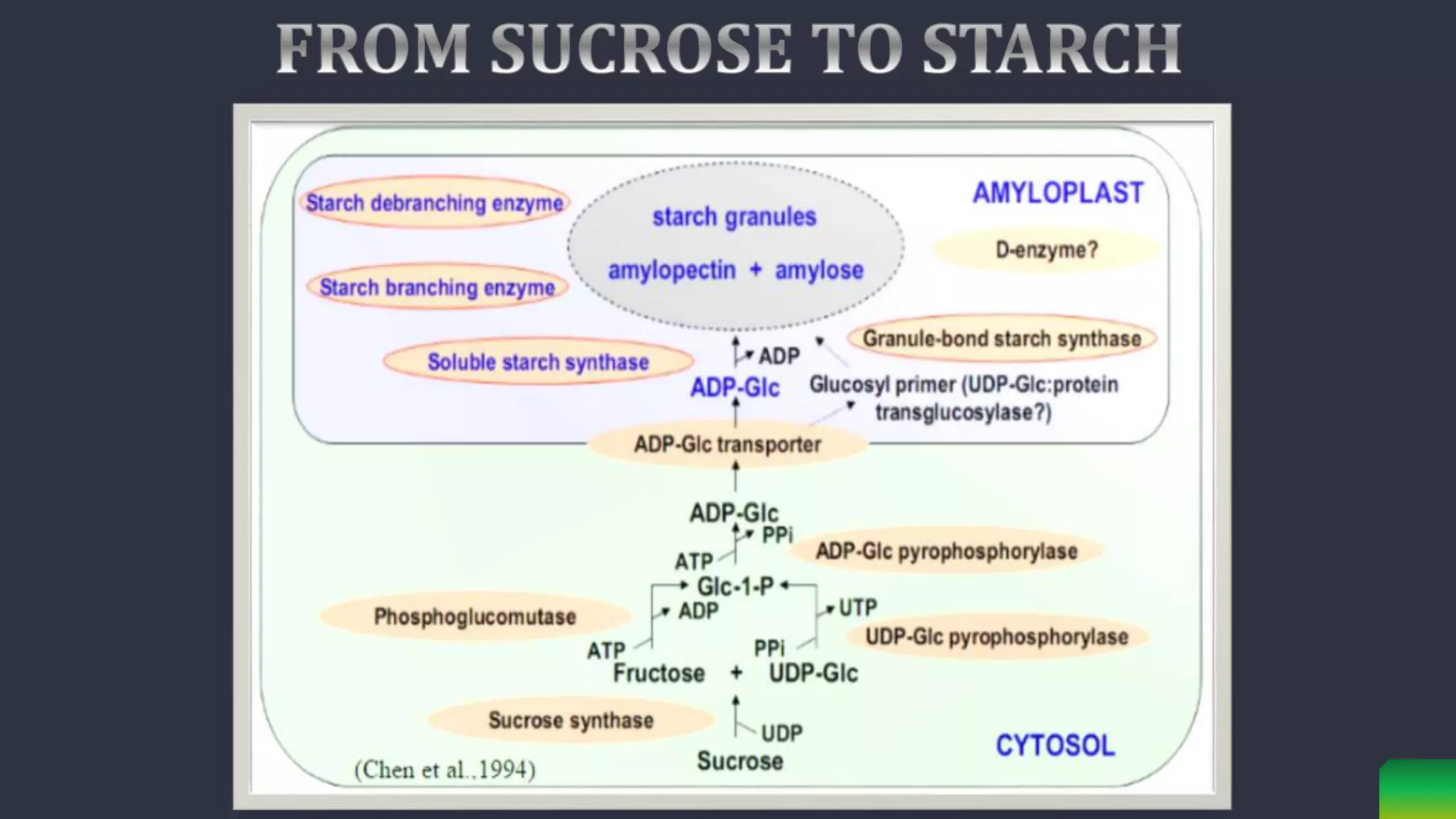
Starch is synthesized from glucose monomers in chloroplasts. It consists of two polymers, amylose and amylopectin, which are synthesized through different pathways. Starch biosynthesis is regulated by the enzyme ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, which catalyzes the first committed step by producing ADP-glucose from glucose-1-phosphate and ATP. ADP-glucose is then used by starch synthases and branching enzymes to elongate amylose and amylopectin chains through alpha-1,4 and alpha-1,6 glycosidic linkages. Starch accumulates transiently in chloroplasts or as a long-term reserve in roots, tubers and seeds.