The document discusses the cell wall structure and function of bacteria, focusing on the role of peptidoglycan. It describes peptidoglycan as a polymer that forms a mesh-like layer outside the plasma membrane, acting as the cell wall's backbone and maintaining cell shape. Peptidoglycan is thicker in gram-positive bacteria compared to gram-negative. The structure and biosynthesis of peptidoglycan is also explained, noting it is composed of alternating sugars and amino acids cross-linked together. Peptidoglycan helps maintain osmotic pressure and regulates molecule diffusion in bacteria.



![What is Peptidoglycan?
• Similar to the roof on our home, the cell wall is
rigid to help secure the shape of the bacteria. The
cell wall contains a layer of peptidoglycan, a
molecule naturally found only in bacteria. The
peptidoglycan layer acts as the cell wall's backbone,
offering strength to the cell wall.
• Peptidoglycan, also known as murein, is a polymer
consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a
mesh-like layer outside the plasma membrane of
most bacteria, forming the cell wall [1].
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-4-320.jpg)
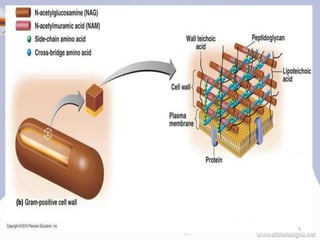
![PEPTIDOGLYCAN
• The peptidoglycan layer is substantially thicker in
gram-positive bacteria (20 to 80 nanometers) than in
gram-negative bacteria (7 to 8 nanometers), with the
attachment of the S-layer [2][3][4].
• Peptidoglycan forms around 90% of the dry weight of
gram-positive bacteria but only 10% of gram-negative
strains.
• Presence of high levels of peptidoglycan is the primary
determinant of the characterization of bacteria as gram-
positive.[5]
• In gram-positive strains, it is important in attachment
roles and serotyping purposes.[6]
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-6-320.jpg)
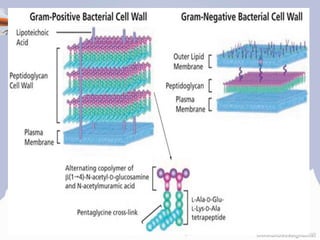
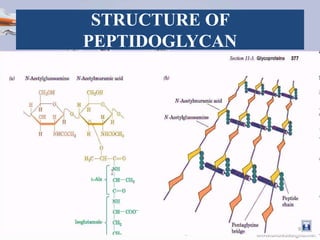
![STRUCTURE OF PEPTIDOGLYCAN
• The peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall is a crystal
lattice structure formed from linear chains of two alternating
amino sugars, namely N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc or
NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc or NAM).
• The alternating sugars are connected by a β-(1,4)-glycosidic
bond [2][3][4][6].
• Each MurNAc is attached to a short (4- to 5-residue) amino
acid chain, containing L-alanine, D-glutamic acid, meso-
diaminopimelic acid, and D-alanine in the case of Escherichia
coli (a Gram-negative bacterium) or L-alanine, D-glutamine,
L-lysine, and D-alanine with a 5-glycine interbridge between
tetrapeptides in the case of Staphylococcus aureus (a gram-
positive bacterium) [2][3][4][6]. 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-8-320.jpg)
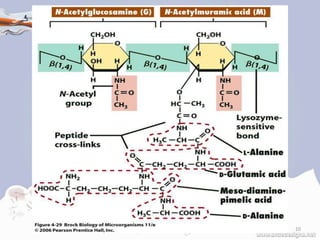
![Transpeptidase
• Cross-linking between
amino acids in different
linear amino sugar
chains occurs with the
help of the enzyme DD-
transpeptidase and
results in a 3-
dimensional structure
that is strong and rigid.
• The specific amino acid
sequence and molecular
structure vary with the
bacterial species [8].
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![BIOSYNTHESIS OF PEPTIDOGLYCANS
• The peptidoglycan monomers are synthesized
in the cytosol and are then attached to a
membrane carrier bactoprenol.
• Bactoprenol transports peptidoglycan
monomers across the cell membrane where
they are inserted into the existing
peptidoglycan.[11]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-12-320.jpg)
![STEPS OF BIOSYNTHESIS
In the first step of peptidoglycan synthesis, the
glutamine, which is an amino acid, donates an amino
group to a sugar, fructose 6-phosphate. This turns
fructose 6-phosphate into glucosamine-6-phosphate.
In step two, an acetyl group is transferred from acetyl
CoA to the amino group on the glucosamine-6-
phosphate creating N-acetyl-glucosamine-6-
phosphate.[12]
In step three of the synthesis process, the N-acetyl-
glucosamine-6-phosphate is isomerized, which will
change N-acetyl-glucosamine-6-phosphate to N-
acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphate.[12]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-13-320.jpg)

![STEPS OF BIOSYNTHESIS
In step six, NADPH reduce enol derivative
into “lactyl moiety”.
In step 7, the UDP–MurNAc is converted to
UDP-MurNAc pentapeptide by the addition of
five amino acids, usually including the
dipeptide D-alanyl-D-alanine.[12]
Each of these reactions requires the energy
source ATP.[12]
This is all referred to as Stage one.
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-15-320.jpg)
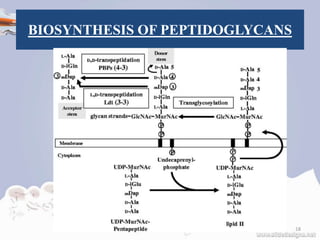
![STEPS OF BIOSYNTHESIS
Stage two occurs in the cytoplasmic
membrane.
It is in the membrane where a lipid carrier
called bactoprenol carries peptidoglycan
precursors through the cell membrane.
Bactoprenol will attack the UDP-MurNAc
penta, creating a PP-MurNac penta, which is
now a lipid. UDP-GlcNAc is then transported
to MurNAc, creating Lipid-PP-MurNAc
penta-GlcNAc, a disaccharide, also a
precursor to peptidoglycan.[12]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-16-320.jpg)
![STEPS OF BIOSYNTHESIS
How this molecule is transported through the
membrane is still not understood. However, once it is
there, it is added to the growing glycan chain.[12]
The next reaction is known as Tranglycosylation. In
the reaction, the hydroxyl group of the GlcNAc will
attach to the MurNAc in the glycan, which will
displace the lipid-PP from the glycan chain. The
enzyme responsible for this is Transglycosylase.[12]
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-17-320.jpg)

![FUNCTIONS OF PEPTIDOGLYCAS
Diffusion of molecules into cells is also
regulated by peptidoglycans that play
important role in division of cell and anchoring
structure for cell wall, teichoic acid.
Peptidoglycan fragments are also release by
some bacteria that play role in cell to cell
communication [12][11].
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-20-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS OF PEPTIDOGLYCAS
A common misconception is that
peptidoglycan gives the cell its shape;
however, whereas peptidoglycan helps
maintain the structural strength of the cell, it is
actually the MreB protein that facilitates cell
shape.[2][3][4]
Peptidoglycan is also involved in binary
fission during bacterial cell reproduction.
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peptidoglycan-180511093856/85/Peptidoglycan-ppt-21-320.jpg)


