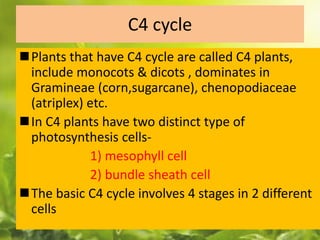
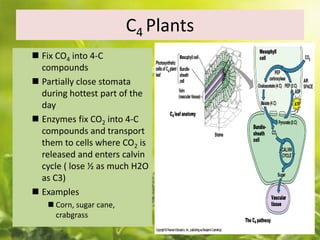
Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds like sugars using sunlight. It occurs through two stages - light reactions and dark reactions. Dark reactions, also called carbon reactions, occur after light reactions and use the energy from light reactions to reduce carbon dioxide into carbohydrates. Specifically, the Calvin cycle reduces carbon dioxide into organic three-carbon molecules that can then be assembled into sugars like glucose. Some plants use alternative pathways like C4 or CAM cycling to more efficiently conduct photosynthesis in hot or dry environments.
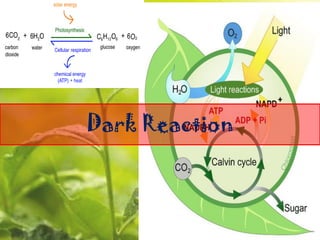


![Overall Perspective
• Light reactions:
– Harvest light energy
– Convert light energy to
chemical energy
• Dark Reactions:
– Expend chemical energy
– Fix Carbon [convert CO2
to organic form]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/darkreaction-181214101003/85/Dark-reaction-4-320.jpg)