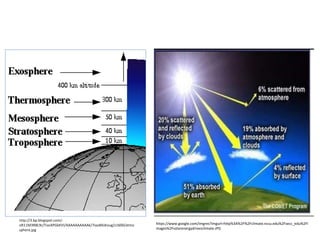
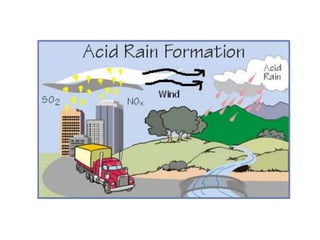
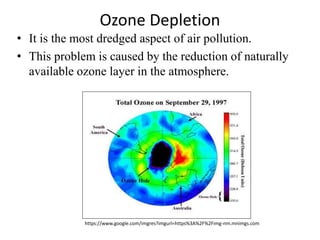
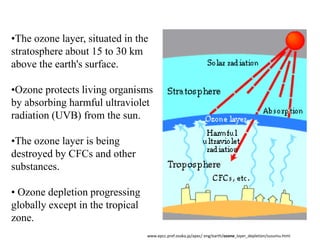
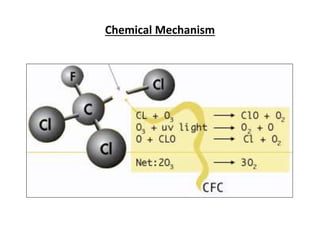
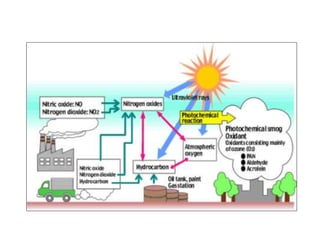
This document discusses several global environmental issues: global warming, acid rain, ozone depletion, and photochemical smog. It provides details on the causes and effects of each issue. For global warming, it notes that greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuel burning and deforestation are increasing Earth's temperature. For acid rain, it explains that sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions from industry produce acid rain that damages forests and aquatic ecosystems. The document also outlines how chlorofluorocarbons are depleting the ozone layer, increasing UV radiation and harming health and ecosystems. Photochemical smog forms from vehicle and industry emissions in sunny conditions.