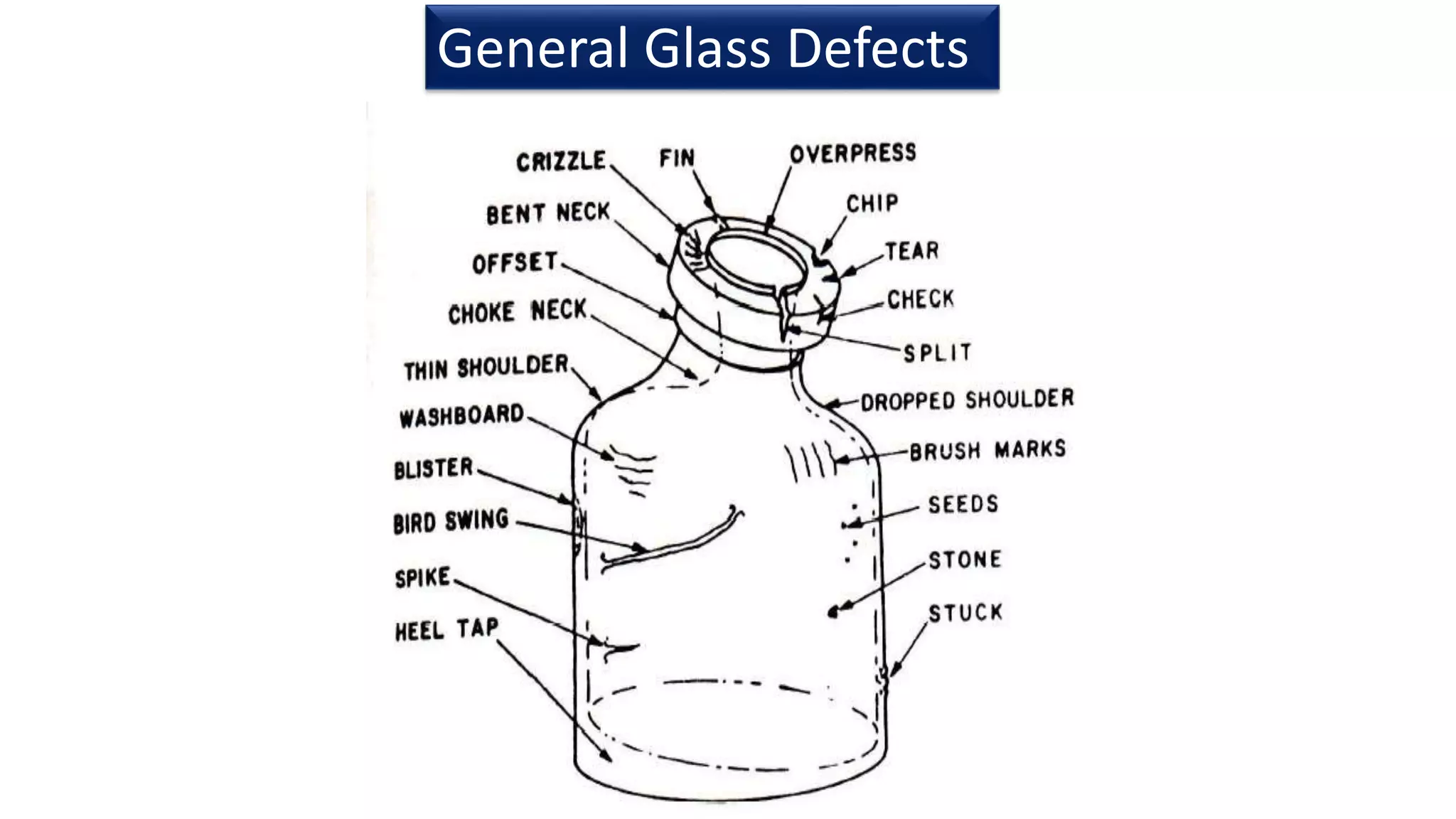
Glass is commonly used as a packaging material due to its advantages such as impermeability, clarity, heat resistance allowing for sterilization, and inertness. The main types of glass used are soda lime glass and borosilicate glass. Glass manufacturing involves batching ingredients like silica, lime, and soda then melting, forming, annealing, sorting, and packaging. Forming methods include blow and blow and press and blow processes. Performance tests are conducted to ensure the quality and safety of glass packaging. Regulations govern the submission of data on glass packaging materials and components.