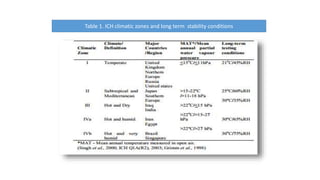
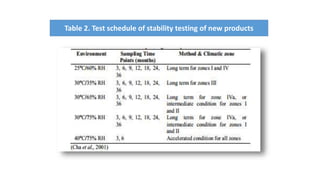
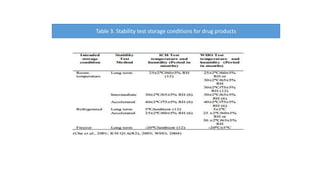
This document discusses stability testing of pharmaceutical packaging. Stability testing ensures that packaging maintains the quality of drugs over time under various environmental conditions like temperature, humidity and light. It involves testing packaging for leakage, strength, impact of distribution processes, and compatibility with drugs. The document outlines guidelines for conducting stability tests, including storage conditions, timepoints for sampling, and parameters to evaluate like appearance, assay and degradation. The goal is to determine shelf life and ensure patient safety.