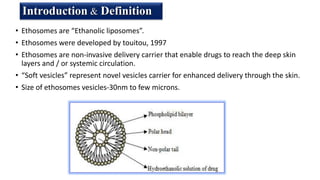
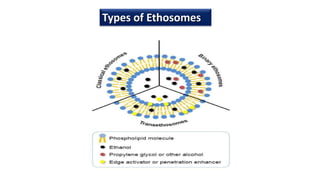
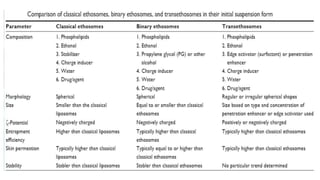
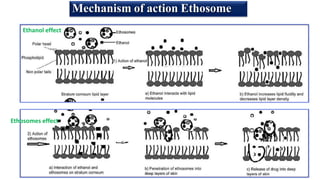
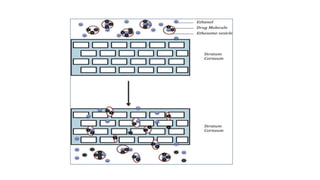
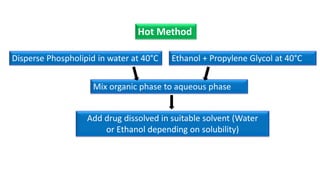
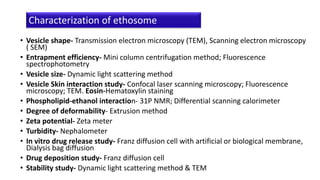
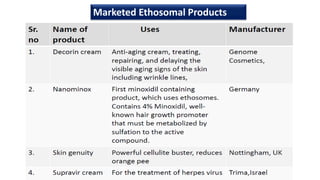
Ethosomes are ethanolic liposomes developed for non-invasive drug delivery that enhance permeation through the skin, utilizing ethanol to increase cell membrane fluidity. They can deliver a wide variety of drugs and are advantageous due to their low risk profile and high patient compliance, although there are challenges such as poor yield and potential coalescence. Their applications include antiviral drug delivery, hormone transdermal delivery, and they represent a promising area for further research in transdermal drug therapies.