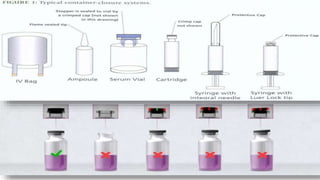
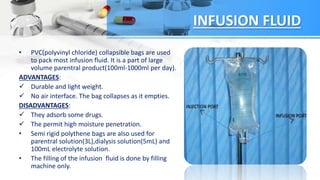
The document discusses the storage and quality control of parenteral products, which are sterile injections administered via means other than the mouth. It covers the types of containers and closures used, including plastic and glass, their advantages and disadvantages, and the quality control tests employed to ensure product integrity, including leaker tests and clarity tests. Additionally, it outlines procedures for filling and sealing, emphasizing the importance of maintaining sterility and ensuring proper drug stability.