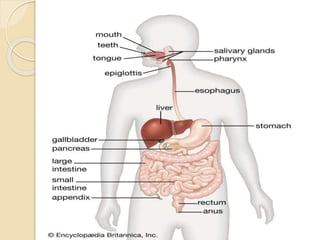
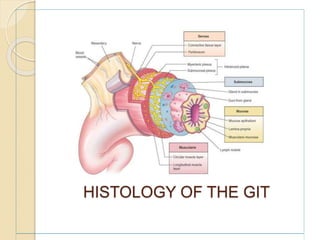
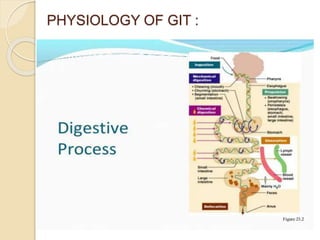
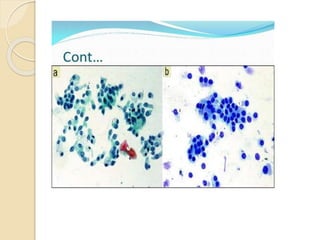
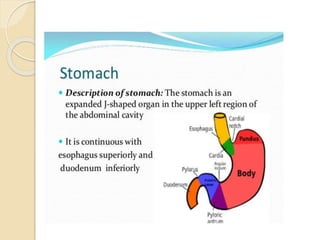
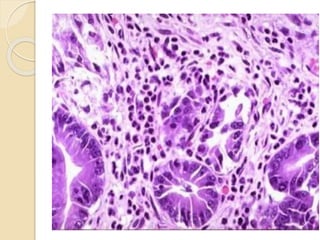
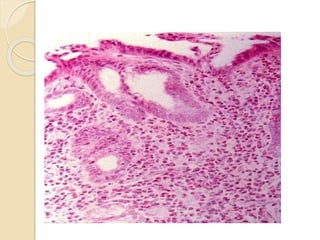
The document discusses the anatomy, histology, physiology, and cytology of the gastrointestinal tract. It provides details on:
- The layers of the GI tract including the mucosa, muscularis, and serosa.
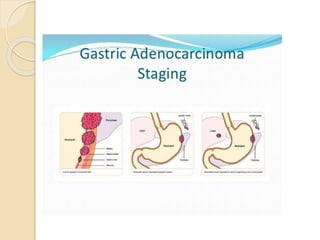
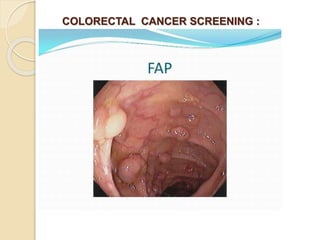
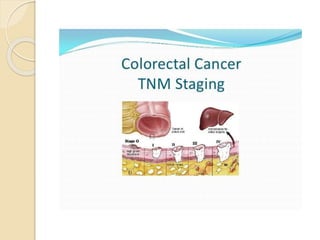
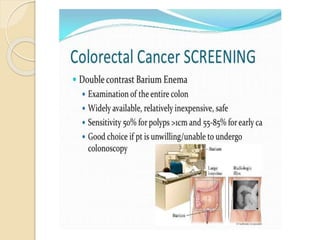
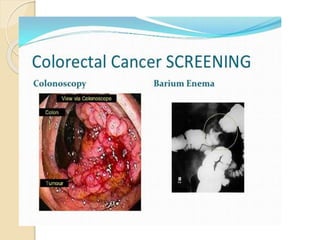
- Common malignant conditions like gastric adenocarcinoma, gastric lymphoma, and colorectal cancer. Risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis and screening are covered.
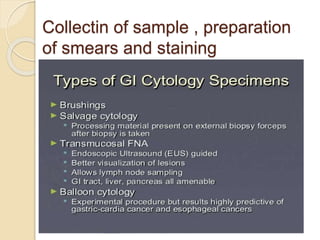
- Non-malignant GI conditions and techniques for sample collection, smear preparation, and staining of GI biopsy specimens.