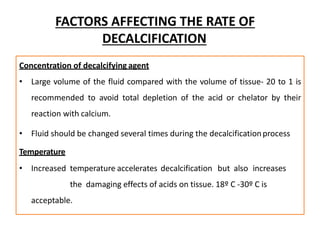
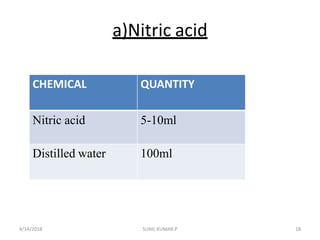
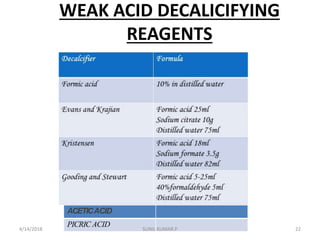
This document discusses decalcification, which is the process of removing calcium from bone and other calcified tissues prior to sectioning and microscopic examination. It defines decalcification and lists the criteria for an ideal decalcifying agent. Various factors that affect the rate of decalcification are described, including concentration, temperature, agitation, and suspension of the tissue. The main methods of decalcification are outlined as well as the principles, types, compositions, and procedures for different decalcifying agents such as acids, ion exchange resins, and chelating agents.