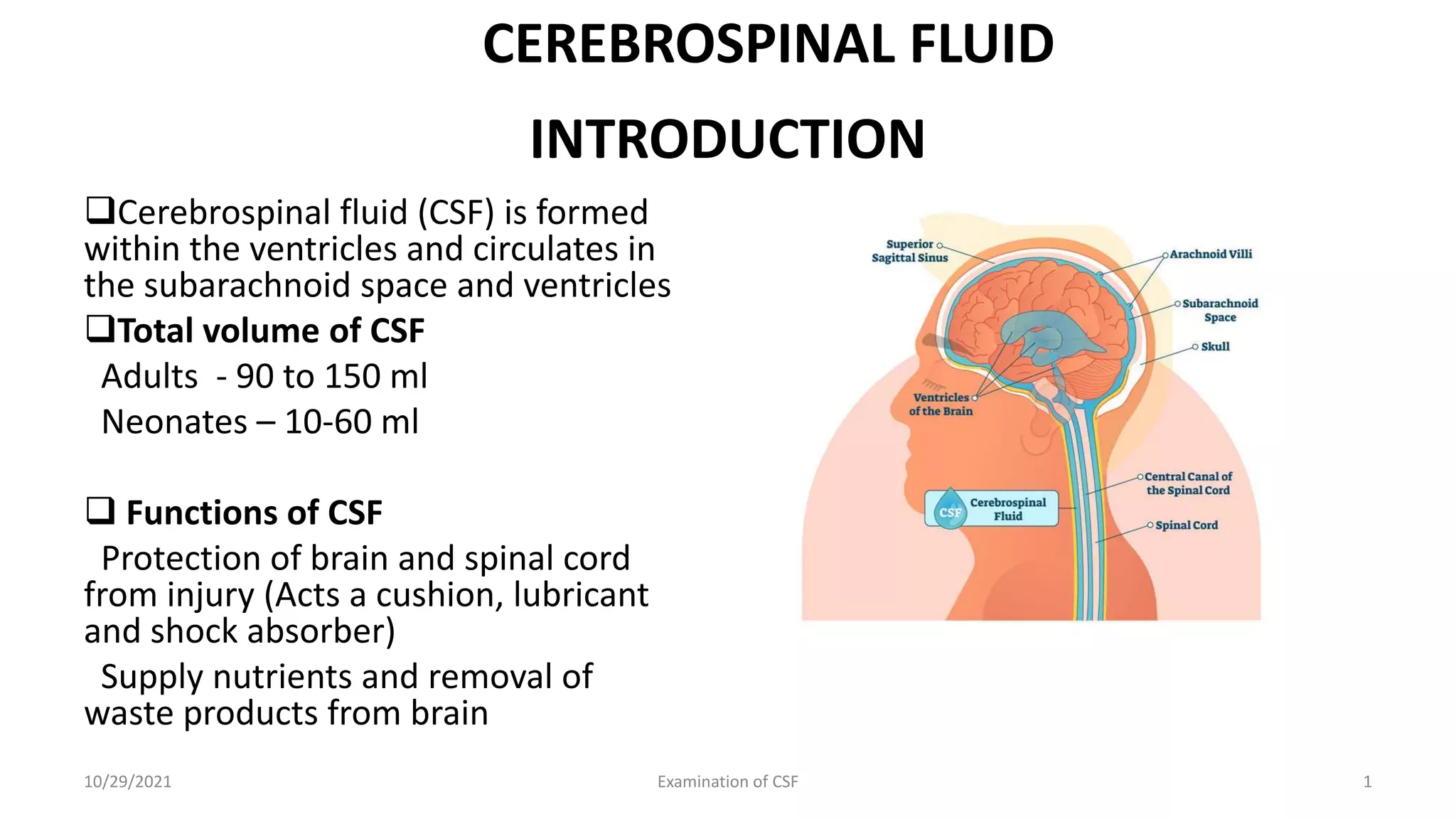
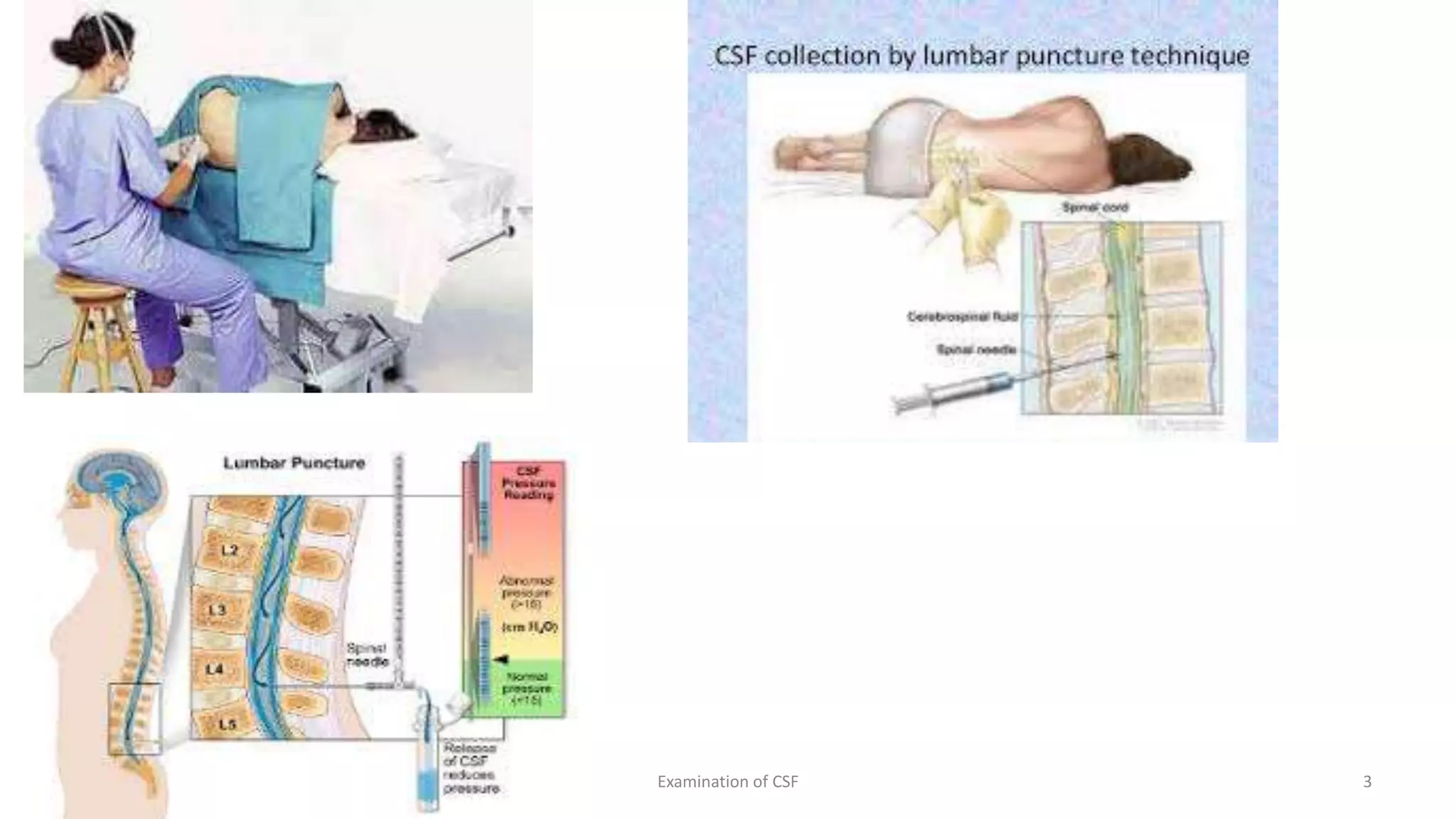
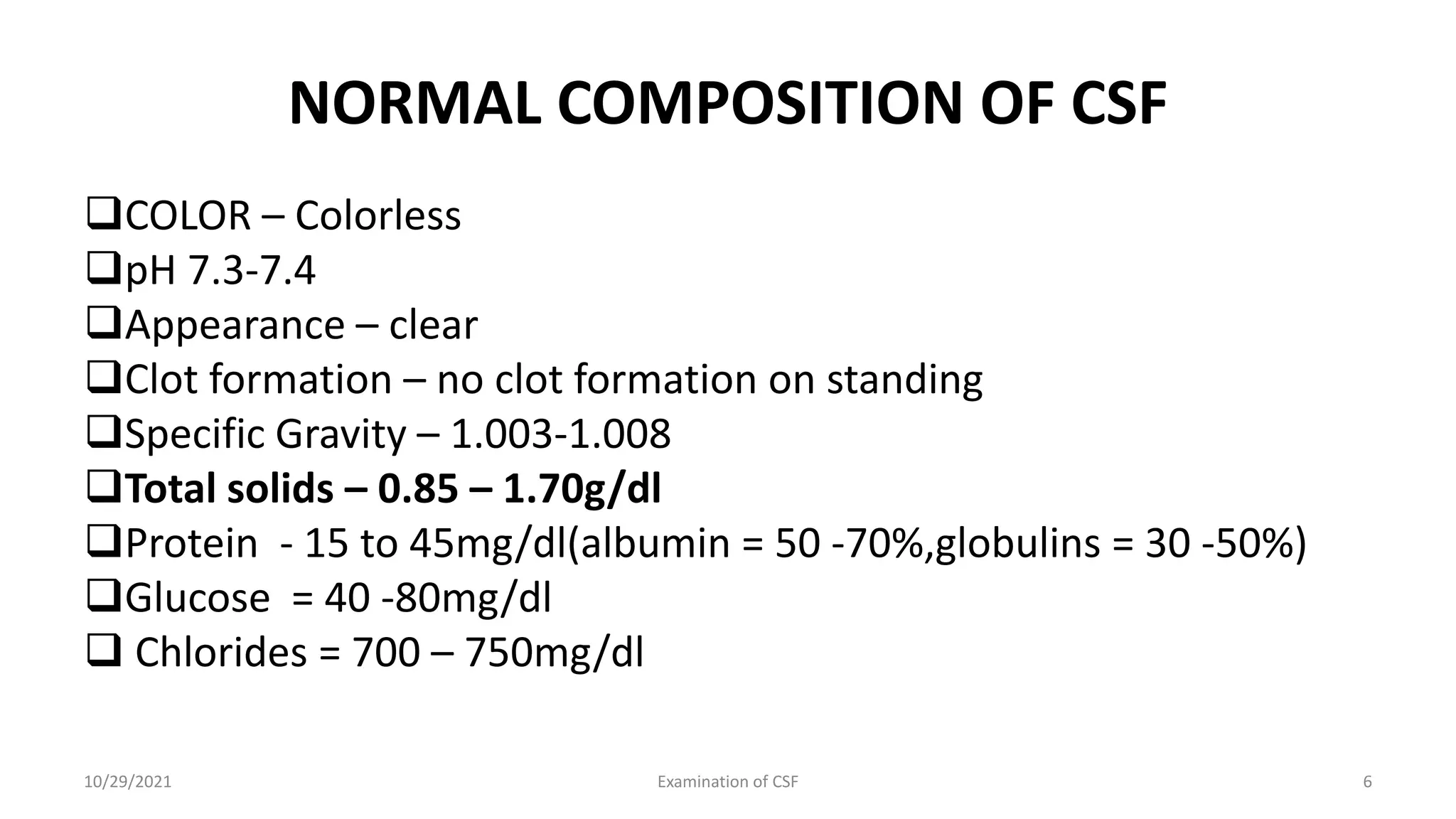
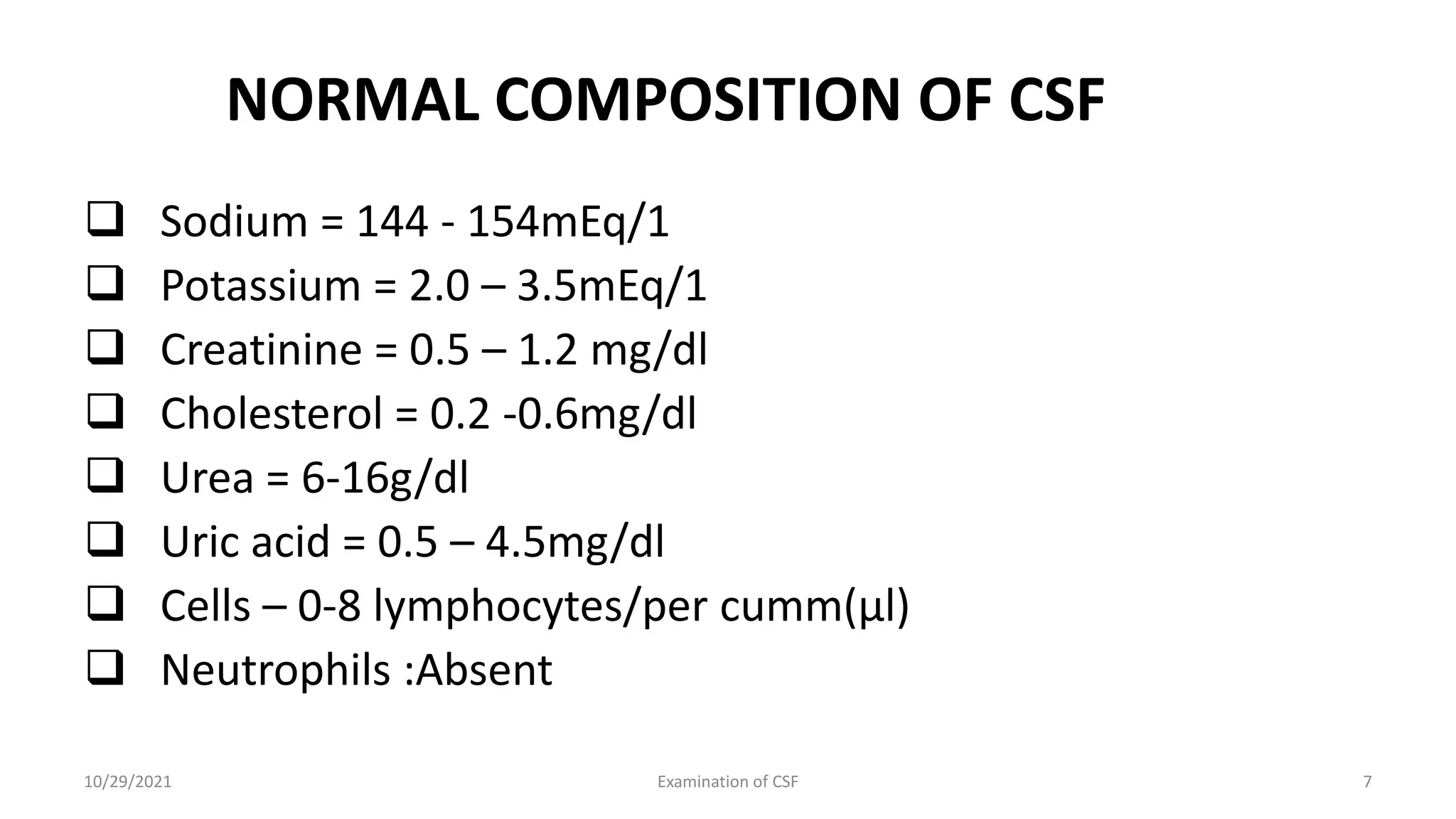
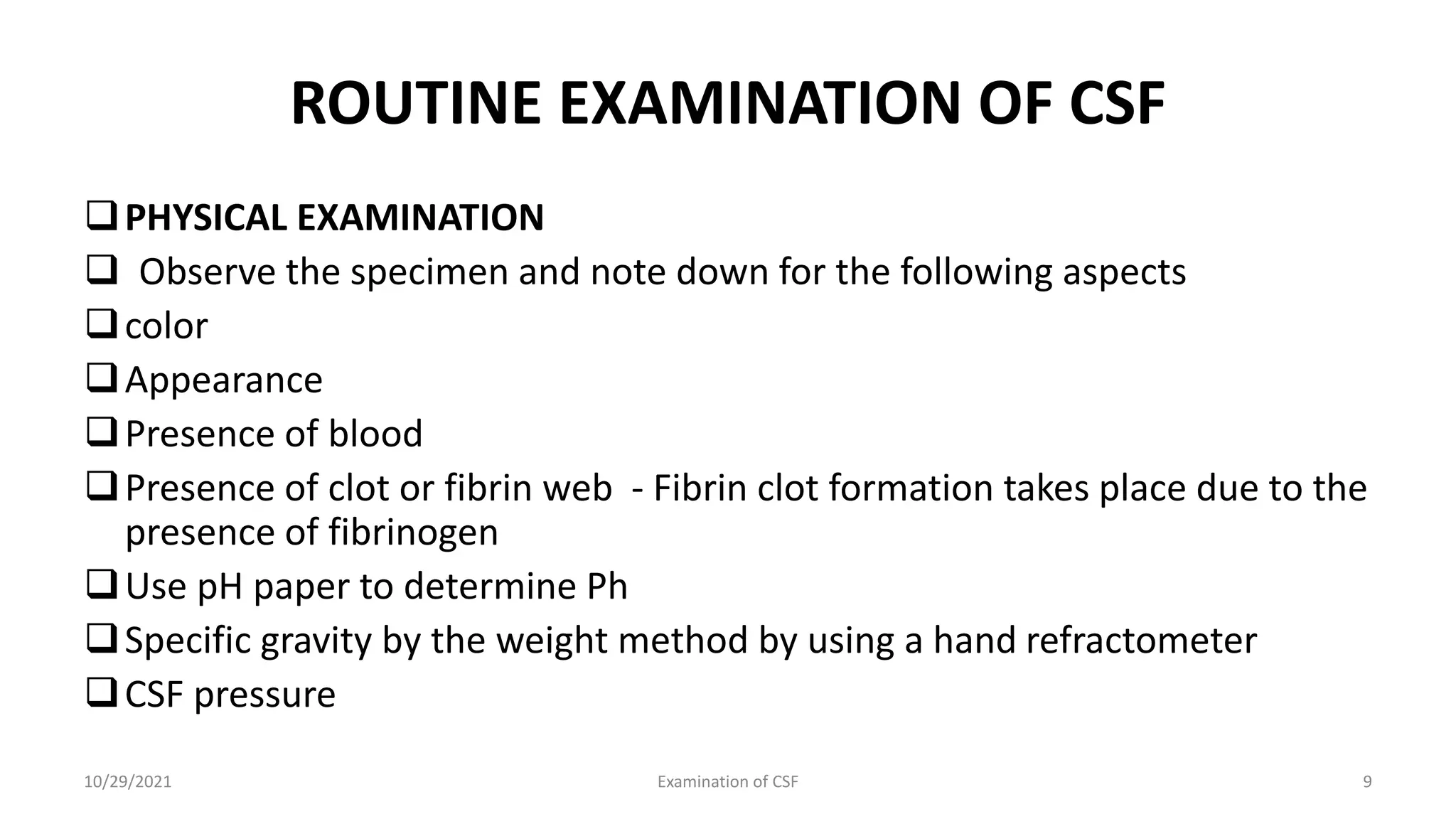
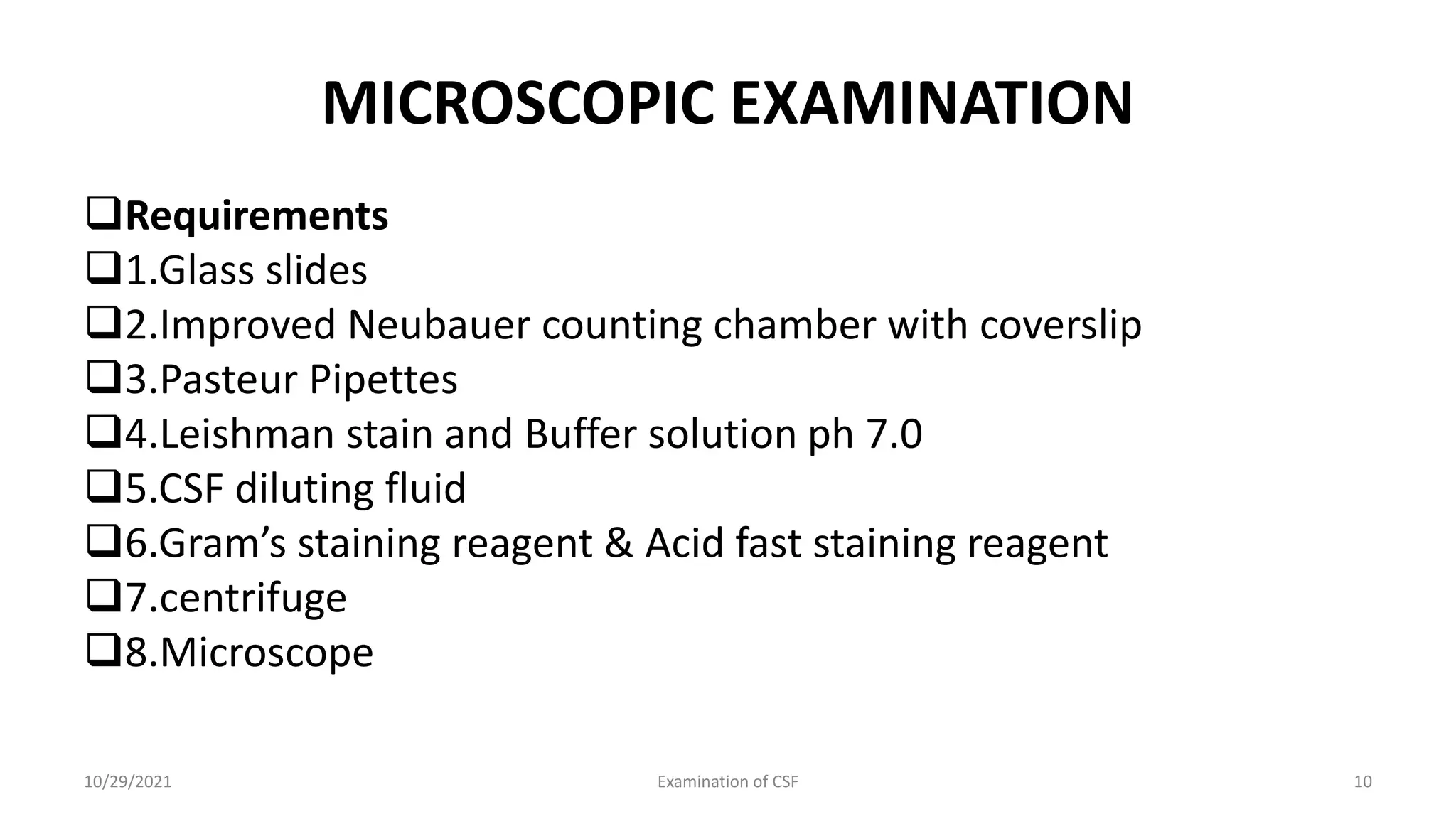
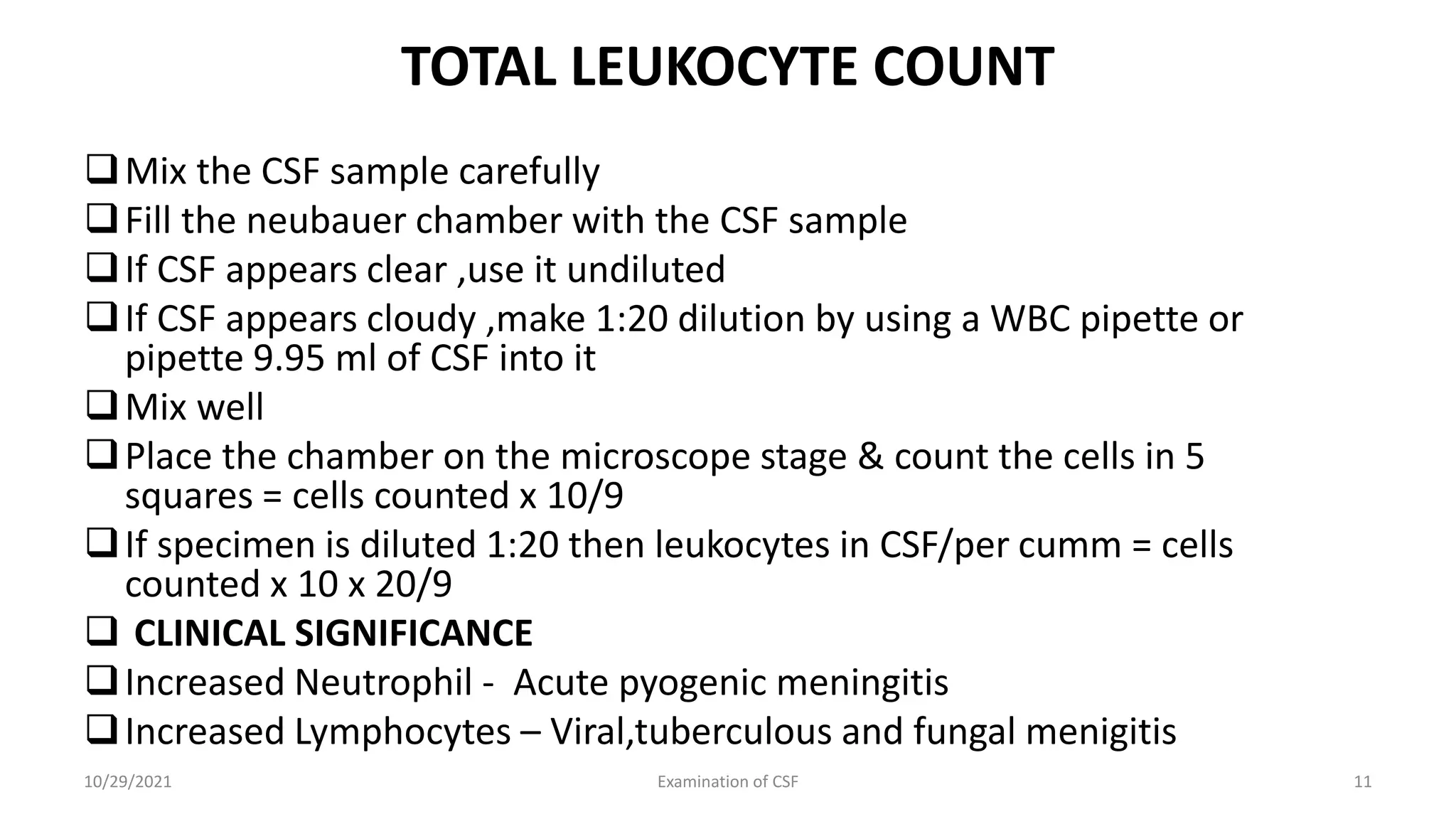
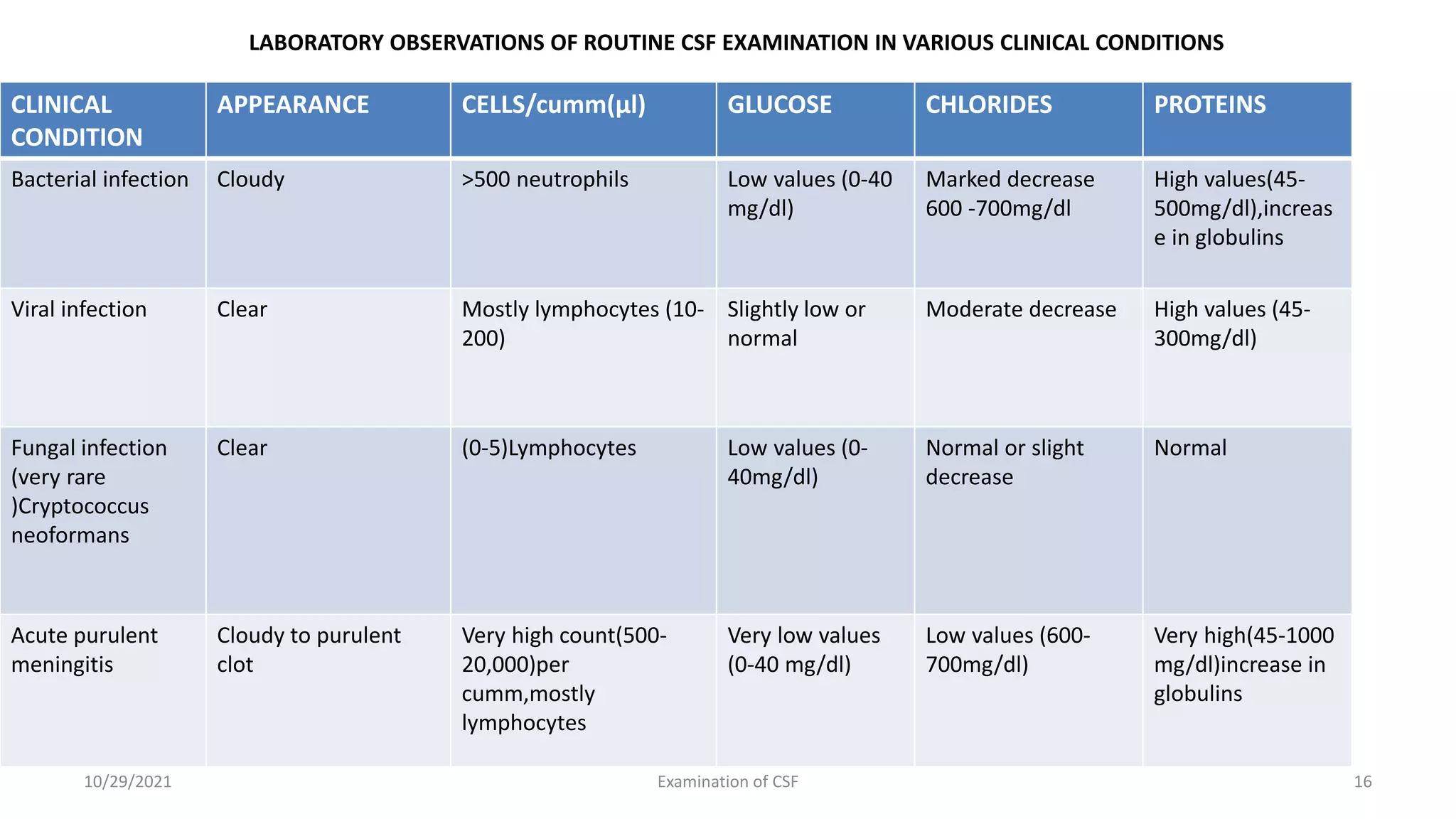
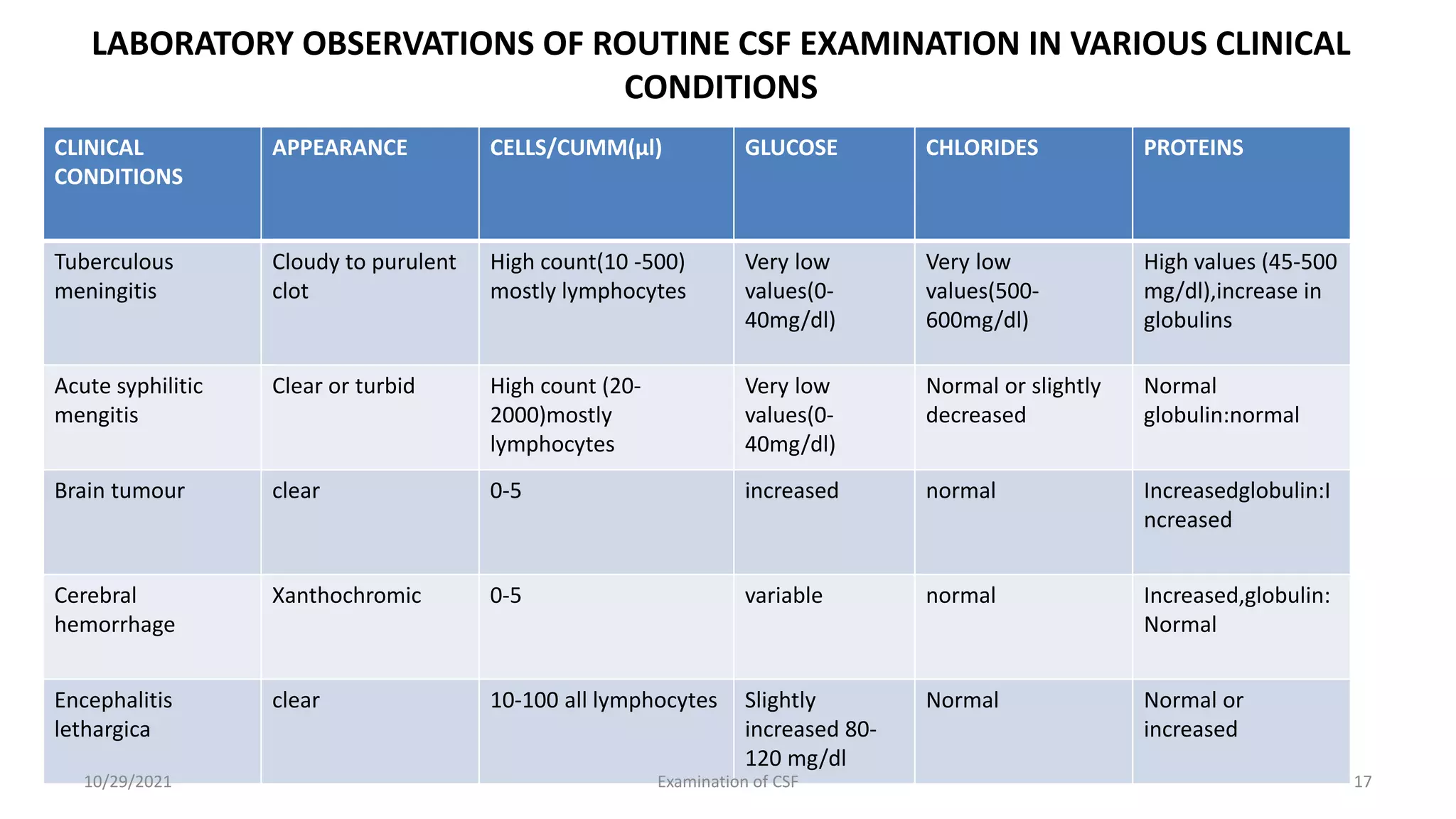
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is formed within the ventricles and circulates in the subarachnoid space and ventricles. CSF examination is important for diagnosing conditions like meningitis, tumors, and multiple sclerosis. A lumbar puncture is performed to collect CSF specimens, which are then examined for properties like color, clarity, cell count, glucose and protein levels, and presence of microorganisms. Abnormal CSF findings can indicate conditions such as bacterial meningitis (elevated white blood cells and proteins, low glucose) or viral meningitis (elevated lymphocytes and proteins, normal or slightly low glucose).