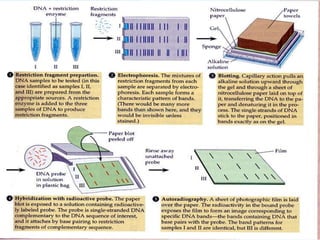
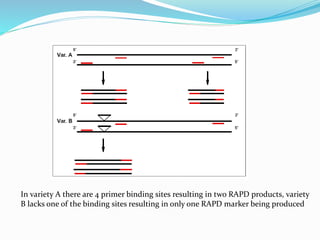
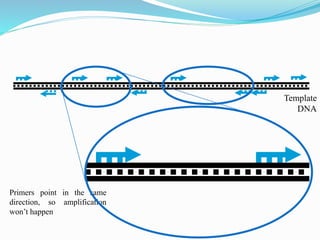
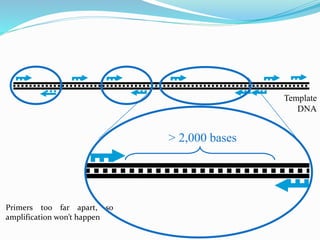
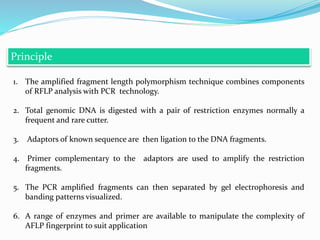
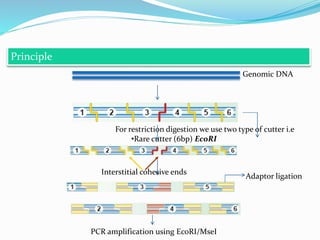
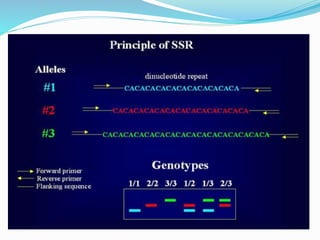
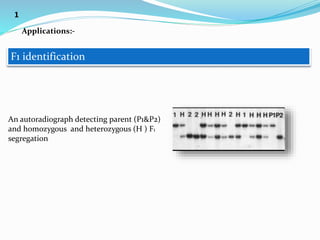
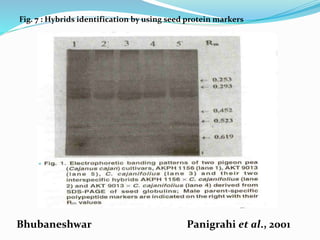
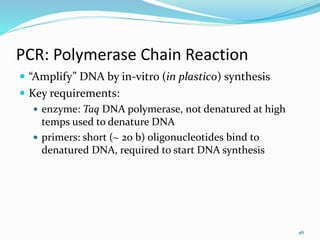
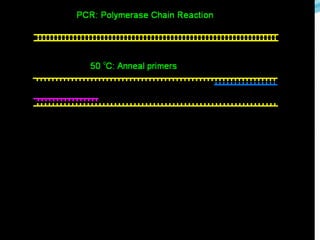
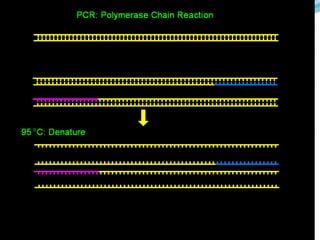
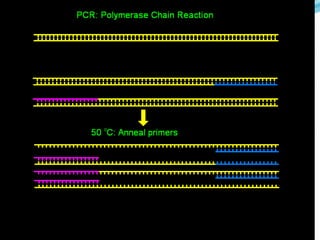
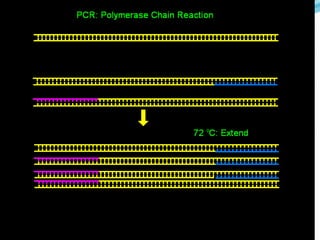
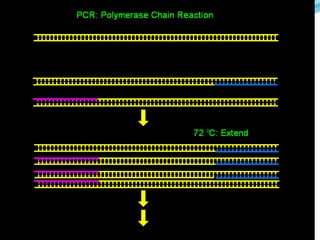
Molecular markers are DNA sequences that can be used to identify differences between individuals. They are found at specific locations in the genome and can be used to track inheritance of traits. Common types include RFLPs, RAPDs, AFLPs, SSRs, and SNPs. RFLPs detect differences in fragment lengths after restriction enzyme digestion and probing. RAPDs use random PCR primers to amplify polymorphic loci. AFLPs combine restriction digestion and PCR to detect multiple loci. SSRs are co-dominant markers based on differences in repeated microsatellite sequences. Molecular markers are powerful tools for genetic mapping, diversity analysis, fingerprinting, and marker-assisted selection.