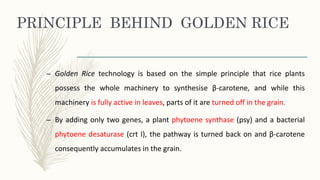
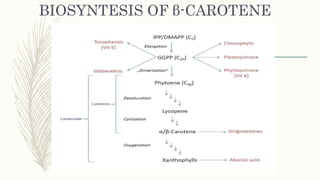
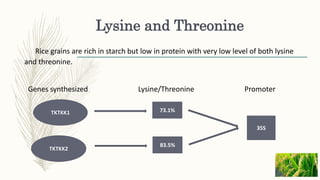
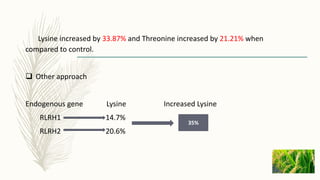
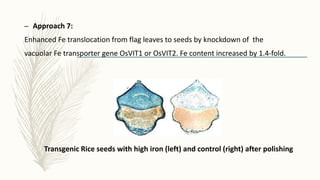
Transgenic approaches were used to improve the nutritional quality of rice by increasing essential amino acids and iron. Genes were introduced to increase cysteine and methionine by overexpressing EcSAT to produce O-acetylserine. Lysine and threonine were increased by genes synthesizing these amino acids under endosperm promoters. Iron content was increased through various approaches including expressing ferritin in the endosperm, enhancing iron transport and influx genes, and modifying iron uptake and translocation genes. These transgenic modifications successfully led to significant increases in targeted nutrients important for human nutrition and health.