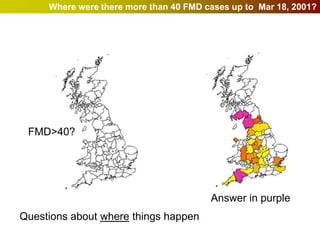
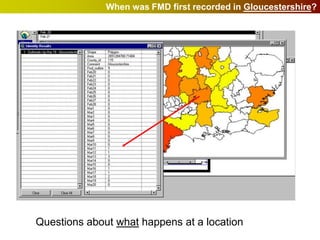
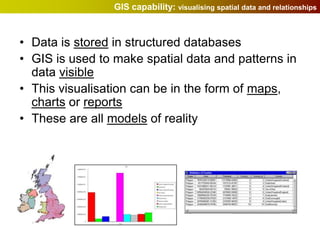
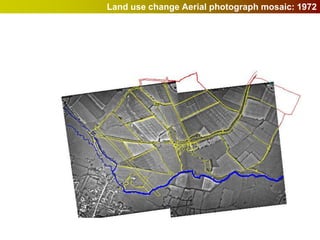
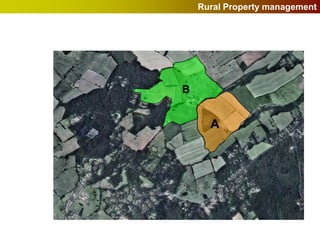
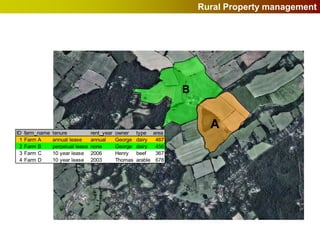
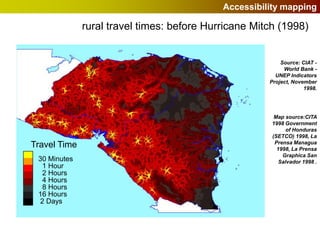
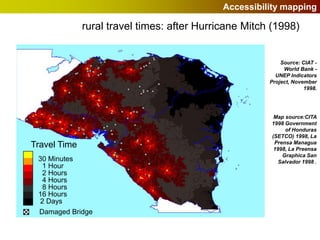
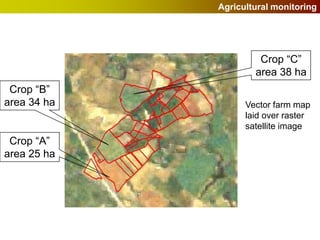
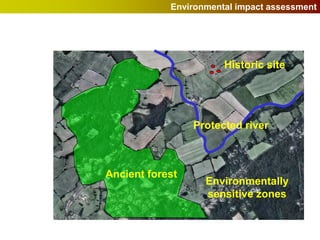
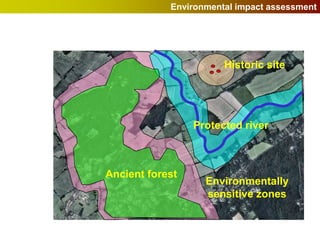
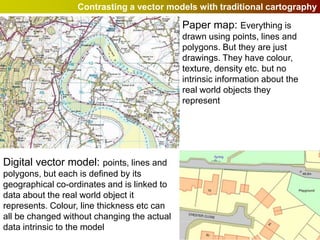
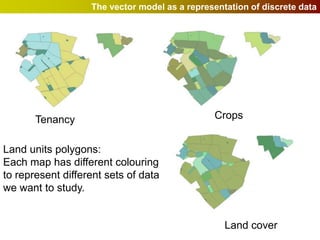
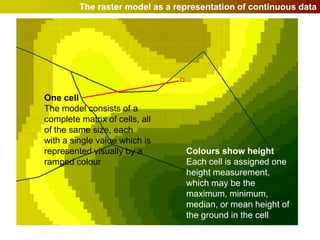
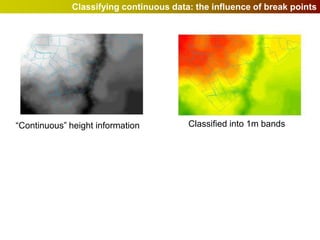
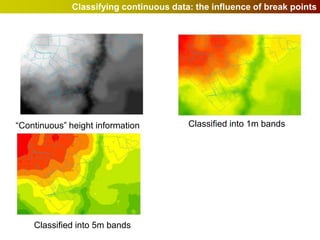
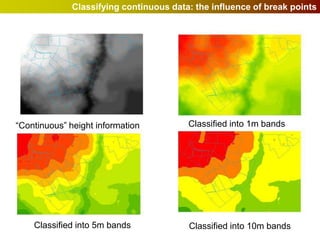
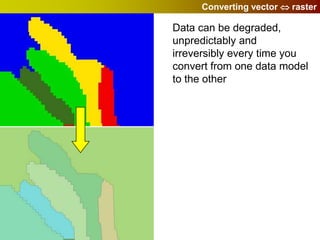
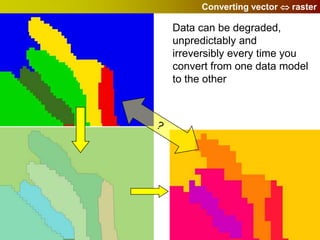
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow users to store, visualize, and analyze spatial data in digital formats. GIS can be used to ask questions about the location of things, what happens at locations, and how things are spatially related. Spatial data can be represented using vector models of discrete data like points, lines, and polygons, or raster models of continuous data like elevation or land cover which have no clear edges. Real world entities may have both discrete and continuous qualities, and different GIS data structures are suited to representing each type of data.