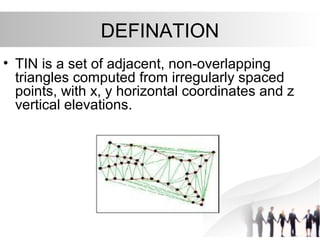
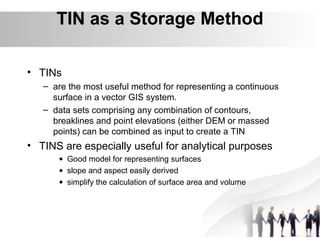
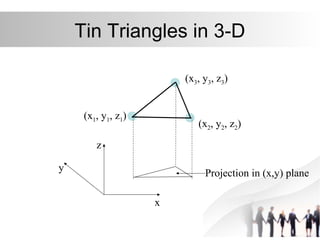
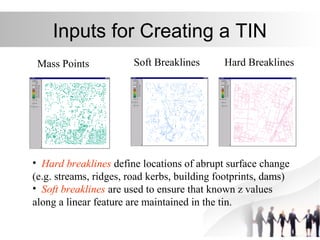
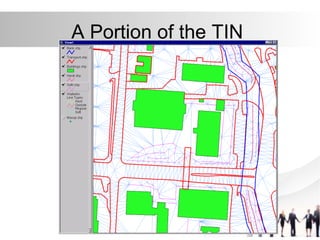
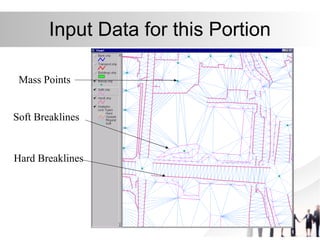
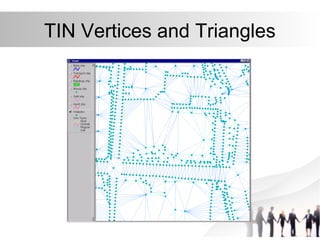
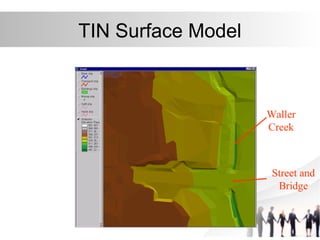
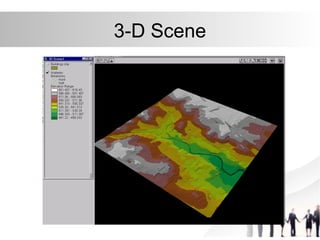
Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN) is a digital representation of a surface as non-overlapping triangles computed from irregularly spaced 3D points, where each point has x, y, and z coordinates. TINs are useful for representing continuous surfaces in GIS as they can accurately model terrain with significant slopes and variations while using fewer triangles in flat areas. TINs allow for easy derivation and analysis of surface properties like slope, aspect, area, and volume from mass point data, contours, and breaklines.