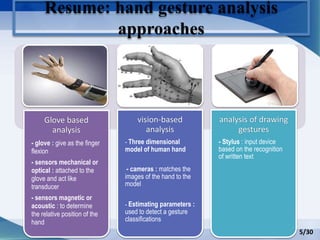
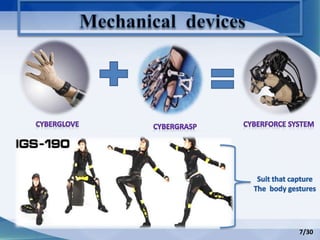
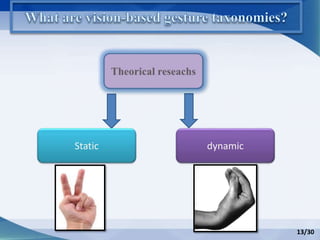
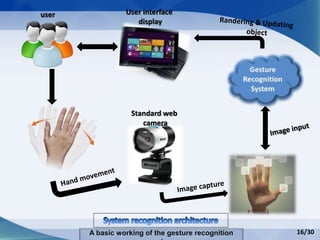
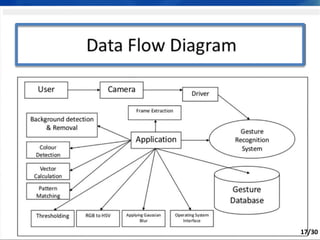
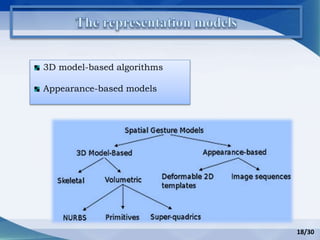
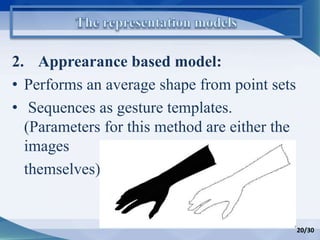
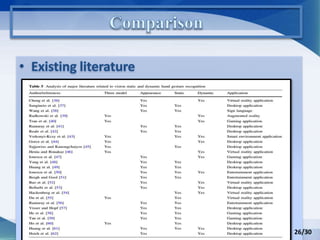
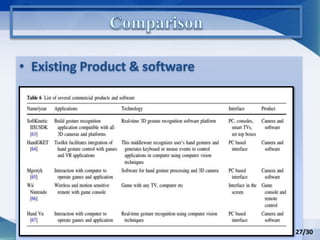
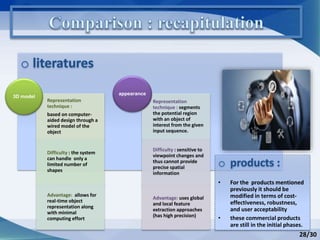
Hand gesture analysis approaches can be categorized as either glove-based or vision-based. Glove-based approaches use sensors attached to a glove to detect finger flexion, while vision-based approaches use cameras and 3D modeling to analyze images of the hand. There are challenges to both approaches related to sensor accuracy, viewpoint changes, and processing requirements. Existing literature analyzes taxonomy of gestures and different algorithms for gesture recognition including HMM, KNN, and SVM. Applications of gesture recognition include virtual controllers, sign language translation, and assistive robotics. Key difficulties are handling variability in appearances and balancing performance, cost, and user independence.