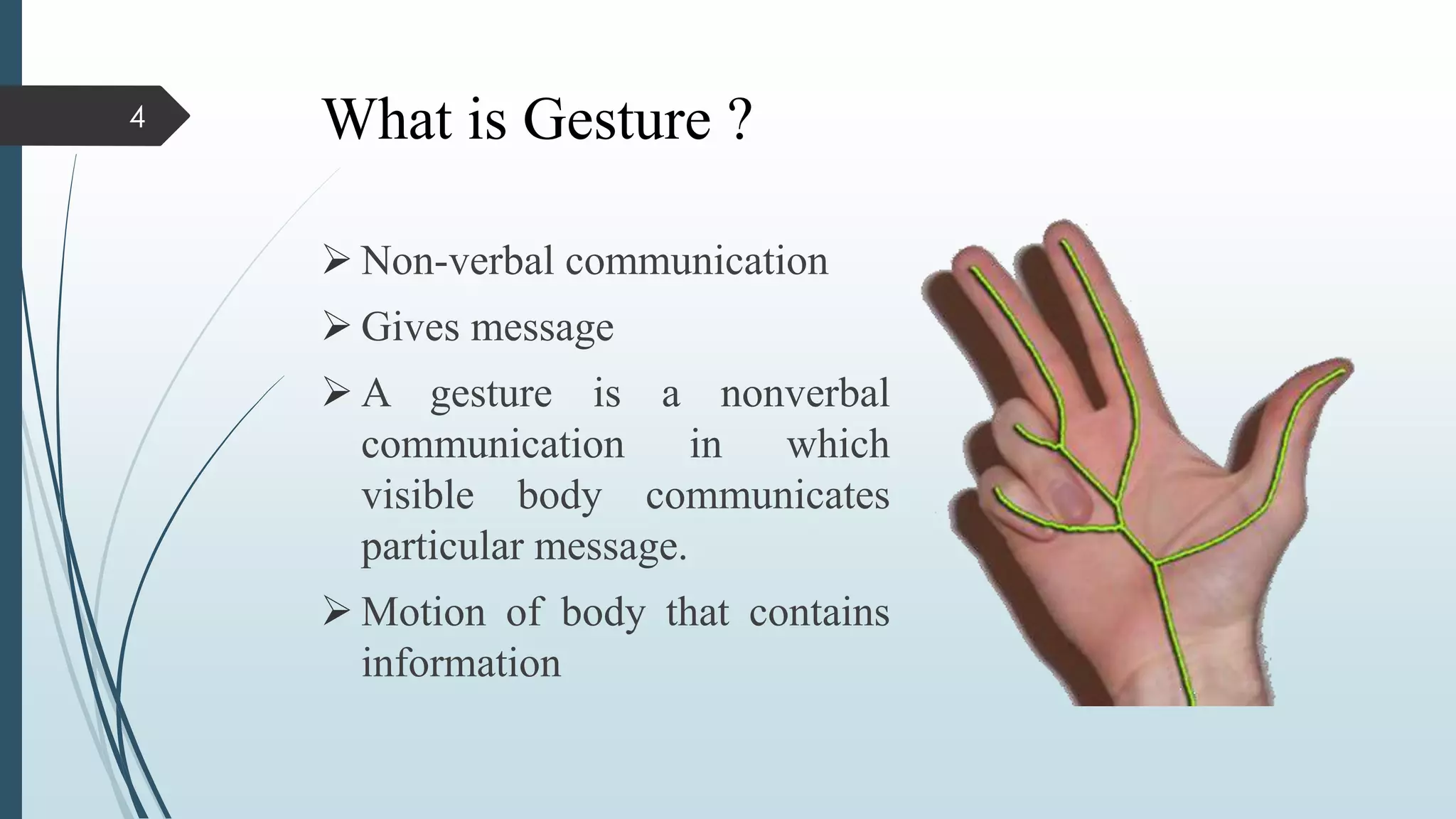
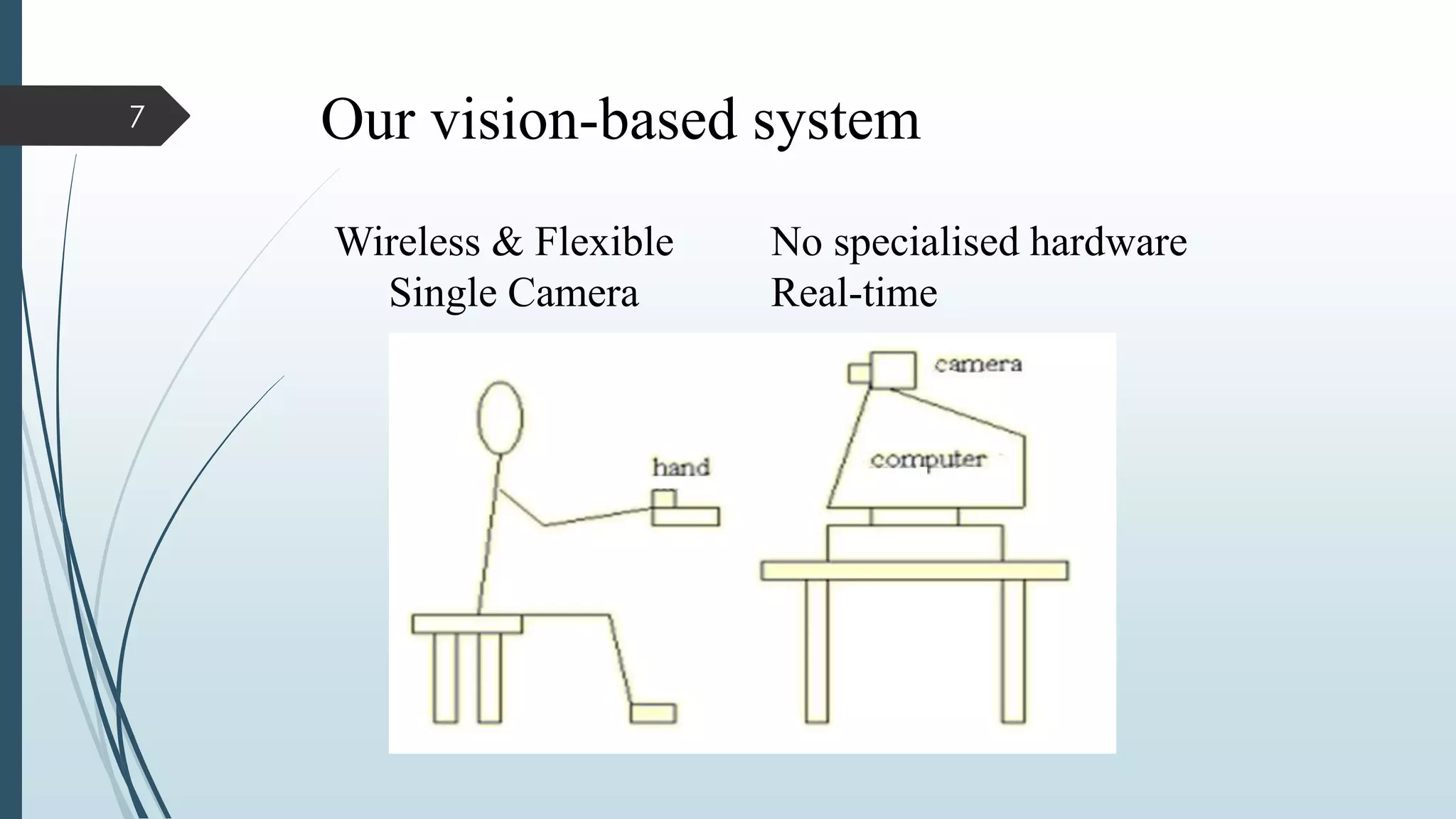
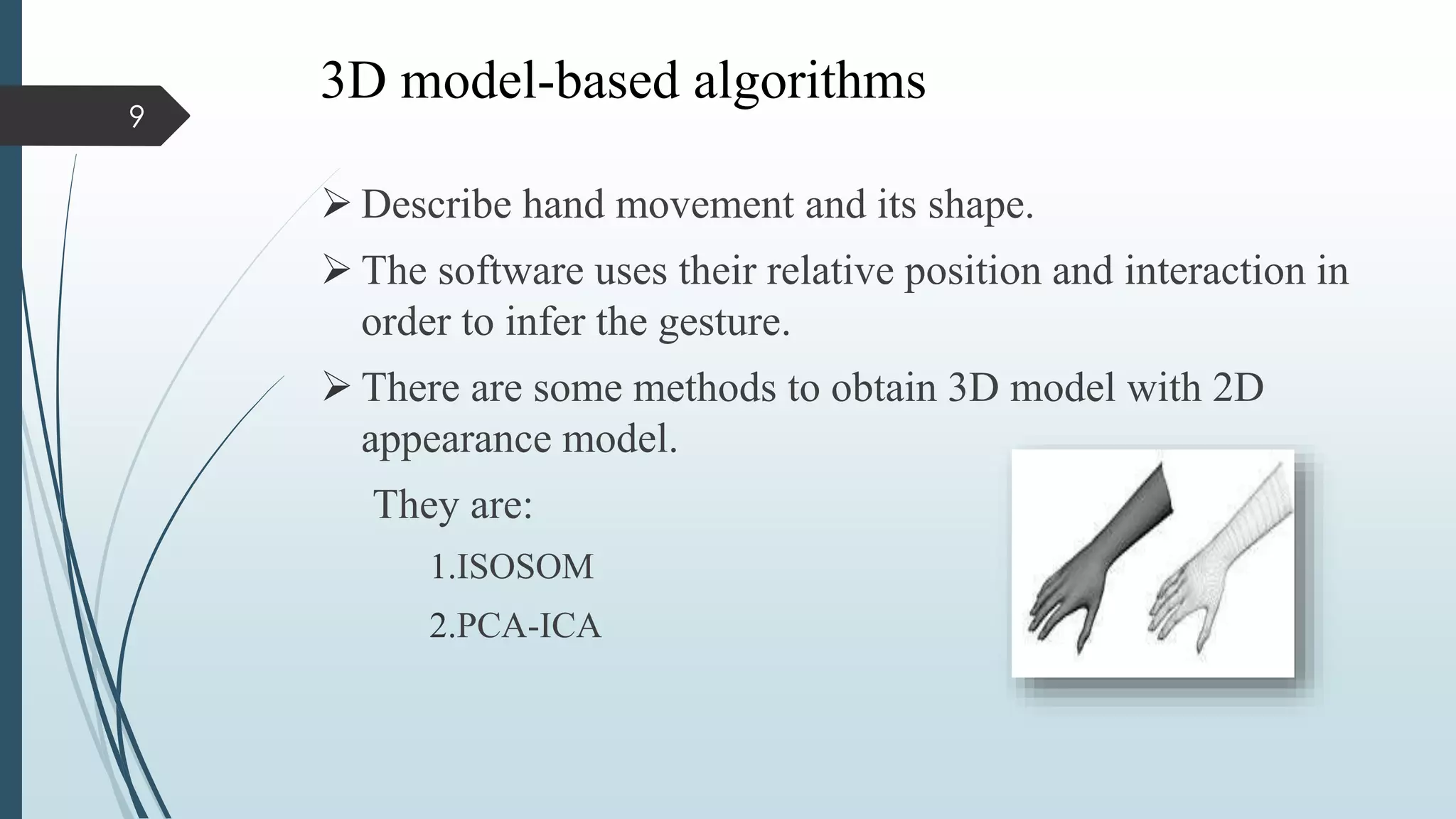
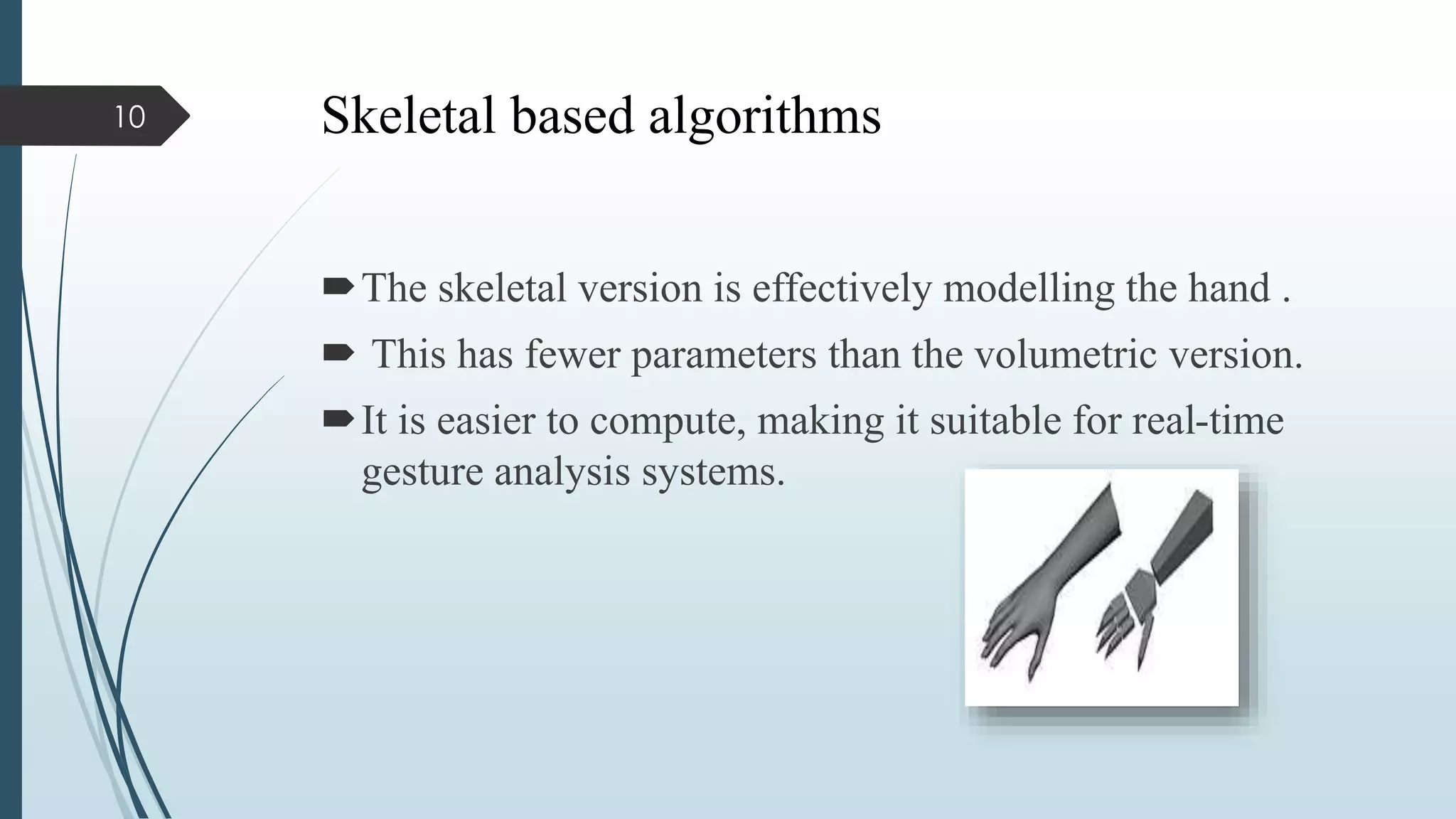
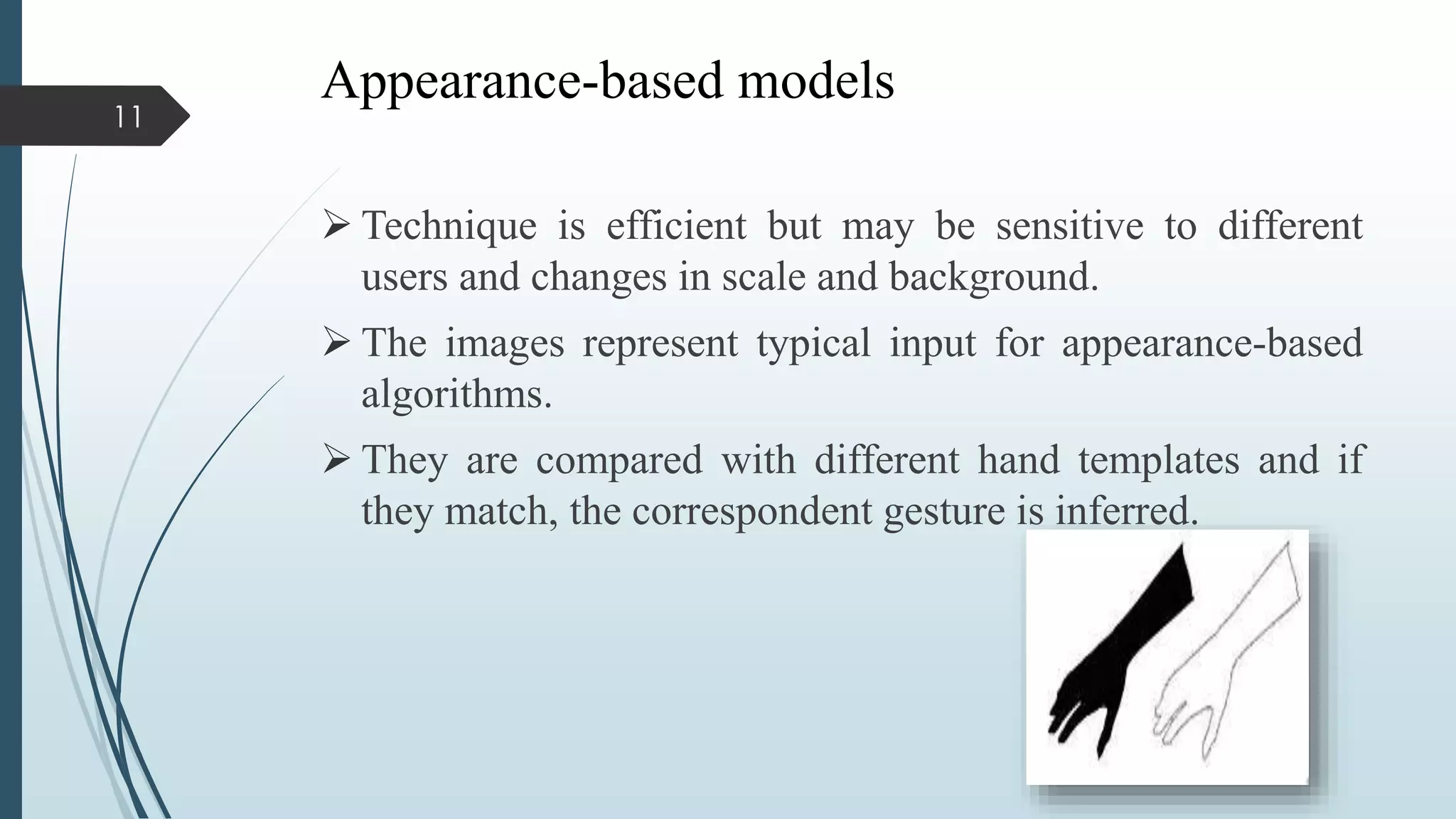
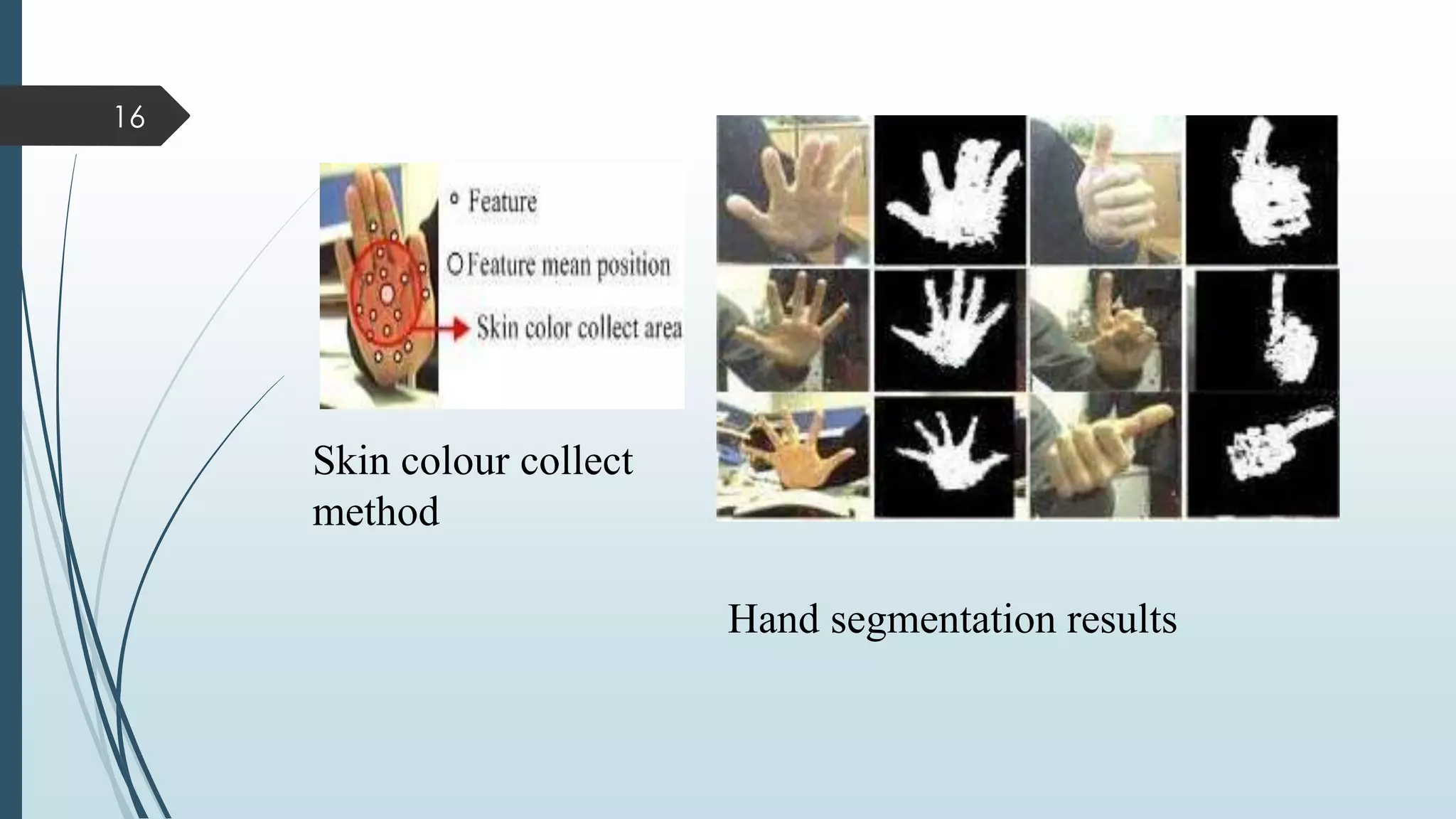
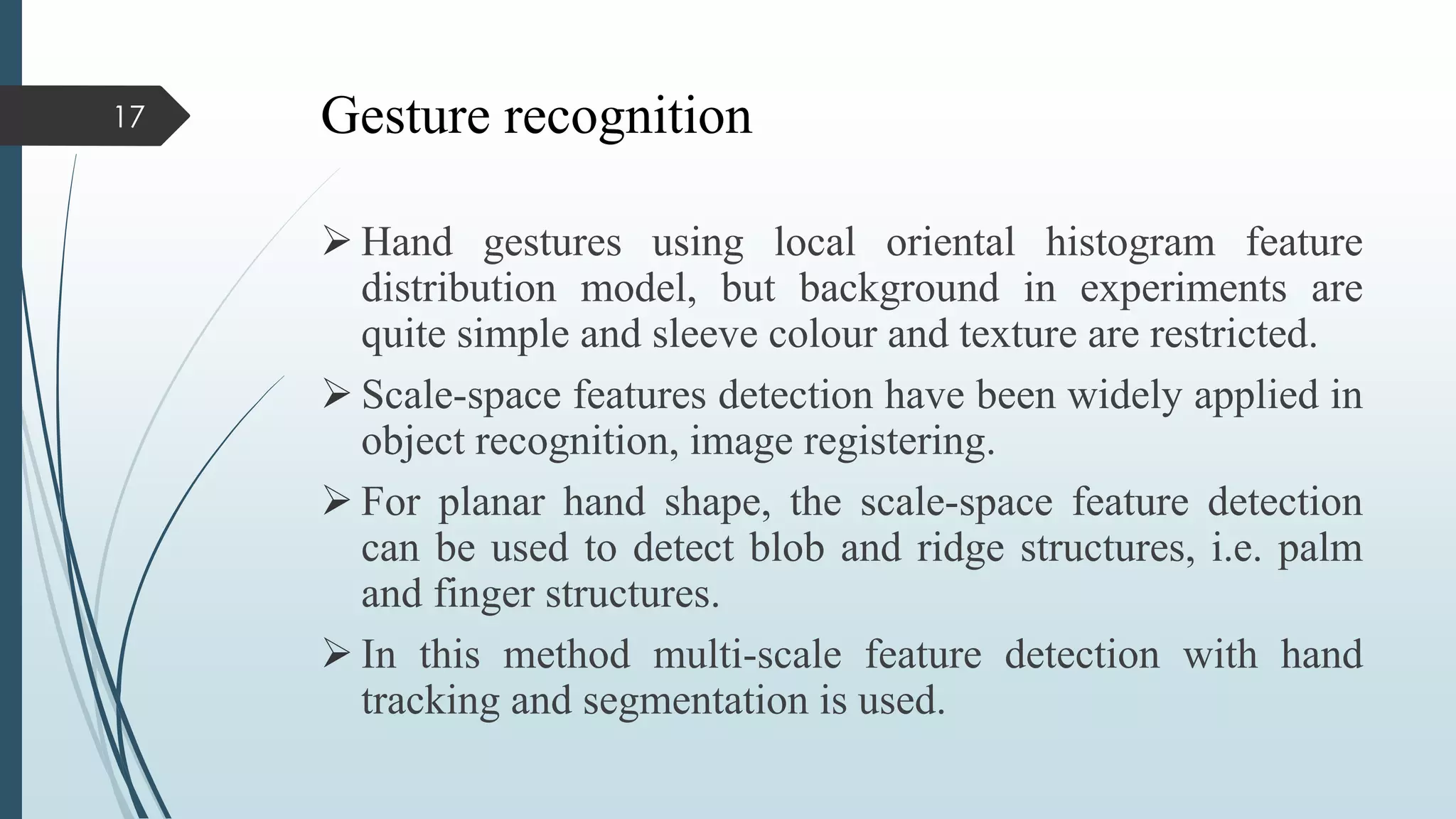
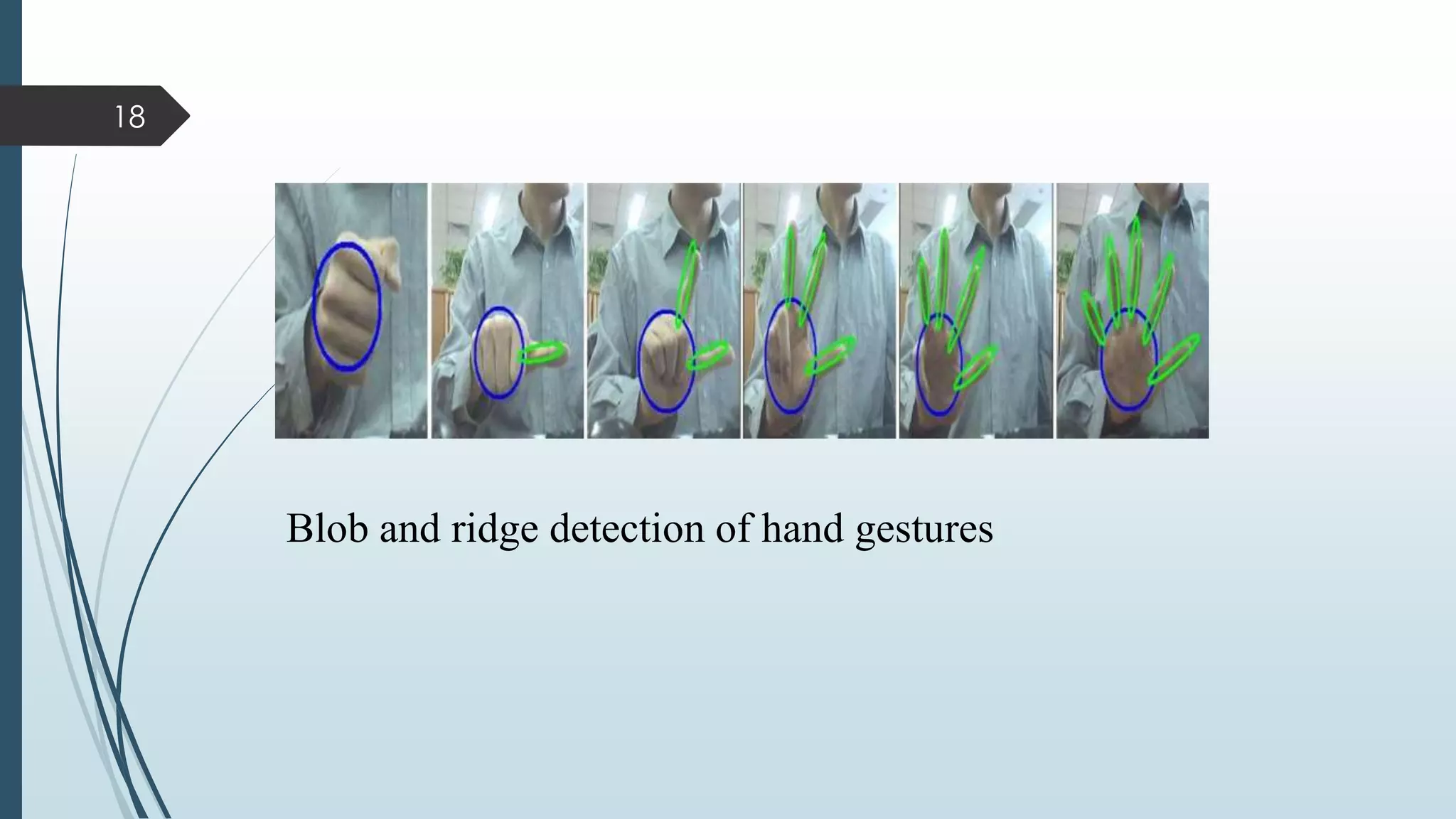
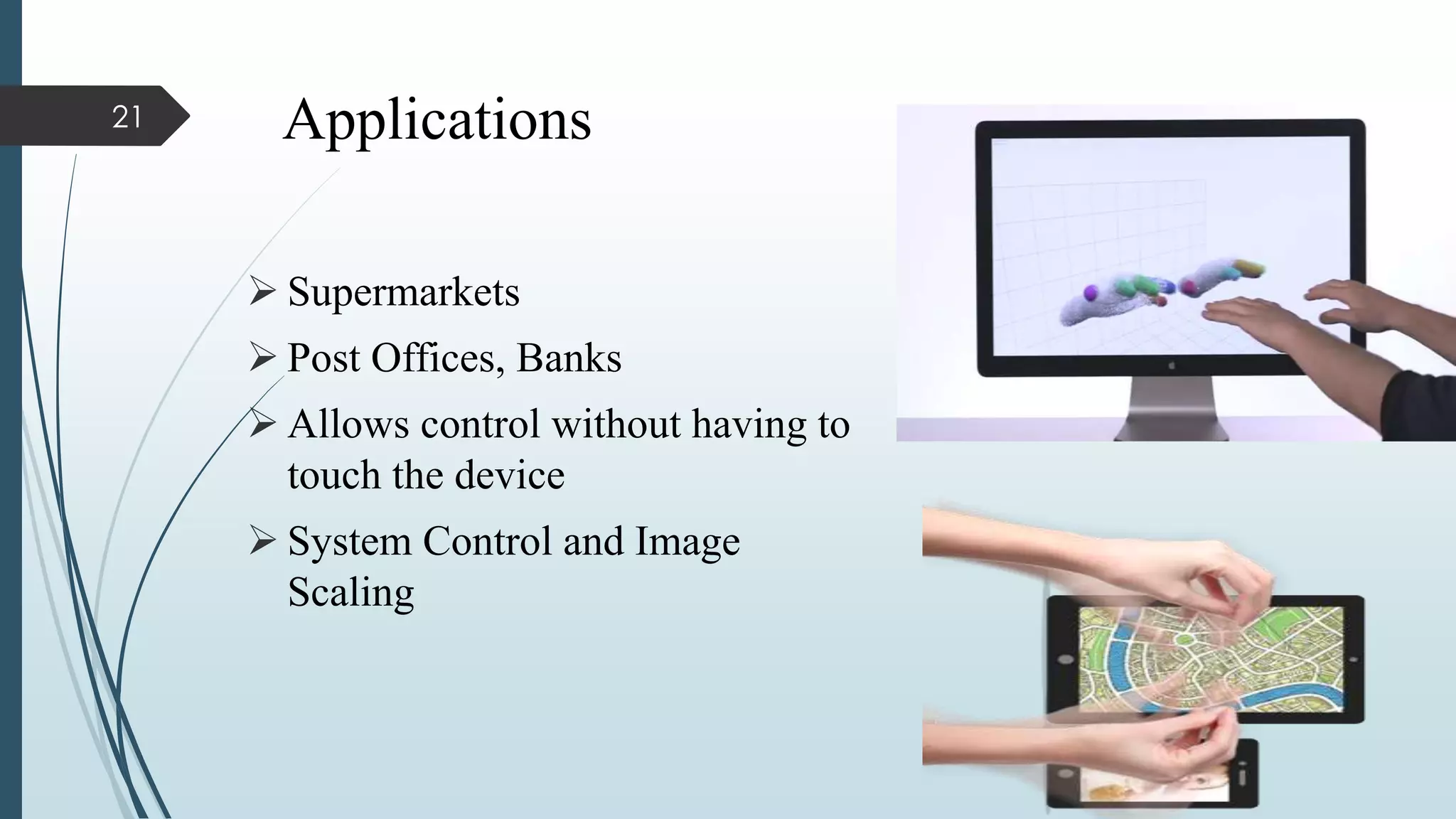
This document presents a real-time hand gesture recognition method. It discusses algorithms like 3D model-based, skeletal-based, and appearance-based for hand gesture recognition. The process involves hand detection, tracking, segmentation, and recognition. Features, advantages, and applications are also covered. The method uses fast hand tracking, segmentation, and multi-scale feature extraction for accurate recognition. It concludes with discussing potential for continued progress in areas like sign language recognition and accessibility.