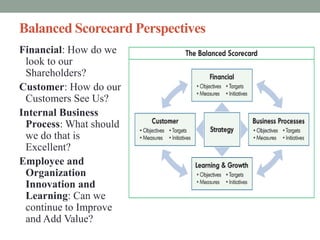
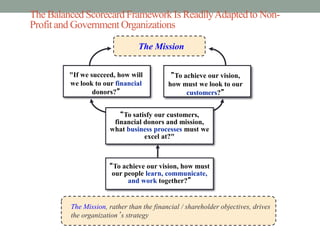
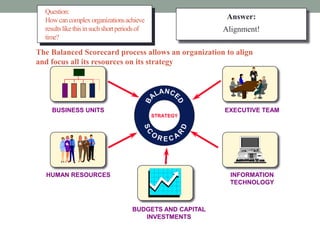
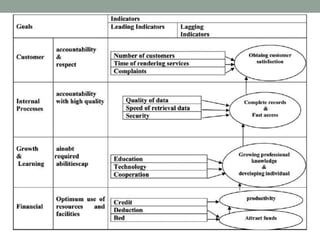
The balanced scorecard is a strategic management framework introduced by Kaplan and Norton in 1992 that enhances organizational performance by integrating both financial and non-financial measures. Its purpose is to implement business strategies through performance measures linked to strategic goals, ensuring alignment across all levels of an organization. With widespread adoption among Fortune 1000 companies, the balanced scorecard aids in focusing on critical measures that drive strategy and improve overall effectiveness.