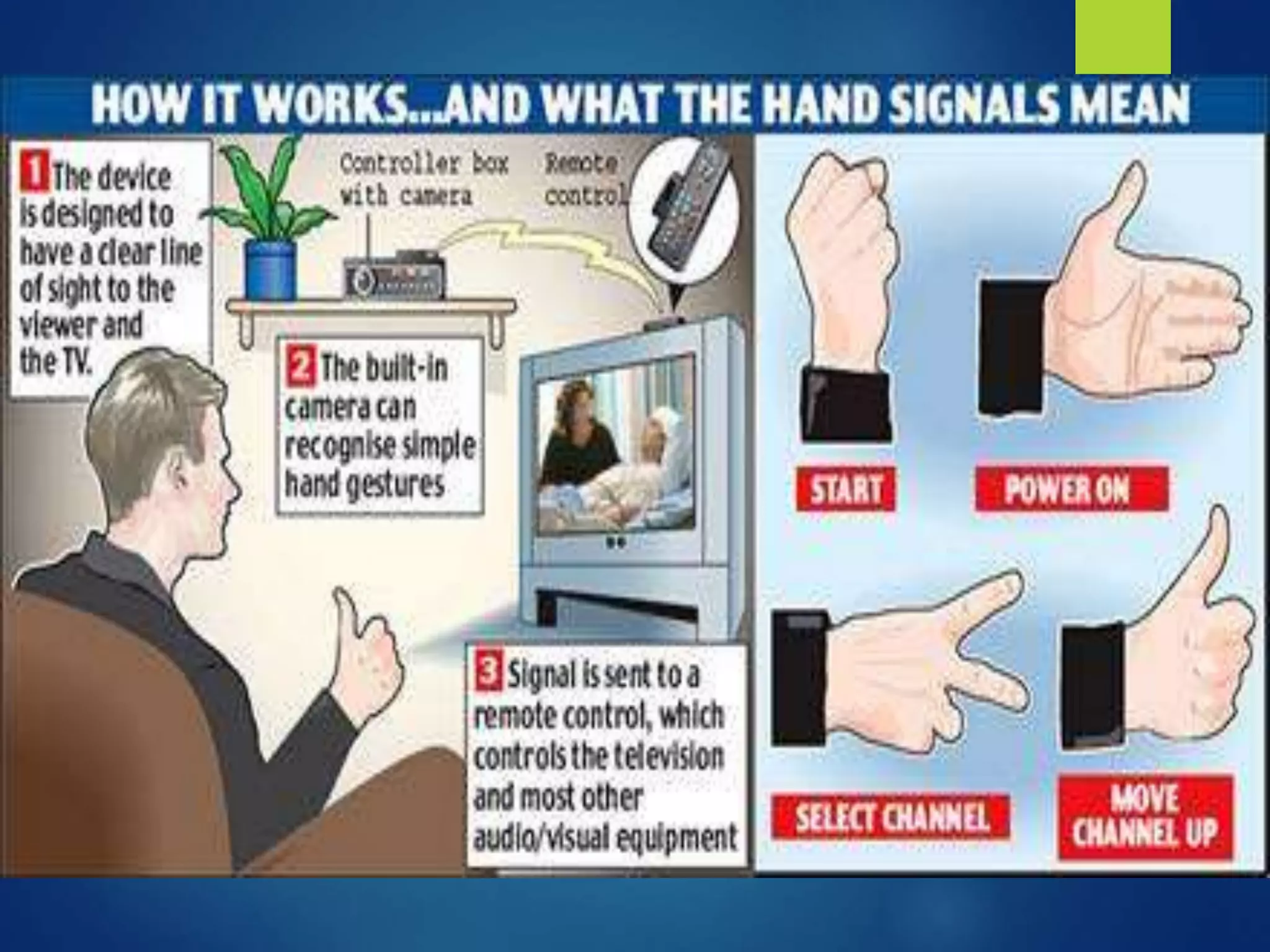
The document discusses gesture recognition technology. It describes how cameras can read human body movements and communicate that data to computers to interpret gestures. Gestures can be used as inputs to control devices or applications. The document outlines different types of gestures, image processing techniques used, input devices like gloves and cameras, challenges, and potential uses like sign language recognition and immersive gaming.