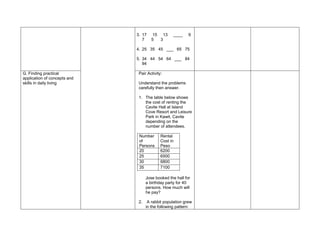
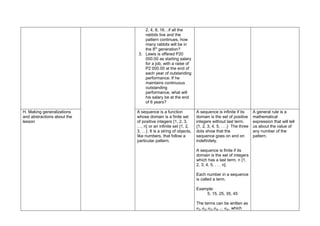
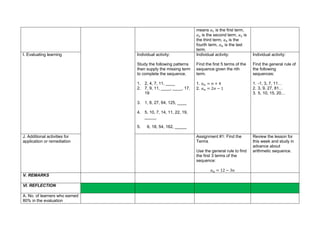
This document contains a daily lesson log for a 10th grade mathematics class. The lesson covers sequences, including defining sequences, identifying patterns in sequences, generating the general rule of a sequence, and solving problems involving sequences. The lesson procedures include reviewing previous concepts, presenting examples of sequences, discussing sequence concepts, practicing identifying patterns and terms, applying sequences to word problems, making generalizations about sequences, and evaluating student learning. The log details the objectives, content, resources, procedures, and reflections for the mathematics lesson on sequences taught over multiple days.