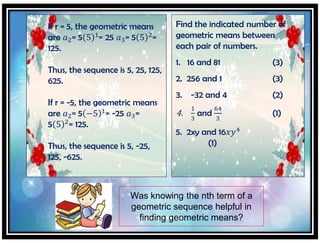
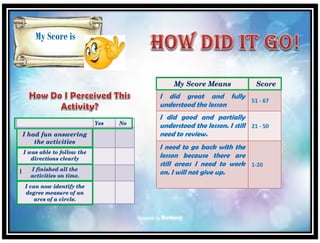
This document provides a strategic intervention material on illustrating geometric sequences for mathematics learners in 10th grade. It contains various activities to distinguish between arithmetic and geometric sequences, identify the common ratio of geometric sequences, find the nth term and sum of finite and infinite geometric sequences, and determine geometric means. The activities include examples of dividing terms to find ratios, identifying common ratios, stating whether sequences are geometric or not, finding missing terms, using the nth term formula, and assessing understanding. The document was prepared by a teacher and submitted for approval to help students master the key skills of working with geometric sequences.