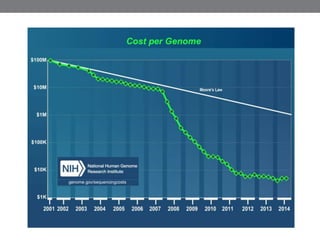
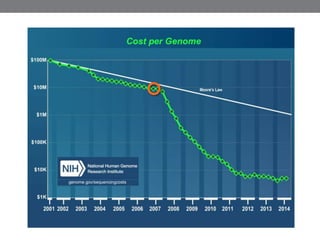
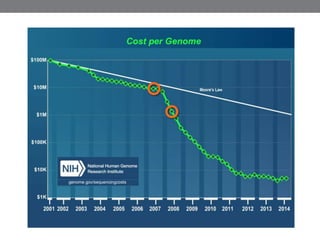
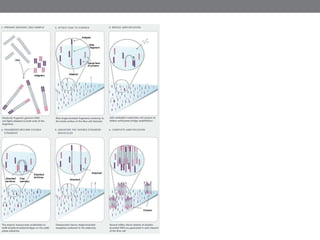
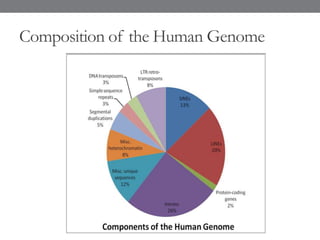
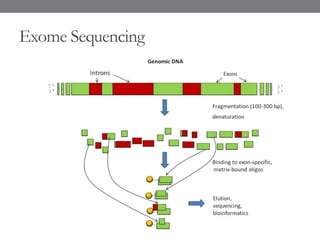
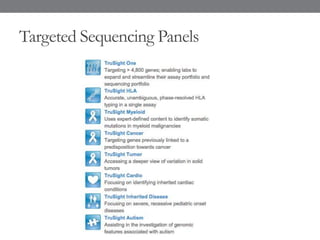
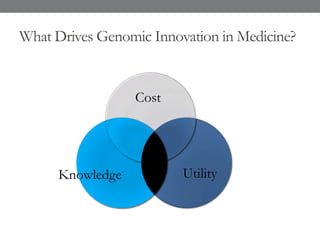
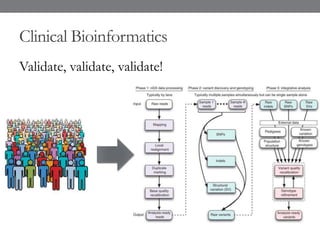
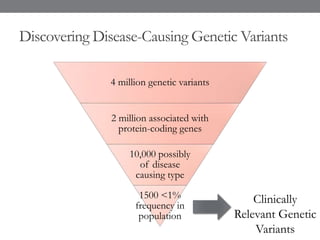
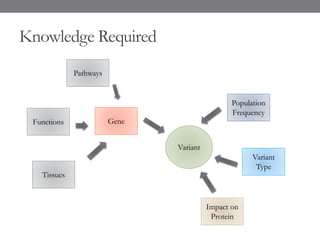
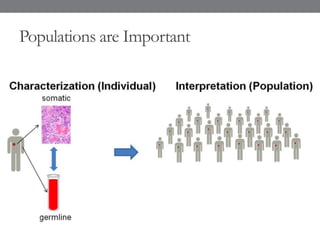
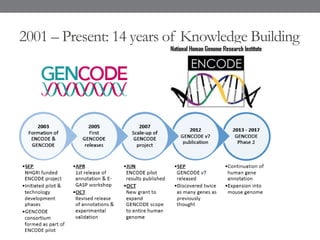
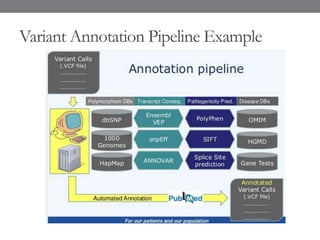
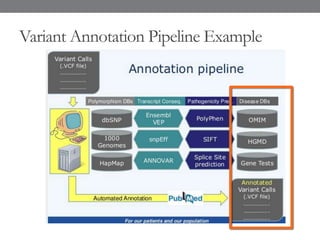
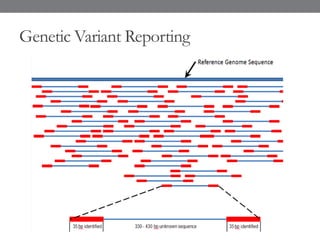
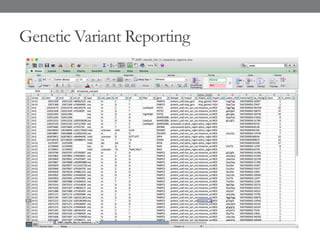
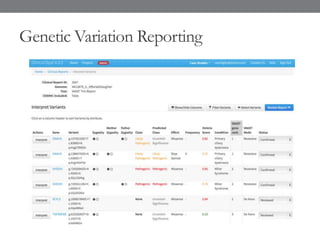
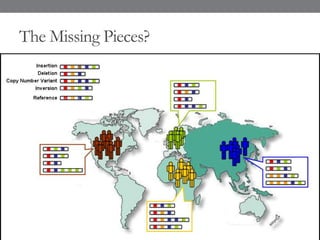
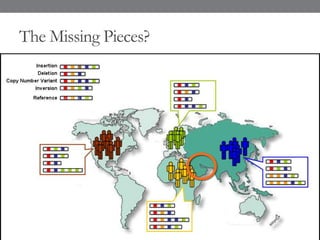
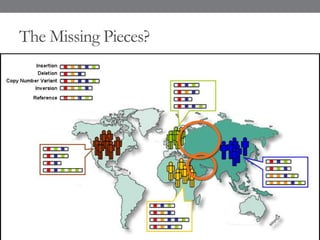
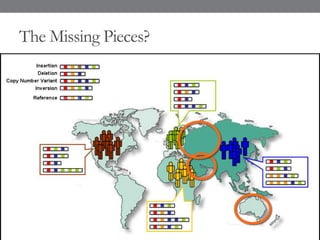
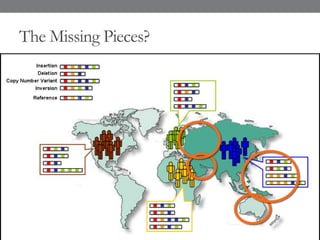
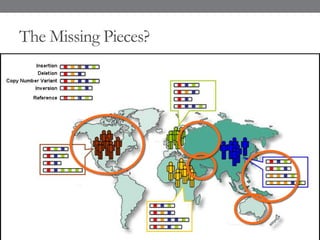
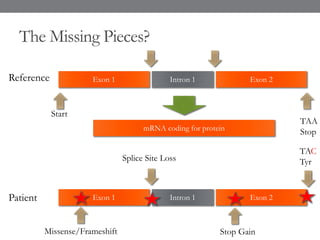
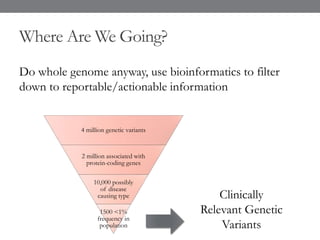
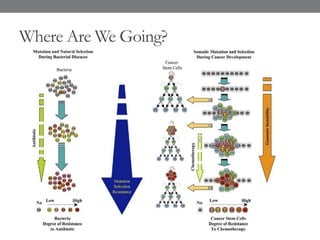
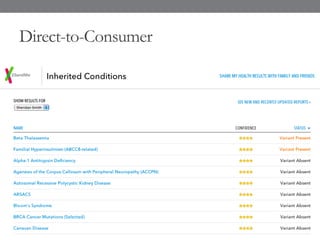
Genomic medicine aims to identify genetic variations that cause disease and inform treatment. While whole genome sequencing is technically possible for $1000, analysis costs remain high. Current clinical applications include diagnosing rare childhood disorders and guiding cancer treatment. Continued cost reductions and expanding biological knowledge databases will drive further innovation, though challenges around data interpretation and reporting remain. Large reference populations and functional studies are still needed to realize genomics' full potential in healthcare.